ABSTRACT
This paper investigates the relationship between the preload level of a ball screw drive and the detected natural frequency of the system in an axial direction. A dynamic model to study the preload variation of the system is derived, and then a preload feature is proposed for extracting preload conditions based on the detected natural frequency of the system. A modified double-nut ball screw drive system with adjustable preload level is constructed. This is for the purpose of experimental verification. An accelerometer is attached to the ball screw nuts of the drive system to acquire vibration signals. The signals are analyzed to obtain the natural frequency of the ball screw drive system in an axial direction. By investigating the variation of the detected natural frequency, it is shown that the preload level can be diagnosed by the proposed preload feature. Both the experiment results and mathematical model show a direct correlation between the natural frequency and preload levels. Natural frequency increases when the preload level increases. This study provides a method to monitor the preload of a ball screw system which can be used as an indicator of the health status of the drive system.
-
KEYWORDS: Ball screw, Preload monitoring, Dynamic model, Vibration, Natural frequency
-
KEYWORDS: 볼 스크류, 예압 모니터링, 동적 모델, 진동, 고유 진동수
1. Introduction
Ball screw is the most widely used mechanism to convert rotational motion to linear motion in high speed machine tools because of its high rigidity, efficiency, and accuracy.
1-3 In CNC machines, ball screws are used to improve the positioning accuracy as well as to elongate their service life. In practical establishment of a machine tool, the ball screw is usually preloaded via using oversize balls for a single nut, an offset pitch single nut or a double nut to eliminate backlash of machine movement and increase the stiffness of the drive system for precision motion control. However, after a long time of operation, this presetting preload will gradually degenerate because rolling and sliding friction wear out the balls, nut or screw of the drive system. The preload loss then may lead to a lower stiffness, strong vibration, inaccurate positioning and even fail of the machine tool.
2 On the other hand, over preload will increase friction and generate heat which also has negative impact on the thermal behavior, life expectancy and efficiency of the ball screw. Therefore, it is critical to monitor the preload loss of the ball screw.
In order to monitor the preload variation of a ball screw drive system, many methods were proposed in recent years.
12-15 Studies
12-14 estimated the preload level by analyzing the vibration signals obtained from an accelerometer attached on the ball screw nut while Tsai et al. monitored the preload variation through ball passing frequency.
15 Huang and Shin
12 diagnosed the preload loss through the Hilbert-Huang transform (HHT) and Multiscale Entropy (MSE) process. Although it was successfully to diagnose dynamic preload of 2%, 4%, 6%, this method used a complicated technique which prevents it from being applied to real time operation. Similarly, Fery
13 and Feng
14 used the frequency analysis of vibration signal to extract some features and estimated the preload variation through these features. The problem is that the resonant frequency depends on several parameters rather than just only the preload level such as working table position. This means that the resonant frequency changes with time and thus makes it difficult and nonintuitive to monitor the preload loss through frequency analysis. Tsai et al.
15 detected the ball screw preload loss through ball passing frequency by using Computed Order Tracking (COT) and Angular Velocity Vold – Kalman Filtering Order Tracking (AV VKF – OT) method. However, this method only gives a qualitative result but not a quantitative result which also means that it is not an effective and intuitive method for monitoring the ball screw preload variation. Therefore, it is necessary to derive a method which can indicate the ball screw preload value directly and efficiently.
This study focuses on building a physical model-based monitoring method for ball screw drive preload variation by firstly proposing a lumped dynamic model to investigate the impact of preload to other measurable signals such as the natural frequency and then deriving a preload feature from the measured natural frequency. This preload feature should be independent on the working table position. Secondly, a preload adjustable ball screw drive system is constructed and a program using the derived preload feature is developed to demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed method in monitoring preload level variation. The dynamic model in this study is built to aim at fault-diagnosis application so it should be simple enough to express the relationship between variables clearly but still be able to capture the insights of a ball screw system. Therefore, although many models were built using the Finite Element Method (FEM) or complex modeling techniques,
3-8 they are not exploited in this study. Instead a discrete model based on previous researches
9-11 will be deployed to extract the dominant characteristics of a ball screw drive system.
2. Dynamic Modeling and Preload Feature
2.1 Dynamic Modeling of Preload Adjustable Ball Screw Drive System
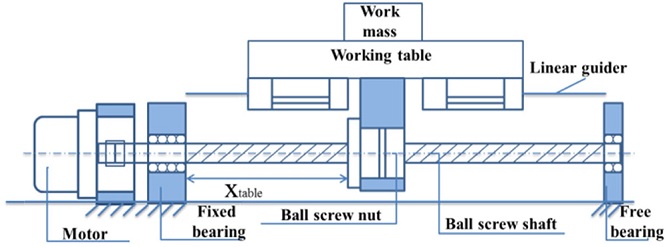
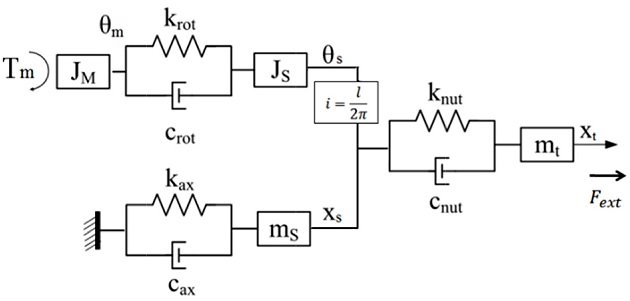
Fig. 1 schematically outlines a typical ball screw assembly with its basic components. In this system, the motor and bearings are fixed to the system base, and the torque from the motor is transmitted through a flexible coupling on to the ball screw shaft. The ball nut is attached to the working table that is constrained to move linearly on LM guides.
Fig. 1Mechanical components of a ball screw feed drive

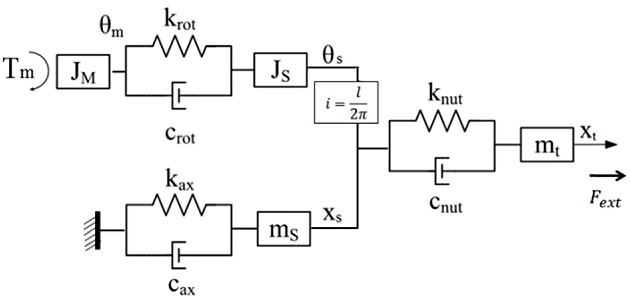
In order to analyze the dynamic characteristics of the ball screw under varied preload levels, the ball screw drive system is modeled using a lumped parameter model as shown in
Fig. 2. The effect of the screw shaft is divided into two parts: axial and rotational part. The rotational part of the screw is in serial with the motor
JM and is modeled as a combination of three elements: a rotational spring
krot is parallel to a damper
crot and both are in serial with a mass component of second polar moment of the cross section of the screw,
Js. When the motor rotates an angle of
θm, it exerts an torque of
TM to the rotational branch making it rotate an angle of
θs. The axial part of the screw is modeled as another combination of three elements: an axial spring
kax is parallel to a damper
cax and both are in serial with a mass component of the screw
ms. This part is forced to move to a position
xs of the screw. The two parts are coupled by the transmission ratio
i =
l/2
π, with l is the lead of screw.
9 Similarly, the screw nut is modeled to comprise three component: an axial spring
knut parallel to a damper
cnut and both in serial with a mass component of the nut and table
mt. The nut is supposed to be excited by an external force
Fext, and position of the table is denoted as
xt.
Fig. 2Discrete model of a ball screw feed drive
When the preload is less than 10% of the ball screw dynamic rating, the stiffness of the screw nut (
knut) can be expressed as a function of the preload (
P) and dynamic load rating (
Ca)
16 as following:
where
K is the nut stiffness from manufacturer catalog. In normal installation, the preload level is in rage of 4-7% of its dynamic load rating, and should not be set larger than 10% of the dynamic load rating. After a long time of operation, however, the presetting preload value will gradually degenerate due to rolling and sliding which cause friction to wear the balls and screw. From
Eq. (1), it is reasonable to model the preload level variation through stiffness of the nut.
As shown in Vicente et al.
7 the ball screw can be considered to possess three fundamental types of eigenmodes: axial, rotational and flexural modes. The flexural deformation relates to the fabrication, installation process and operating conditions of the ball screw drive system. This deformation can be discarded assuming that the screw is properly mounted and operates in normal conditions. The fundamental axial mode and rotational mode which are caused by traction or compression and by torsion respectively have a dominant effect on the overall dynamics of the drive system. These axial and rotational modes are basically determined by the geometrical properties of the ball screw and the position of the table.
Because all components are considered as a combination of lumped mass, discrete spring and damper, the axial and torsional rigidity values of screw can be approximately calculated as following:
where: kshaftax and kshaftrotare the axial and rotational stiffness of the ball screw shaft respectively, E and G are Young modulus and torsional modulus of the screw shaft respectively, L is the screw shaft length while A is the shaft cross sectional area, and dminor is its minor radius.
In this model, both the axial and torsional rigidity of the screw shaft depend on the distance between the fixed bearing which connects motor and screw and the table position
xtable. This can be explained to reflect the effect of table position to both axial part and torsional part of the screw. These two rigidity values are combined with other stiffness of the nut, couplings and bearings to form the overall axial rigidity
kax and rotational rigidity
krot values. These overall axial rigidity and rotational rigidity thus also depend on the table position and can be approximately expressed
9:
In these equations,
knut,
kbearing,
kcoupling and
kbracket are the stiffness of the screw nut, bearing, couplers and nut bracket respectively. In addition, because the rotational part and the axial part of the screw shaft are coupled by the transmission ratio
i, the overall axial stiffness
kax is composed partly by the overall rotational stiffness
krot as shown in
Eq. (4).
The axial and rotational modes of the ball screw drive are characterized by two eigenfrequencies
fax and
frot respectively. These eigenfrequencies are approximated as following
9:
where: mtable, mscrew and mnut are mass of working table, screw nut and screw shaft correspondingly, and Js is the inertial moment of ball screw.
Table 1 lists the values of the parameters used in
Eqs. (1)-
(7). These values were obtained from manufacturer catalogs and calculated based on configurations of a ball screw drive system constructed in this study.
Table 1Parameter values used in modeling the constructed ball screw drive system
Table 1
|
Parameters |
Value |
Unit |
|
mtable: table mass |
20.54 |
[kg] |
|
mscrew: screw mass |
2.024 |
[kg] |
|
mnut: nut mass |
1.3 |
[Kg] |
|
Js: inertial moment of ball screw |
1.169E-4 |
[kgm2] |
|
L: screw length |
971 |
[mm] |
|
E: Young modulus |
206 E9 |
[N/m2] |
|
kbracket: bracket stiffness |
2.1E7 |
[N/m] |
|
knut: nut stiffness from catalog |
470E6 |
[N/m] |
|
kbearling: bearing stiffness |
100E6 |
[N/m] |
|
kcoupling: coupler stiffness |
849 |
[N-m/rad] |
|
dminor: screw minor diameter |
17.2 |
[mm] |
|
l: screw lead |
6 |
[mm] |
|
d: screw diameter |
20 |
[mm] |
Eqs. (6) and
(7) show that only the axial mode depends on the nut stiffness while the rotational mode is not affected by the nut stiffness variation; this means that only the axial mode depends on the preload level. Thus, the axial eigenfrequency is used to investigate the variation of preload level through variation of nut stiffness.
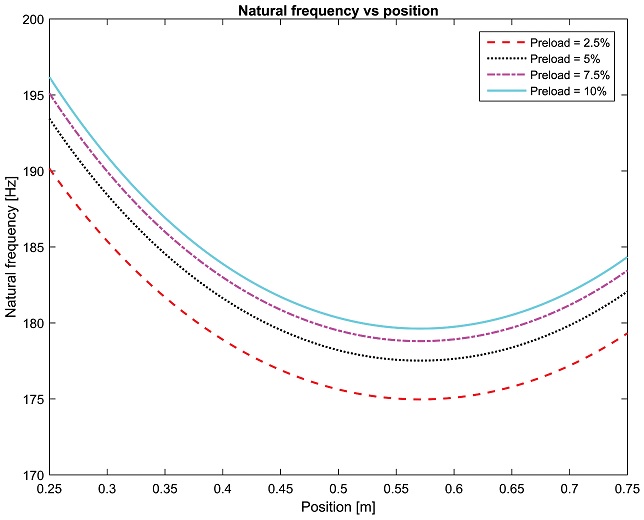
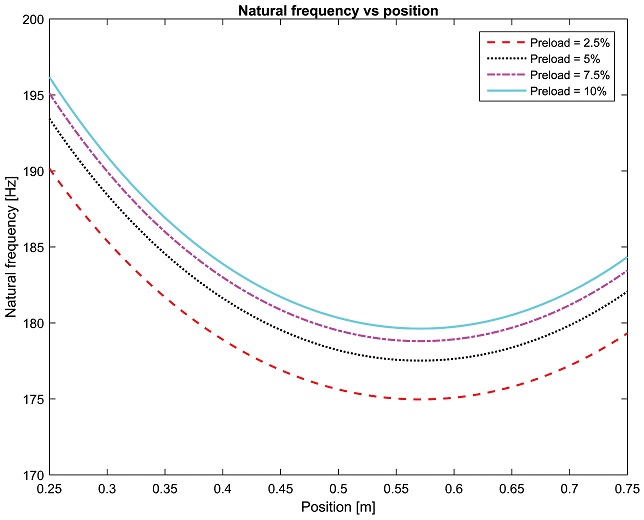
Fig. 3 shows the axial natural frequencies in different positions under the preload level of 2.5%, 5%, 7.5% and 10%. The axial natural frequency varies with both preload level and table position. The higher the preload value is set, the higher the axial natural frequency is, however the change of axial natural frequency values decrease as the preload level closes to the maximum level of 10%. This indicates that the axial natural frequency tends to saturated value when the preload level increases close to the maximum value of 10%. For the relationship with the table position, the axial natural frequency decreases as the position increases but to some distance it will increase while the position continues to increase.
Fig. 3Axial natural frequency as the preload level and table position varies
2.2 Diagnosis Ball Screw Preload Loss Based on Preload Feature
Results from
Eq. (6) and
Fig. 3 show that the axial natural frequency can be used as an indicator for the preload level, however it also varies with the table position. A new parameter called ‘Preload feature’ which depends only on the preload level will be derived so that it can be used as a direct indicator for the preload level as below. From
Eqs. (4) and
(6),
fax can be rewritten as:
then:
where
Ai and
ki are constant parameters calculated from the stiffness values of the ball screw drive system with the parameters in
Table 1. The variable
P'2 is proportional to the preload level so it can be used as an indicator of the preload level, and then is call “Preload feature”. More importantly, this Preload feature is independent on the table position so by monitoring this value, the preload level of the ball screw drive system is monitored directly. This study focuses on employing this value to build a preload loss monitoring system for the constructed ball screw drive system.
3. Experimental Results
3.1 Preload- Adjustable Ball Screw System Setup
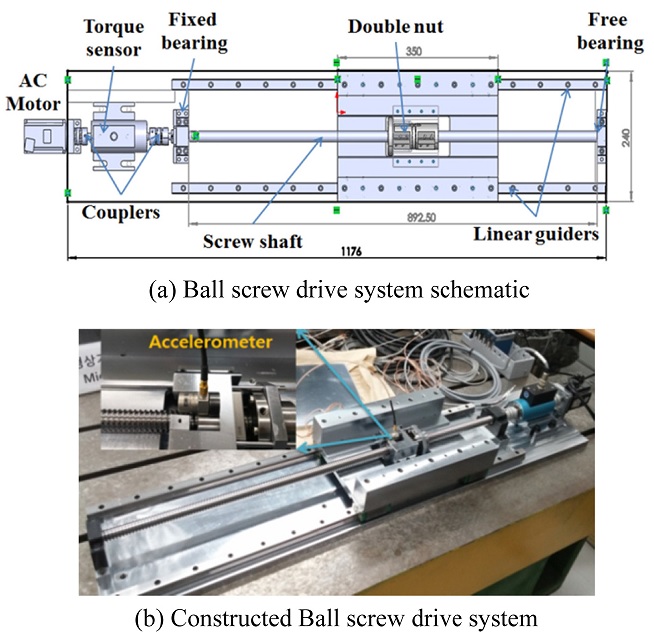
A single axis ball screw drive system is built to study the preload monitoring using the derived Preload feature.
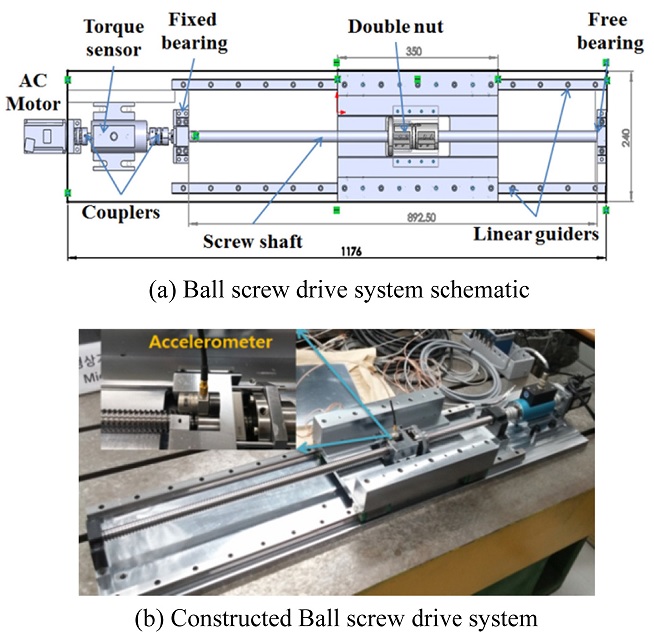
Fig. 4 shows the configuration of the entire ball screw drive system comprising: an AC motor and driver, a torque sensor, two couplers for coupling the motor, torque sensor and the screw; one fixed bearing between the torque sensor and the screw and one free bearing at the other end of the screw shaft for supporting the screw. The specifications of the screw are: length 950 mm, lead 6 mm and diameter: 20 mm (Model: BNFN2006). The drive system is formed with a double-nut which is equipped with a preload adjustment mechanism to change the preload level of the drive system.
Fig. 4Experimental set-up with a double-nut Ball screw drive system
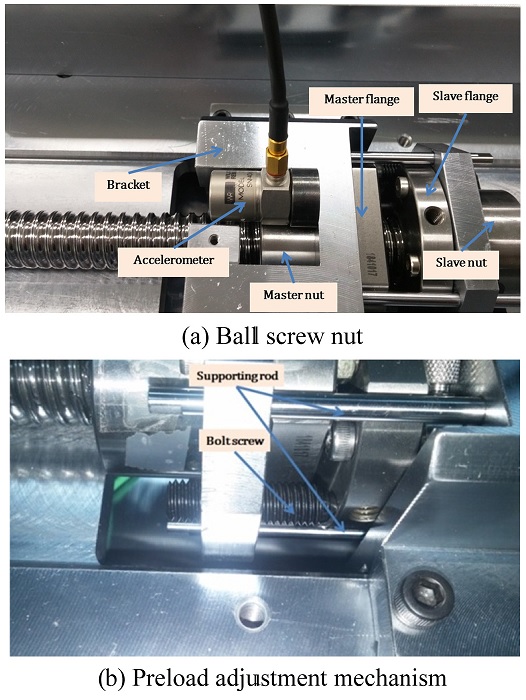
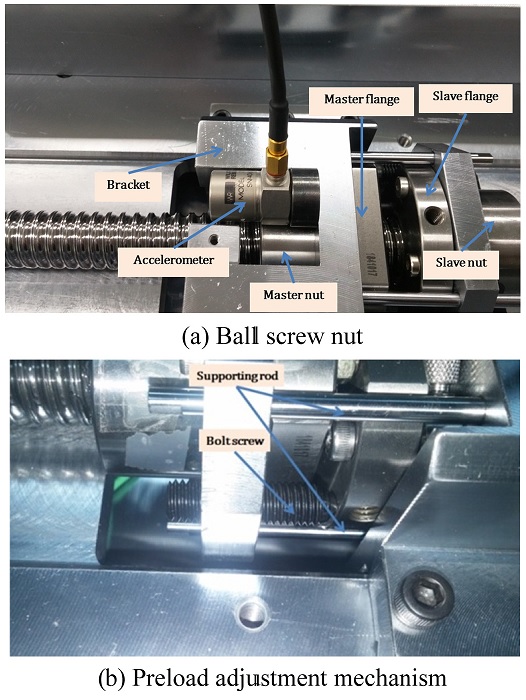
In order to investigate variation of the ball screw drive preload level, a preload adjustment mechanism is built to regulate the force acting on the master and slave nuts. The double nut provided by the manufacturer is modified to construct the adjustment mechanism as shown in
Fig. 5. The flanges on master nut and slave nut are placed opposite each other. Two holes are machined on the master flange for two positioning bolt screws put there. It is these bolt screws create force on the nuts when they are rotated. These positioning bolt screws are placed on two symmetric sides of the flanges so that equal forces will be created on two sides of the flange preventing screw nut from eccentric mounting. This configuration also secures a symmetric preload on the nuts reducing vibration during operation. Once the positioning bolt screws are rotated, they exert an axial force to the slave nut, stretching the distance between the master and slave nut larger. This movement displaces the balls inside master and slave nuts axially creating the preload to the ball screw drive.
Fig. 5The double-nut set-up for preload adjustment and vibration measurement
From the datasheet of manufacturer and previous experiments, the maximum preload value for this study is 400N corresponding to 10% of the dynamic rating. A torque wrench is used to set the preload value to the ball screw by rotating the positioning bolt screws. The relationship between torque and axial force of a bolt screw is:
where d is the nominal outside diameter of the bolt and λ is the correction factor that depends on the material, size, surface friction, and threading of the bolt. In most of the cases, K is approximately equals to 0.2. In this constructed system, the bolt screws have a nominal diameter of 4 mm. Thus, to apply a preload of 100 N to the ball screw, a torque of 4 kgf.cm should be applied to each positioning bolt screw. For the purpose of investigating the preload variation, three levels of preload will be applied to the ball screw respectively to three basic statuses of preload level: 100 N, 200 N and 300 N corresponding to slightly preloaded (2.5%), normal preloaded (5%) and tightly preloaded level (7.5%).
To implement the ball screw drive system, both the working table and the slave nut are attached to the master nut. A bracket bolted to the master nut flange is used to connect the working table and master nut while the slave nut is fixed by 4 symmetric supporting columns as shown in
Fig. 5(b). These column structures also help to prevent the master and slave nut from rotating around the screw as well as bending effect, making the system more rigid and decreasing the vibration when in operation. Thus, it is appropriate to consider the master nut, slave nut, bracket, supporting columns and the working table as a rigid body.
Because only the axial natural frequency is exploited to monitor the preload level variation, an uniaxial accelerometer is suitable for this study. Due to the closer distance to the balls inside the nuts, the vibration on the nuts is much stronger than on the working table so the accelerometer is attached to the master nut. The bracket is specially designed to create space near the master nut for attaching the accelerometer to the master nut as shown in
Fig. 5(a).
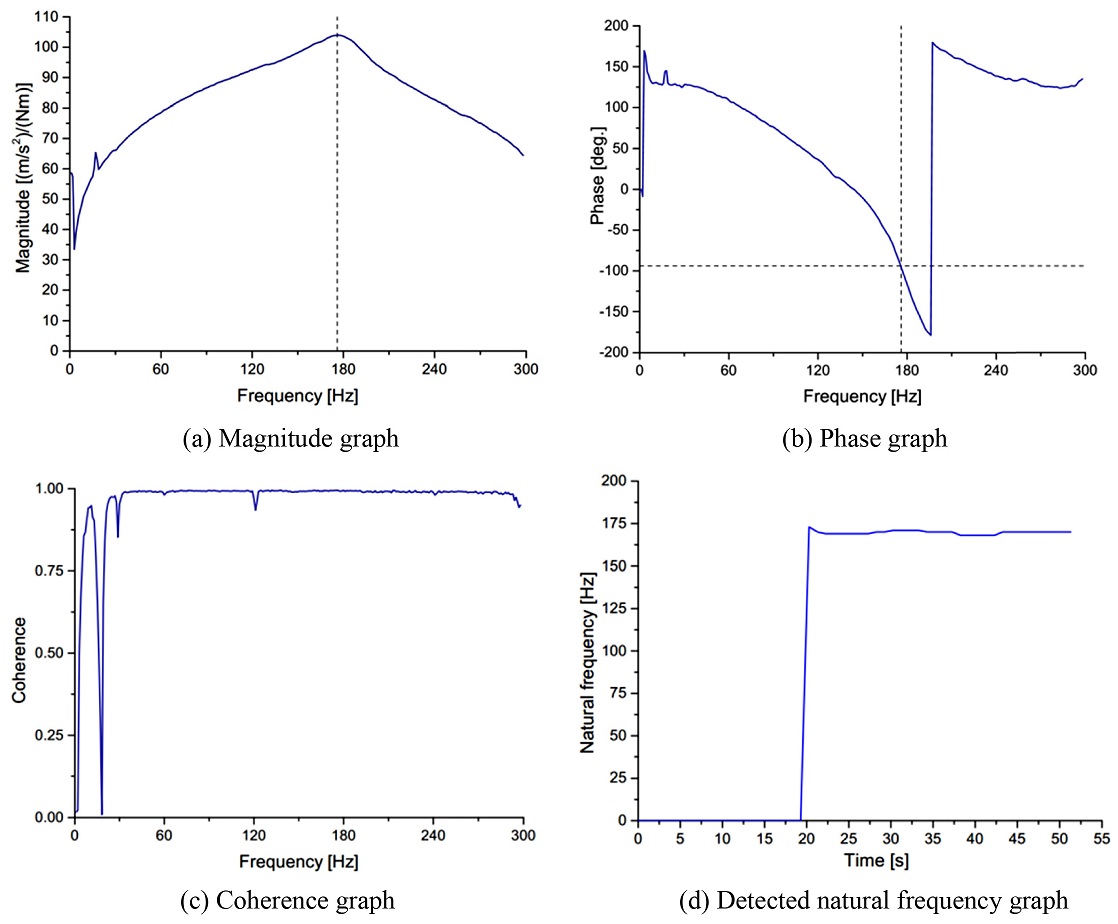
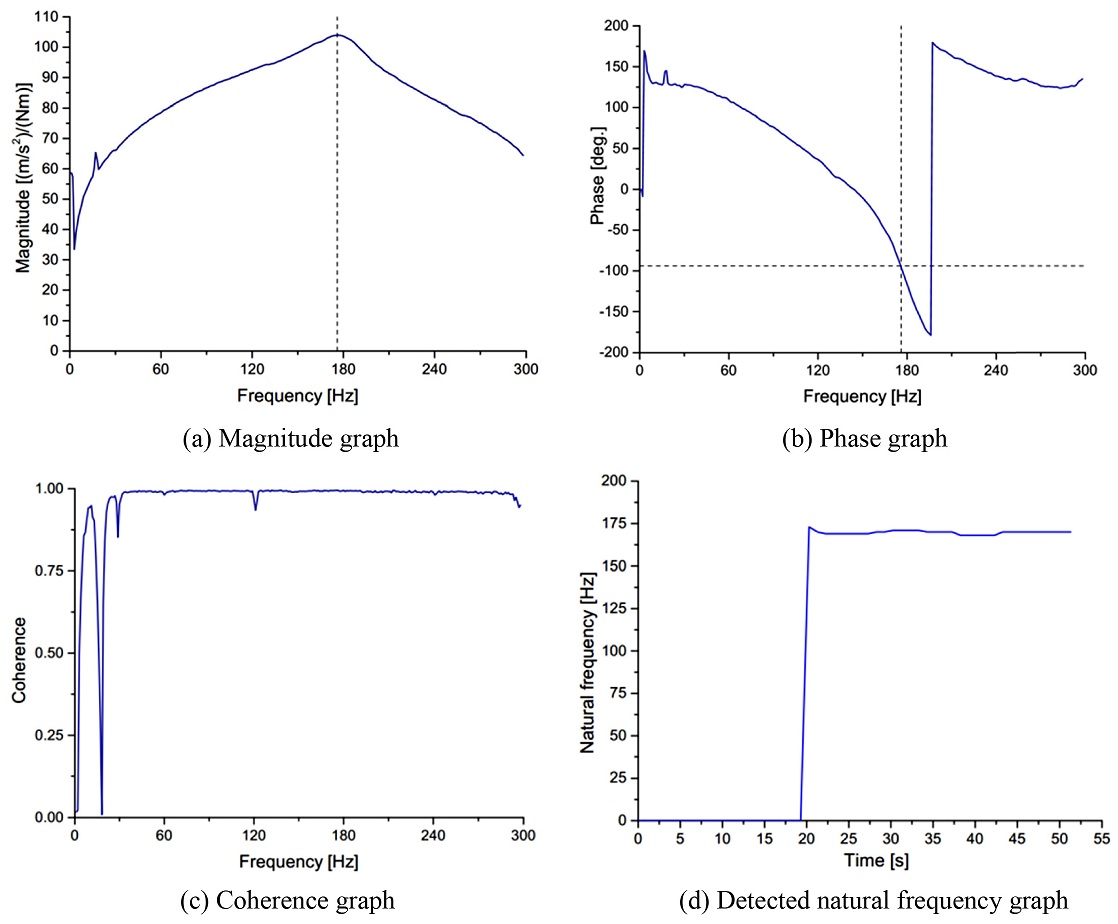
The acquired vibration signal is then transferred to a signal processing circuit via an NI DAQ system and stored in computer for further analysis. The DAQ system provides processing functionality for condition monitoring and anti-aliasing filters. A processing program using Peak picking algorithm is built in LabVIEW to detect the natural frequency from the vibration signals. The result is confirmed by the Coherence and Phase change graphs as shown in
Fig. 6.
Figs. 6(a)-
6(c) respectively show the magnitude, phase and coherence of the Frequency Response Function (FRF) which is created by torque signal as input and vibration signal as output. In
Fig. 6(a), the magnitude peak is at frequency approximately 175 Hz, the corresponding phase of the FRF at that frequency is about -90
o as shown by dash line in
Fig. 6(b), and the coherence value is nearly 1 as shown in
Fig. 6(c). The values of detected natural frequency is plotted versus time as shown in
Fig. 6(d).
Fig. 6Measured frequency response functions by the monitoring program
The motor is controlled by a PMAC controller program which included an encoder whose values can be converted to the position of the working table. The LabVIEW monitoring program also is interfaced to the PMAC controller to get the encoder value, converting it to the position of working table. The detected natural frequency will be combined with the table position values for further process to indicate the current preload level as schemed in
Eq. (8).
The ball screw drive system is actuated by the AC motor through command of PMAC ramp position program. The program moves the ball screw forth and back in a short time with high speed mimicking the effect of an impact test. Each command repeats the movement 30 times (15 forward movements and 15 backward movements). The vibration signal is then processed by following functionalities: filtered by a low pass filter to eliminate the aliasing effect; Hanning window and averaging 15 times to increase Signal-to-Noise ratio and finally Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) to present vibration signal in frequency domain as in
Fig. 6.
In order to validate the proposed dynamic model and preload monitoring using the Preload feature, the parameters
ki in
Eq. (8) will be evaluated again from detected natural frequencies. Thus, natural frequencies under various preload levels and different positions are measured and parameters
ki will be regressed from the measured values. At each position, the natural frequencies are measured 20 times and average values are used as natural frequency at that point.
Table 2 shows the measured natural frequencies and the corresponding standard deviations when working table is at different positions.
Table 2Natural frequency under different preload levels and positions
Table 2
Preload level
(N) |
Table position
(mm) |
Average natural
frequency (Hz) |
Standard
deviation (Hz) |
|
50 |
250 |
189.093 |
0.475 |
|
50 |
500 |
172.876 |
0.538 |
|
50 |
750 |
175.553 |
0.238 |
|
100 |
250 |
192.533 |
0.853 |
|
100 |
500 |
176.052 |
0.335 |
|
100 |
750 |
178.123 |
0.790 |
|
150 |
250 |
194.210 |
0.730 |
|
150 |
500 |
177.377 |
0.245 |
|
150 |
750 |
179.69 |
0.827 |
|
200 |
250 |
195.528 |
0.861 |
|
200 |
500 |
178.724 |
0.36 |
|
200 |
750 |
180.826 |
0.285 |
|
250 |
250 |
196.325 |
0.555 |
|
250 |
500 |
179.145 |
0.646 |
|
250 |
750 |
180.996 |
0.568 |
|
300 |
250 |
197.021 |
0.669 |
|
300 |
500 |
179.830 |
0.301 |
|
300 |
750 |
182.379 |
0.473 |
From the measured results, values of
ki are evaluated and shown in the
Table 3. The difference between mathematical model and measured results are acceptable and can be explained as following. In the proposed dynamic model, only the stiffness of screw nut, bearing and screw shaft (axial and rotational modes) are counted. The other components such screw nut pedestal, bracket and supporting columns which also add some more mass and stiffness components to the overall drive system are not included. In addition, the coupled effect of the axial and rotational parts of the screw shaft, which is simplified in the proposed model, also contributes to the difference. However, the mathematically calculated results and the measured results are still close enough to confirm that the proposed dynamic model is validated.
Table 3Natural frequency under different preload levels and positions
Table 3
|
Parameter |
Calulated value |
Regressed value |
|
k
1
|
-4557E-8 |
-4872E-8 |
|
k
2
|
5173E-8 |
5561E-8 |
|
k
3
|
2096E-8 |
2097E-8 |
|
k
4
|
1287E-8 |
1228E-8 |
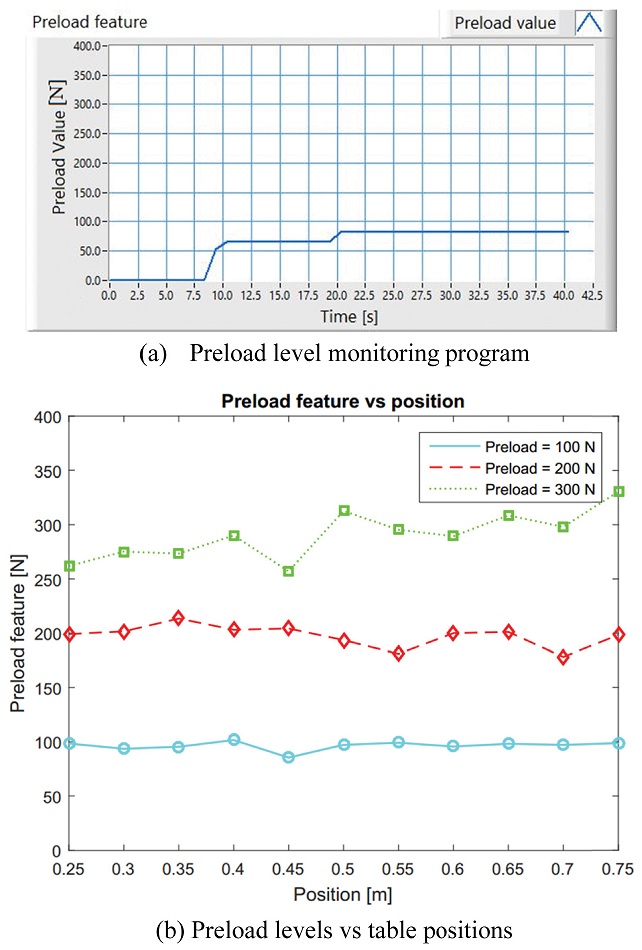
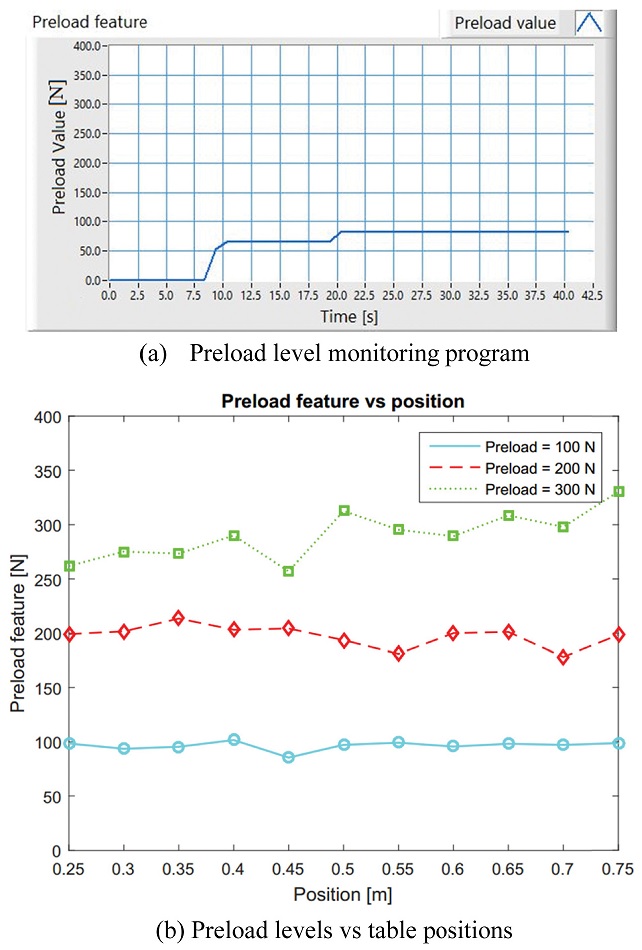
A preload level monitoring program then is built in LabVIEW using the regressed
ki parameters as shown in
Fig. 7(a). As shown in
Eq. (8), the program should eliminate the effect of working table position on the natural frequencies so the measured preload level is independent on the table positions. Three preload levels of 100 N, 200 N and 300 N will be preset to the ball screw perspectively to 2.5%, 5%, and 7.5% of the dynamic rating value. The preload levels are again measured in different positions to secure that they are constant to the table position. At each position, the preload values are measured 20 time. The measured preload level versus the table position is shown in
Fig. 7(b). It is clearly shown that the average preload levels are different insignificantly from the presetting values. More importantly, the measured preload levels are almost constant at different positions of the working table.
Fig. 7Preload measurement and results
3.3 Discussion
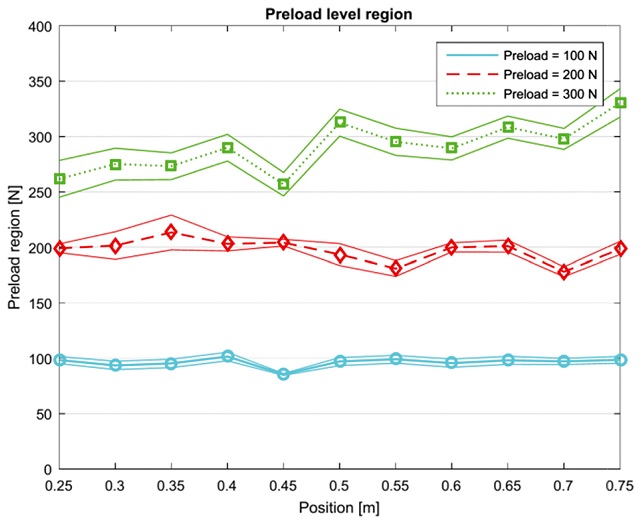
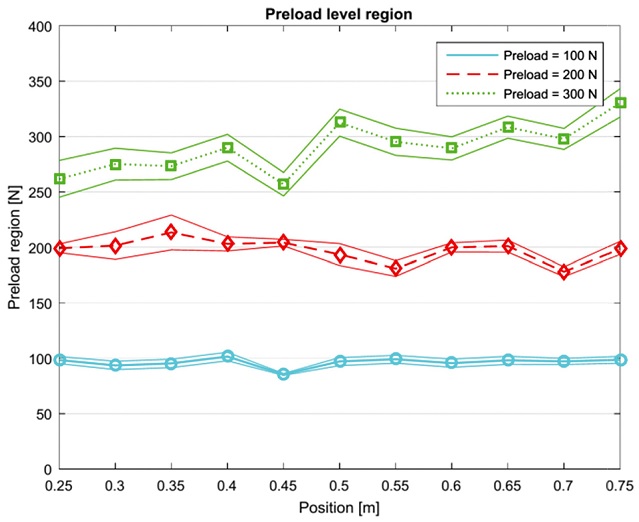
In order to secure the proposed method more firmly and make it applicable in practical for monitoring preload level of a ball screw drive system, the 95% confidence interval of measured results is calculated to secure that the proposed method can distinguish two preload levels clearly. For a population with unknown mean and unknown standard deviation, a confidence interval for the population mean, based on a random sample of size n, is:
where
t* is the upper (1-
C)/2 critical value for the t distribution with
n-1 degrees of freedom,
t(
n-1). In this study, the number of samples is 20 and the corresponding
t* value is 2.086, and the confidence intervals are calculated and shown in
Fig. 8. The solid lines are the upper and lower boundary levels of the confidence interval while the dash lines are the average measured values. It is shown that there is no overlap in the regime of the 95% confidence intervals of the three typical levels. This result confirms that the method distinguishes three typical preload levels of a ball screw drive system. In addition, the gap of boundaries increases with the presetting preload values. When the presetting value of preload is 100 N, the measured values are the most consistent with smallest standard deviations from 1.68 to 8.25 N. The standard deviation value increases to higher values when the preload value is 200 N, and reaches the maximum value at 35.51 N when the measured preload is 261 N and the corresponding presetting preload value is 300 N. These standard deviation values assert that the measured results are close to the expected value as well as the presetting preload levels. These results again confirm the derivation from
Eq. (8) as well as the applicability of the proposed method for monitoring preload variation of a ball screw drive.
Fig. 8Preload level region vs table positions
In practical installation, a fixed value of preload level is set by the manufacturer before operations. If this value and other parameters in
Table 1 are known, a dynamic model can be built using the proposed method, and a preload variation monitoring can be implemented using method in this study. In the case the presetting preload value is unknown, the variation of preload between two measuring times still can be estimated using the propose method. Thus, at least the tendency of preload variation can be diagnosed and an appropriate maintenance process will be concluded from the results.
The proposed method can be simply applied to practical machine tools for monitoring the preload variation. For more accurate results, other parameters related to operating conditions such as temperature, drive system speed must be included.
4. Conclusion
A discrete dynamic model for a ball screw drive system is proposed to study the variation of the system preload. A preload feature parameter indicating the onset preload level is derived from the dynamic model and implemented in a program for monitoring the preload variation. This parameter is intuitive and effective to monitor the preload variation of the ball screw drive system because it is independent on the table position and indicates the preload value directly instead of using the natural frequency variation or the magnitude of vibration at peak frequencies which also vary with the working table position. The constructed ball screw drive system successfully demonstrates the validation of the proposed method. The agreement of the mathematically dynamic model and experimental results shows that the method proposed in this study is applicable to monitor the preload status of the feed drive system after an operation period. This could be extended to monitor the overall the health status of the ball screw drive system as well as the machine tool in practical manufacturing.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the Technology Innovation Program (10060188, Development of ICT-based smart machine tools and flexible automation systems) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE, Korea).
REFERENCES
- 1.
Altintas, Y., Verl, A., Brecher, C., Uriarte, L., and Pritschow, G., “Machine Tool Feed Drives,” CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 60, No. 2, pp. 779-796, 2011.
10.1016/j.cirp.2011.05.010
- 2.
Frey, S., Walther, M., and Verl, A., “Periodic Variation of Preloading in Ball Screws,” Production Engineering, Vol. 4, Nos. 2-3, pp. 261-267, 2010.
10.1007/s11740-010-0207-8
- 3.
Zaeh, M., Oertli, T., and Milberg, J., “Finite Element Modelling of Ball Screw Feed Drive Systems,” CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 53, No. 1, pp. 289-292, 2004.
10.1016/S0007-8506(07)60700-8
- 4.
Okwudire, C. E. and Altintas, Y., “Hybrid Modeling of Ball Screw Drives with Coupled Axial, Torsional, and Lateral Dynamics,” Journal of Mechanical Design, Vol. 131, No. 7, Paper No. 071002, 2009.
10.1115/1.3125887
- 5.
Holroyd, G., Pislaru, C., and Ford, D. G., “Modelling the Dynamic Behaviour of a Ballscrew System Taking into Account the Changing Position of the Ball-Screw Nut,” WIT Transactions on Engineering Sciences, Vol. 44, pp. 337-348, 2003.
- 6.
Varanasi, K. K. and Nayfeh, S. A., “The Dynamics of Lead-Screw Drives: Low-Order Modeling and Experiments,” Transactions-American Society of Mechanical Engineers Journal of Dynamic Systems Measurement and Control, Vol. 126, No. 2, pp. 388-396, 2004.
10.1115/1.1771690
- 7.
Vicente, D. A., Hecker, R. L., Villegas, F. J., and Flores, G. M., “Modeling and Vibration Mode Analysis of a Ball Screw Drive,” International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 58, No. 1, pp. 257-265, 2012.
10.1007/s00170-011-3375-6
- 8.
Chen, J.-S., Huang, Y.-K., and Cheng, C.-C., “Mechanical Model and Contouring Analysis of High-Speed Ball-Screw Drive Systems with Compliance Effect,” International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 24, Nos. 3-4, pp. 241-250, 2004.
10.1007/s00170-003-1777-9
- 9.
Frey, S., Dadalau, A., and Verl, A., “Expedient Modeling of Ball Screw Feed Drives,” Production Engineering, Vol. 6, No. 2, pp. 205-211, 2012.
10.1007/s11740-012-0371-0
- 10.
Isermann, R., “Fault-Diagnosis Applications: Model-Based Condition Monitoring: Actuators, Drives, Machinery, Plants, Sensors, and Fault-Tolerant Systems,” Springer Science & Business Media, pp. 226-229, 2011.
10.1007/978-3-642-12767-0_12
- 11.
Sobolewski, J. Z., “Vibration of the Ball Screw Drive,” Engineering Failure Analysis, Vol. 24, pp. 1-8, 2012.
10.1016/j.engfailanal.2012.03.002
- 12.
Huang, Y.-C. and Shin, Y.-C., “Method of Intelligent Fault Diagnosis of Preload Loss for Single Nut Ball Screws through the Sensed Vibration Signals,” Proc. of International Conference on Machine Learning and Data Analysis, pp. 1394-1401, 2012.
- 13.
Frey, S., Walther, M., and Verl, A., “Periodic Variation of Preloading in Ball Screws,” Production Engineering, Vol. 4, Nos. 2-3, pp. 261-267, 2010.
10.1007/s11740-010-0207-8
- 14.
Feng, G.-H. and Pan, Y.-L., “Investigation of Ball Screw Preload Variation Based on Dynamic Modeling of a Preload Adjustable Feed-Drive System and Spectrum Analysis of Ball-Nuts Sensed Vibration Signals,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 52, No. 1, pp. 85-96, 2012.
10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2011.09.008
- 15.
Tsai, P., Cheng, C., and Hwang, Y., “Ball Screw Preload Loss Detection Using Ball Pass Frequency,” Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Vol. 48, No. 1, pp. 77-91, 2014.
10.1016/j.ymssp.2014.02.017
- 16.
THK Corporation, “Ball Screw THK General Catalog,”
www.thk.com (Accessed 23 JAN 2018)