ABSTRACT
Recently, titanium alloys have been widely used in aerospace, biomedical engineering, and military industries due to their high strength to weight ratio and corrosion resistance. However, it is well known that titanium alloys are difficult-to-cut materials because of a poor machinability characteristic caused by low thermal conductivity, chemical reactivity with all tool materials at high temperature, and high hardness. To improve the machinability of titanium alloys, cryogenic cooling with LN2 (Liquid Nitrogen) and nanofluid MQL (Minimum Quantity Lubrication) technologies have been studied while turning a Ti-6Al-4V alloy. For the analysis of turning process characteristics, the cutting force, the coefficient of friction, and the surface roughness are measured and analyzed according to varying lubrication and cooling conditions. The experimental results show that combined cryogenic cooling and nanofluid MQL significantly reduces the cutting forces, coefficients of friction and surface roughness when compared to wet condition during the turning process of Ti-6Al-4V.
-
KEYWORDS: Titanium alloy, Turning process, Cryogenic cooling, Nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication
-
KEYWORDS: 티타늄 합금, 선반절삭가공, 극저온 냉각, 나노유체 극미량 윤활
1. 서론
최근 항공, 우주, 의료 산업에서 티타늄 합금은 높은 강도, 내부식성 등의 우수한 기계적 성질로 인해 널리 사용되고 있지만 낮은 절삭성으로 인해 가공하기 어려운 난삭재로 분류되고 있다.
1
티타늄 합금 가공 시 가공영역의 높은 온도를 낮춰주고 윤활성능 향상을 위한 방법으로 절삭유가 사용되고 있으나 이러한 절삭유를 과도하게 사용할 경우 환경 오염 및 작업자 건강에 유해한 영향을 미치는 것으로 알려져 있다.
2,3
절삭유 사용을 최소화 하기 위한 가공 방법으로는 극미량 윤활이라고 불리는 MQL (Minimum Quantity Lubrication) 가공 기술이 활발하게 연구되고 있는데
4 이 MQL 가공 기술은 절삭유를 공기압을 통해 미스트 형태로 분사 시켜 주어 기존 Flood 분사 방식의 절삭유 사용량을 수천에서 수만분의 일로 줄일 수 있다. 최근에는 일반 절삭유에 특유의 성질을 가지는 나노고체 입자를 첨가시킨 나노유체를 절삭유로 사용하는 나노유체 MQL 가공 기술도 여러 연구를 통해 소개되고 있으며 이 나노유체 MQL 가공 기술은 일반 MQL 가공에 비해 더욱 향상된 가공성능을 나타낸다.
5,6
그러나 이러한 절삭유 및 나노유체 사용만으로는 가공 시 발생하는 열을 냉각시키기 부족하기 때문에 액체질소(Liquid Nitrogen, LN2) 냉각을 이용하여 극저온 조건에서 가공하는 극저온 냉각 가공 기술 또한 활발하게 연구 중이다. Venugopal 등은 극저온 냉각 조건에서 티타늄 합금 선반 절삭가공 시 공구마모 감소효과를 확인하였고
7 Yap 등도 극저온 냉각 조건에서 탄소강의 선반 절삭가공 시 마찰계수 감소 및 칩 형상 개선 효과를 확인하였다.
8 또한, Pusavec 등은 인코넬 소재의 선반 절삭가공 시 극저온 냉각 기술과 MQL 가공 기술을 함께 적용한 후 가공면의 표면 특성을 분석하였다.
9
본 연구에서는 육방정 결정구조를 가지며 윤활성이 뛰어난 hBN (Hexagonal Boron Nitride) 입자를 식물성 오일에 첨가해 제조된 나노유체를 절삭유로 활용한 나노유체 MQL 및 액체질소를 활용한 극저온 냉각 기반 티타늄 합금의 선반 절삭 가공시스템을 구성하였고 총 6가지 실험을 설계한 후 윤활 및 냉각조건에 따른 선반 절삭가공의 특성평가를 수행하였다. 실험 결과를 통해 극저온 냉각과 나노유체 MQL을 동시에 적용한 경우의 선반절삭가공 시 절삭력의 감소, 마찰계수의 감소 및 표면거칠기의 개선효과를 확인하였다.
2. 극저온 기반 나노유체 MQL 가공 실험 시스템 구성
2.1 실험 장치 구성
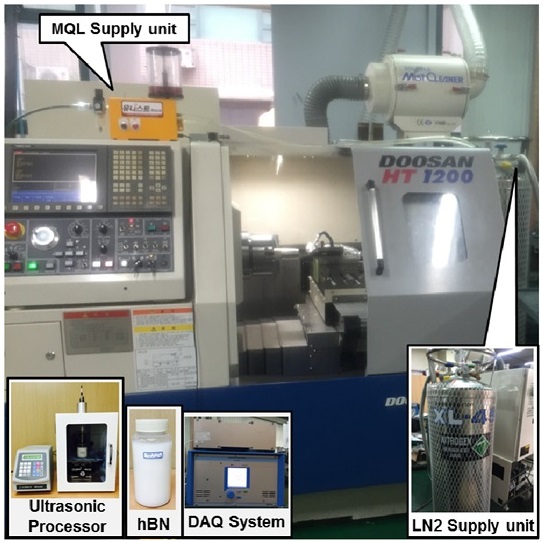
냉각 및 윤활조건에 따른 선반 절삭가공 특성 분석을 위해 전체 실험 시스템을
Fig. 1과 같이 구성하였다. 선반 절삭가공 실험 시스템은 터닝센터(HT 1200, DOOSAN)와 이송 및 제어장치(Vision 640i, DOOSAN) 그리고 데이터 획득 장치(Multichannel Charge Amplifier Type 5070, Kistler)로 구성하였고 가공 시 냉각 및 윤활을 위한 외부장치는 MQL 미스트 분사장치(UNIMA202F, UNIST)와 액화질소 공급탱크(XL-45, Taylor Wharton)이다. MQL 미스트 분사장치는 유량 0.04 - 200 ml/min의 범위로 가공영역에 공급되며 윤활유로 사용한 나노유체(hBN 0.5 wt.%)의 제조를 위해 식물성 오일(NEO-01, NAOMI TECH)과 초음파분산기(VCX 750, Sonic&Materials)가 사용되었다.
Fig. 1Entire experimental system with cryogenic cooling (LN2) and nanofluid (hBN) MQL supply units

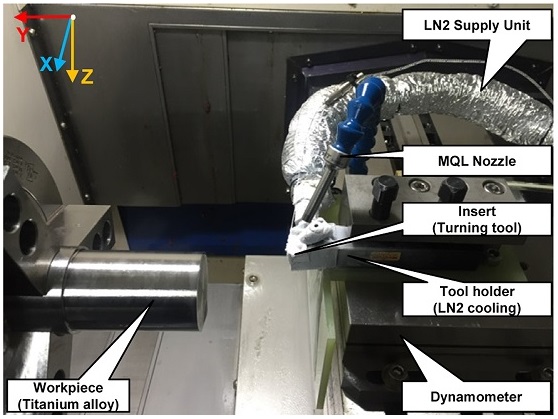
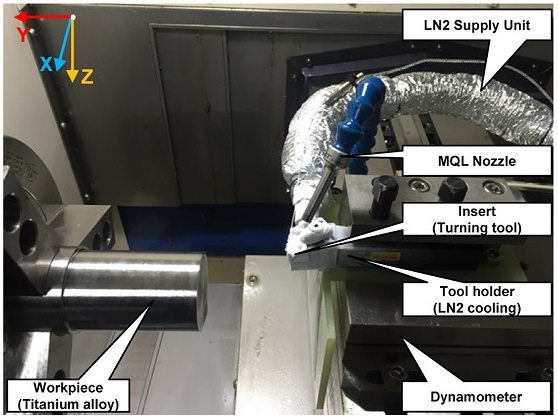
Fig. 2에 주어져 있듯이 가공소재는 지름 50 mm의 원통형 티타늄 합금(Ti-6Al-4V)으로 스핀들에 수평으로 고정시켰으며 선반 절삭공구는 PVD 코팅 인서트(CNMG 12 04 08-SM, Sandvik)로 공구 홀더에 장착하였다. 공구 홀더를 통해 공급된 액화질소는 홀더 내부를 순환한 후 배출된다. 또한 가공 시 X, Y, Z축 방향의 절삭력 측정을 위해서 3축 공구동력계(Multicomponent Dynamometer Type 9275B, Kistler)를 사용하였다. MQL 분사노즐은 공구와 소재 사이에서 45°의 분사 각도 및 30 mm의 분사거리를 갖도록 설치되었다.
Fig. 2Detailed view of the turning experimental system including the insert, workpiece, MQL nozzle and LN2 supply unit
2.2 실험 조건 및 설계
Table 1에는 선반 절삭가공 실험 조건이 주어져 있다. 실험에서 사용된 소재는 티타늄 합금이고 공구는 PVD 코팅 카바이드 인서트이며 절삭속도, 이송량 및 절삭깊이는 각각 60 m/min, 0.25 mm/rev, 2 mm이다. 선반 절삭 가공실험의 절삭조건은 공구 제조사의 권장조건과 기초 실험을 통해 선정하였고 절삭길이는 70 mm로 외경 정삭 가공을 수행하였다. 극저온 조건 실험을 위해 액체질소(LN2)는 1.5 MPa의 압력으로 공급되었다. MQL 분사를 위해 식물성오일과 hBN 나노유체(0.5 wt.%)가 사용되었고 분사 압력 0.5 MPa, 분사유량 0.6 ml/min, 분사각도 45°로 가공영역에 분사되었다.
Table 1Experimental conditions
Table 1
|
Cutting type |
External diameter turning |
|
Workpiece |
Ti-6Al-4V (Ø : 50 mm) |
|
Tool |
PVD coated carbide insert |
|
Cutting speed |
60 m/min |
|
Feed per revolution |
0.25 mm/rev |
|
Depth of cut |
2 mm |
|
Cutting length |
70 mm |
|
Cryogenic cooling pressure |
1.5 MPa |
|
MQL flow rate |
0.6 ml/min |
|
MQL pressure |
0.5 MPa |
|
MQL oil |
Vegetable oil |
|
Nanofluid |
hBN (0.5 wt.%) |
Table 2에는 실험 설계 결과가 주어져 있으며 냉각조건으로 2수준(상온, 극저온)과 윤활조건으로 2수준(MQL, hBN MQL)을 고려하여 총 6가지의 실험 경우를 도출하였다.
Table 2Experimental design
Table 2
|
Run |
Lubrication oil |
Cryogenic cooling |
|
1 |
Wet |
- |
|
2 |
MQL (Vegetable oil) |
- |
|
3 |
hBN (Nanofluid) MQL |
- |
|
4 |
- |
LN2 |
|
5 |
MQL |
LN2 |
|
6 |
hBN MQL |
LN2 |
실험 수행에 있어서 Wet 조건에서는 Flood 방식으로 공급되는 수용성 절삭유를 사용하였고 MQL과 hBN MQL 조건에서는 극미량 미스트 형태로 식물성 오일 절삭유를 분사하였다. LN2 조건에서는 액체질소가 외부 공급탱크에서 노즐을 통해 공구 홀더에 공급되었다.
Table 3에는 MQL 오일과 hBN 나노유체의 물리적 특성이 주어져 있다.
Table 3Characteristics of MQL oil and hBN nanofluid
Table 3
|
MQL oil |
hBN Nanofluid |
|
Base oil |
Vegetable oil |
|
Nano particle |
- |
hBN
(Lamella structure) |
|
Particle size |
- |
Average 70 nm |
|
Concentration |
- |
0.5 wt.% |
3. 실험 결과 및 분석
본 실험을 통한 티타늄 합금의 선반 절삭가공 특성 분석을 위한 관측인자로 절삭력, 마찰계수, 표면거칠기를 선정하였으며 냉각 및 윤활 조건에 따라 측정한 실험 결과를 분석 하였다.
3.1 절삭력(Resultant Cutting Forces)
절삭력 측정을 위해서 3축(X, Y, Z) 공구동력계를 이용하였으며 절삭력 측정 시 신호 데이터의 Sampling Rate는 1 kHz이다. 수집한 절삭력 신호에 Moving Average 기법을 적용하여 각 실험 경우에 있어서 X, Y, Z 축 방향의 절삭력을 구하였다.
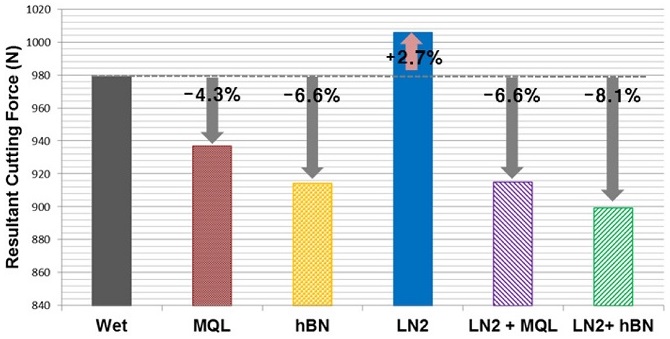
Fig. 3은 X, Y, Z축의 각 절삭력을 벡터합하여 구한 합력을 나타내며 Wet 조건 대비 각 실험 경우의 절삭력 감소율을 함께 표기하였다.
Fig. 3Measured resultant cutting forces
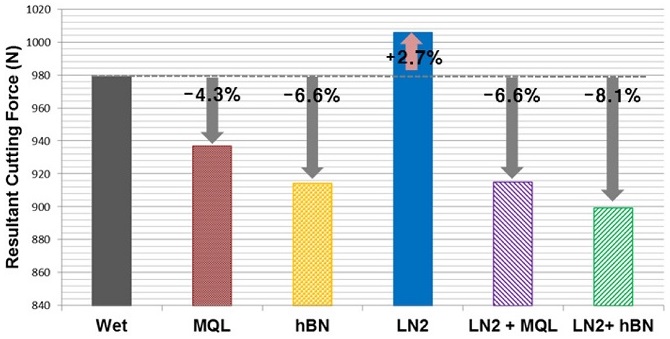
Fig. 3에서 알 수 있듯이 Wet 조건과 비교하였을 때 극미량 분사를 적용한 MQL 및 hBN MQL 조건에서 각각 4.3%, 6.6%의 절삭력 감소를 확인할 수 있었다. 그리고 액체질소 냉각과 극미량 절삭유 윤활을 동시에 적용한 LN2 + MQL 및 LN2 + hBN MQL 조건에서는 각각 6.6%, 8.1%의 절삭력 감소를 확인할 수 있다. 이를 통해 액체질소 냉각과 나노유체 극미량 윤활을 동시에 적용한 LN2 + hBN MQL 조건에서 가장 큰 절삭력 감소 효과가 있는 것으로 확인되었다.
그러나 액체질소만을 적용한 LN2 조건에서는 오히려 절삭력이 Wet 조건 대비 2.7% 증가하였다. 이는 가공영역에서 절삭유의 사용 없이 액체질소만을 분사할 경우에는 냉각작용은 유효하나 윤활작용의 부재로 인해 가공영역의 취성을 증가시키고 공구와 소재 사이에 돌발적인 마모를 발생시켜 절삭력 감소효과를 얻지 못한 것으로 추정된다.
액체질소의 적용을 통한 냉각 효과의 확인을 위해 선반 절삭가공 실험에 있어서 공구인 인서트 내에 장착된 열전대를 이용하여 각 실험 경우에 있어서의 온도를 측정하였다. 액체질소를 사용한 경우인 LN2, LN2 + MQL, LN2 + hBN MQL 조건에 있어서 측정온도는 각각 215°C, 226°C, 222°C이며, 이는 액체질소를 사용하지 않은 MQL 및 hBN MQL 조건의 측정온도보다 약 150°C가 낮다.
상기와 같이 액체질소를 사용한 실험 경우에 있어서 LN2, LN2 + MQL, LN2 + hBN MQL 조건의 공구 인서트 측정온도는 큰 차이가 없으나
Fig. 3에서 알 수 있듯이 LN2 +MQL, LN2 +hBN MQL 조건에서 절삭합력이 크게 감소하는 것은 MQL 및 hBN MQL의 추가를 통한 윤활작용 상승에 기인하는 것으로 이해할 수 있다.
선반 절삭가공 중 공구의 경사면과 소재는 연속적으로 접촉이 이루어진다. 따라서 공구 경사면과 소재 간 심한 마찰과 열이 발생하게 되므로 이러한 마찰은 소재의 표면거칠기 및 전반적인 가공 성능에 영향을 미치게 된다.
가공 시 마찰에 의한 영향을 분석 하기 위해서 3차원인 선반 절삭가공 공정을 2차원의 직교절삭으로 근사화 시킨 후 Merchant의 Cutting Force Circle 이론을 이용하여 가공 시의 마찰계수를 계산하였다.
10 Cutting Force Circle 이론을 통해
식(1)과
식(2)의 관계식이 유도되었고 공구와 소재 사이에 작용하는 마찰계수를
식(3)을 통해 계산하였다.
식(1)의 마찰력(
F)과
식(2)의 수직항력(
N) 값은 절삭가공 공정에서 직접 측정할 수 없지만 공구 동력계에서 측정한 2개의 힘 주분력(
Fc) 및 이송분력(
Ft) 값을 사용하여 계산이 가능하다. 본 실험에서의 주분력과 이송분력은
Fig. 2에서 Z축과 Y축의 절삭력을 의미한다. 공구의 경사각(
α)은 - 5°이며 강도가 비교적 높은 난삭재인 티타늄합금의 가공을 수행하기 위해 음(−)의 경사각을 적용하였다.
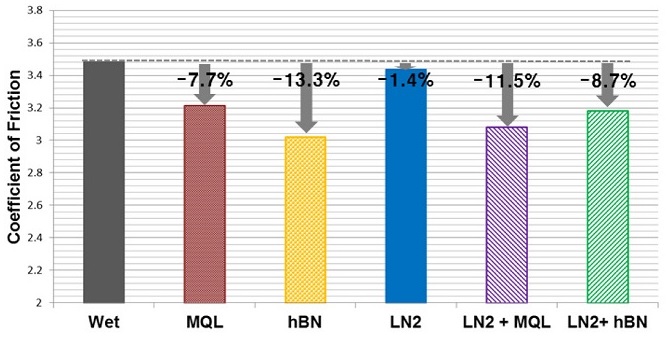
Fig. 4는 각 실험 경우 별 계산된 마찰계수 값을 나타내며 Wet 조건 대비 마찰계수 감소율을 함께 표기하였다. 절삭력 실험결과와 마찬가지로 액체질소 냉각만을 사용한 LN2 조건에서는 마찰계수 감소율이 1.4%로 다른 실험 경우와 비교하여 가장 적은 것을 볼 수 있는데, 이는 절삭유 미사용으로 인한 윤활 효과 저하로 인해 가공 시 공구와 소재 사이 마찰 감소 효과가 상대적으로 미미한 것으로 추정된다.
Fig. 4Calculated coefficients of friction
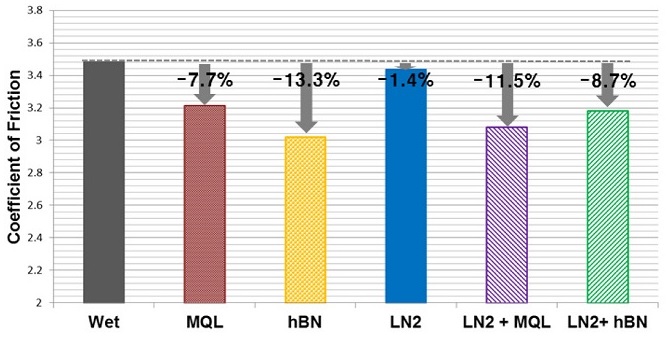
MQL 조건과 hBN MQL 조건에서는 Wet 조건 대비 마찰계수가 각각 7.7%, 13.3% 감소하였고 특히 나노유체 극미량 윤활을 사용한 hBN MQL 조건이 다른 실험조건에 비해 가장 낮은 마찰계수를 나타내었다.
또한 액체질소 냉각과 극미량(나노유체) 절삭유 윤활을 동시에 적용한 LN2 + MQL 및 LN2 + hBN MQL 조건에서도 각각 11.5%, 8.7%의 마찰계수 감소효과가 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
3.3 표면 거칠기(Surface Roughness)
절삭가공 공정에서 가공면의 표면거칠기는 제품의 최종 품질과 아주 밀접한 연관이 있기 때문에 가공성능 평가에 있어서 주요한 관측인자이다. 따라서 본 실험을 진행한 후 가공이 완료된 티타늄 합금 시편에 3D 레이저 스캐닝 현미경(VK-X Series, Keyence)을 적용하여 가공면의 표면거칠기를 측정하였다. 이 때 표면거칠기는 중심선 평균거칠기인 Ra 값으로 나타내었다.
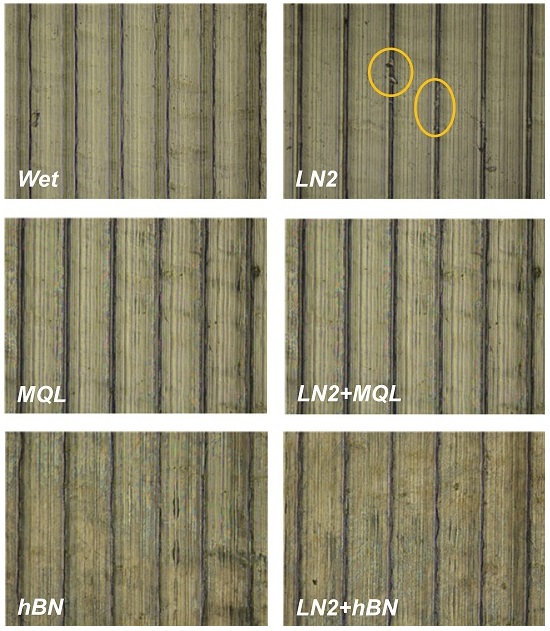
Fig. 5는 냉각 및 윤활조건에 따른 각 실험 경우, 가공면의 광학 현미경 사진을 보여주며
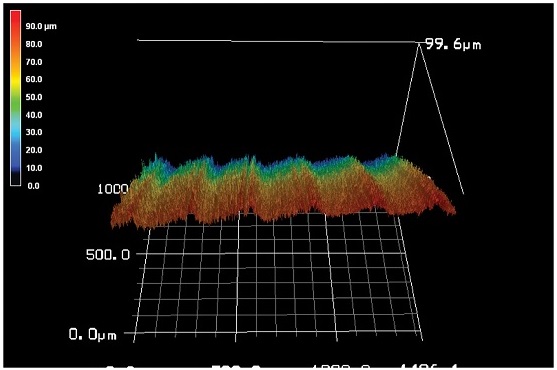
Fig. 6에는 LN2 조건에서의 가공 표면 3D 프로파일 사진이 주어져 있다.
Fig. 5에 주어진 광학 현미경 사진을 확인하여 실험조건에 따른 가공표면의 상태를 정성적으로 분석할 때 절삭유의 사용 없이 액체질소 냉각만을 적용한 LN2 조건의 경우, 가공 후 표면의 일부분이 미소하게 떨어져 나간 흔적을 확인할 수 있다.
Fig. 5Optical images of machined surfaces
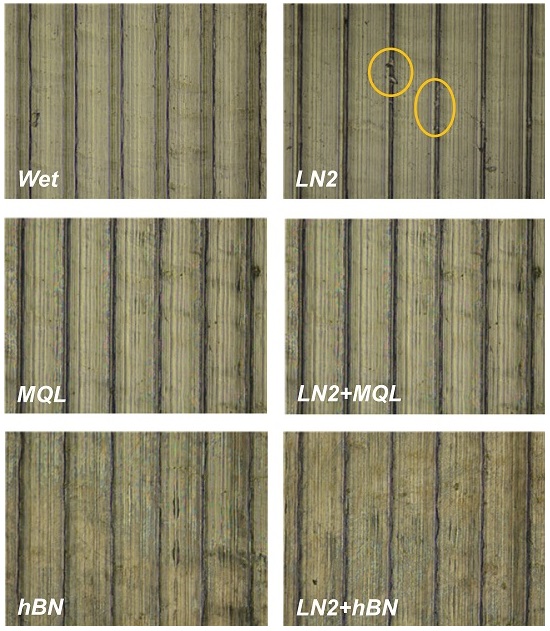
Fig. 63D Profile of machined surface in LN2 condition
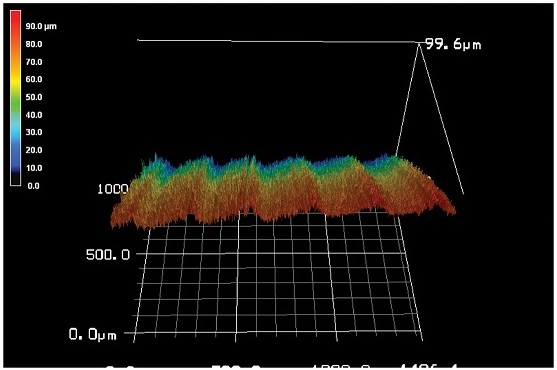
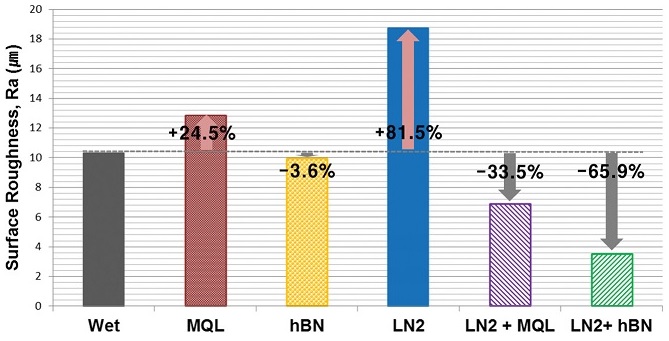
Fig. 7에 주어진 정량적 표면거칠기 값 비교에 있어서 Wet 조건과 대비했을 때 LN2 및 MQL 조건에서는 표면거칠기 개선효과가 좋지 않은 것을 확인할 수 있었고, 특히 LN2 조건은 광학 현미경 사진 분석 결과에서 확인했듯이 표면이 떨어져 나간 영향으로 표면거칠기 값이 가장 높게 측정되었다. 이를 통해 절삭유의 사용 없이 액체질소 냉각만을 사용했을 때는 오히려 가공성능에 좋지 않은 영향을 미친다는 것을 다시 한 번 확인하였다.
Fig. 7Measured surface roughness values (Ra) of machined workpiece
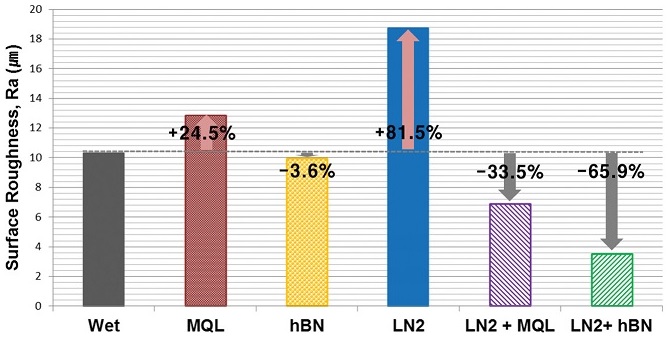
MQL 조건과 hBN MQL 조건을 비교했을 때 식물성오일에 나노입자를 첨가한 hBN MQL 조건이 Wet 조건 대비 표면거칠기 개선효과가 더 좋은 것을 확인하였다. 이는 앞서 분석한 절삭력과 마찰계수 분석 결과와도 일치한다.
액체질소 냉각과 미스트 형태의 극미량 절삭유 윤활을 동시에 적용한 LN2 + MQL 및 LN2 + hBN MQL 조건에서는 MQL 및 hBN MQL 조건과 비교했을 때 표면거칠기 값이 더욱 감소하는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 특히 LN2 + hBN 조건에서는 Wet 조건과 비교하였을 때 표면거칠기 값이 65.9% 감소하였다.
표면거칠기 분석을 통해 앞서 분석한 절삭력과 마찰계수 분석과 마찬가지로 극저온 냉각과 hBN 나노유체 극미량 윤활을 동시에 적용한 경우 냉각과 윤활이 동시에 효과적으로 적용되어 표면 거칠기 개선효과가 최대화됨을 확인할 수 있었고 극저온 냉각과 순수 절삭유 극미량 윤활이 동시에 적용된 경우도 상당한 표면거칠기 개선효과가 있음을 확인하였다.
4. 결론
본 연구에서는 수평형 선반에 극저온 냉각 및 hBN 나노유체 극미량 윤활 시스템을 구성하여 윤활 및 냉각조건 변화에 따라 총 6가지 실험을 설계 후 선반절삭가공 특성평가를 수행하였다. 가공특성 평가를 위한 관측인자로는 절삭력, 마찰계수, 표면거칠기를 선정하였고 실험 결과를 분석하여 다음과 같은 결론을 얻었다.
(1) 절삭유의 사용 없이 극저온 액체질소 냉각만을 적용한 LN2 조건에서 절삭력, 마찰계수, 표면거칠기 분석결과 가공성능이 좋지 않은 것을 공통적으로 확인하였는데 이는 냉각작용은 유효하나 윤활작용의 부재로 인해 가공영역의 공구와 소재의 취성화를 야기하여 돌발적인 공구 파손, 마찰 증가, 표면거칠기 악화를 초래한 것으로 추정된다.
(2) 액체질소 기반 극저온 냉각과 순수 절삭유 및 hBN 나노유체의 극미량 분사를 동시에 적용한 경우는 절삭력, 마찰계수, 표면거칠기 관점의 특성 평가에 있어서 개선효과가 최대화됨을 확인하였는데 이는 액체질소에 의한 극저온 냉각을 통해 공구와 소재사이의 온도 상승을 억제하고 절삭유/나노유체 극미량 윤활을 통한 마찰 감소로 인해 얻는 효과로 판단된다.
본 논문에 주어진 연구 결과를 통해 일반 식물성오일에 나노입자를 첨가한 나노유체 극미량 분사 및 액체질소 냉각 분사를 동시에 적용한 경우 적절한 냉각과 윤활이 이루어져 난삭재인 티타늄 가공에 있어서 가공 성능이 현저히 향상됨을 확인할 수 있었다.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
본 연구는 한국산업기술평가관리원의 산업핵심기술개발사업의 일환으로 수행하였음(No. 10048871).
REFERENCES
- 1.
Rahman, M., Zhi-Gang, W., and Yoke-San, W., “A Review on High-Speed Machining of Titanium Alloys,” International Journal Series C Mechanical Systems, Machine Elements and Manufacturing, Vol. 49, No. 1, pp. 11-20, 2006.
10.1299/jsmec.49.11
- 2.
Greaves, I. A., Eisen, E. A., Smith, T. J., Pothier, L. J., Kriebel, D., et al., “Respiratory Health of Automobile Workers Exposed to Metal Working Fluid Aerosols: Respiratory Symptoms,” American Journal of Industrial Medicine, Vol. 32, No. 5, pp. 450-459, 1997.
10.1002/(SICI)1097-0274(199711)32:5<450::AID-AJIM4>3.0.CO;2-W
- 3.
Raynor, P. C., Cooper, S., and Leith, D., “Evaporation of Polydisperse Multicomponent Oil Droplets,” American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal, Vol. 57, No. 12, pp. 1128-1136, 1996.
10.1080/15428119691014233
- 4.
Priarone, P. C., Robiglio, M., Settineri, L., and Tebaldo, V., “Milling and Turning of Titanium Aluminides by Using Minimum Quantity Lubrication,” Procedia CIRP, Vol. 24, pp. 62-67, 2014.
10.1016/j.procir.2014.07.147
- 5.
Lee, P.-H., Nam, J. S., Li, C., and Lee, S. W., “An Experimental Study on Micro-Grinding Process with Nanofluid Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL),” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 13, No. 3, pp. 331-338, 2012.
10.1007/s12541-012-0042-2
- 6.
Park, K.-H., Ewald, B., and Kwon, P. Y., “Effect of Nano-Enhanced Lubricant in Minimum Quantity Lubrication Balling Milling,” Journal of Tribology, Vol. 133, No. 3, Paper No. 031803, 2011.
10.1115/1.4004339
- 7.
Venugopal, K., Paul, S., and Chattopadhyay, A., “Tool Wear in Cryogenic Turning of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy,” Cryogenics, Vol. 47, No. 1, pp. 12-18, 2007.
10.1016/j.cryogenics.2006.08.011
- 8.
Yap, T., Sivaraos, C., and Leau, J., “Surface Roughness and Cutting Forces in Cryogenic Turning of Carbon Steel,” Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, Vol. 10, No. 7, pp. 911-920, 2015.
- 9.
Pusavec, F., Hamdi, H., Kopac, J., and Jawahir, I., “Surface Integrity in Cryogenic Machining of Nickel Based Alloy-Nconel 718,” Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 211, No. 4, pp. 773-783, 2011.
10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.12.013
- 10.
Groover, M. P., “Fundamentals of Modern Manufacturing: Materials, Processes, and Systems,” John Wiley & Sons, 5th Ed., 2010.