ABSTRACT
The International System of Units (acronym: SI) is founded on seven base units (meter, kilogram, second, ampere, kelvin, mole, and candela) corresponding to seven base quantities (length, mass, time, electric current, thermodynamic temperature, amount of substance, and luminous intensity). SI was formally established in 1960 by the 11th CGPM. It has been revised from time to time in response to requirements of users and advances in science and technology. However, the most significant revision is going to be done in November 2018 by the 26th CGPM. Four base units (kilogram, ampere, kelvin, and mole) will be given new definitions linking them to exactly defined values of Planck constant, elementary charge, Boltzmann constant, and Avogadro constant, respectively. In this paper, historical background for the revision of SI is described and scientific principle of redefinition is explained. The procedure used to redefine meter from the speed of light in a vacuum is used as an example. After this revision, uncertainties of many other fundamental constants will be eliminated or reduced. From May 20, 2019 (World Metrology Day), the revised SI will come to practice.
-
KEYWORDS: SI, Base units, Redefinition, Fundamental constants, Meter, Relative uncertainty
-
KEYWORDS: 국제단위계, 기본단위, 재정의, 기본상수, 미터, 상대불확도
NOMENCLATURE
International system of units
General conference on weights and measures
International committee for weights and measures
International bureau of weights and measures
Committee on DATA for science and technology
Task group on fundamental constants
International prototype of meter
International prototype of kilogram
Mise-en-Pratique= Practical realization
National metrology institute
Speed of light in a vacuum
Relative standard uncertainty
International avogadro coordination
Consultative committee for mass and related quantities
Consultative committee for time and frequency
1. 서론
국제단위계 (SI)는 7개의 기본단위와 22개의 특별한 명칭 및 기호를 가진 유도단위와, 이 유도단위 또는/및 기본단위들의 조합으로 구성된 유도단위와, SI는 아니지만 사용이 허용된 단위들로 구성된 단위계이다.
1
SI는 1960년에 처음 만들어졌다. SI가 만들어지기 전에도 몇몇 단위들은 이미 정의되어 사용되고 있었다. 예를 들면, 길이의 단위인 미터(기호: m)와 질량의 단위인 킬로그램(기호: kg)은 1799년에 백금으로 만들어진 미터 원기와 킬로그램 원기로 각각 정의되었었다.
미터 기반의 단위들을 국제적으로 통용하기 위해 1875년에 파리에서 17개국이 참여하는 ‘미터 협약’이 체결되었다. 이 협약에 의해 미터 원기와 킬로그램 원기를 백금과 이리듐의 합금으로 다시 만들었다.
2 그리고 이것들의 관리 책임이 프랑스에서 국제기구로 이전되었다. 이 때 만들어진 국제기구가 국제도량형총회(CGPM), 국제도량형위원회(CIPM), 그리고 국제도량형국(BIPM)이다. 이 중 CGPM이 최상위 기관으로서 4년마다 개최되며 국제도량형과 관련된 최종 중요한 결정을 내린다. BIPM은 사무국 역할을 하는 기구로서 실제 건물과 운영 인력으로 구성된다. CIPM은 전문가들의 모임으로 매년 개최되는데, 국제도량형과 관련된 과학기술적인 문제를 해결하기 위해 결의안을 만들어 CGPM에 제출하고, 위임된 사항에 대해서는 결의안을 직접 채택한다. 이 국제기구들은 강제 집행력을 갖지 않지만 그 전문성과 권위로 인해 채택된 결의안들은 여러 나라의 과학기술 정책에 큰 영향을 미친다.
1889년에 개최된 제1차 CGPM에서 미터 원기와 킬로그램 원기는 각각 국제미터원기(IPM)와 국제킬로그램원기(IPK)로 승인을 받았다. 그 때부터 이 세 국제기구는 단위 및 도량형과 관련된 모든 국제 활동의 중심 역할을 해오고 있다. 예를 들면, 1946년에 CIPM의 승인을 받아 MKSA 체계(미터-킬로그램-초-암페어)가 만들어졌다. 그리고 1948년에는 광도의 단위인 칸델라(기호: cd)가, 1954년에는 열역학적 온도의 단위인 켈빈(기호: K)이 MKSA 체계에 포함되었다. 이로써 1960년에 SI가 출발할 수 있는 모든 준비가 갖추어졌다.
SI의 일부 기본단위는 그 정의가 바뀌어 왔다. 가장 대표적인 것으로 미터가 있다. 제2장에서는 미터의 재정의의 역사적 변천 내용을 알아본다. 현재 미터는 기본상수의 하나인 진공에서의 빛의 속력(c)을 기반으로 정의되어 있다. 그런데 2018년에 개최되는 제26차 CGPM에서는 4개의 SI 기본단위(킬로그램, 암페어, 켈빈, 몰)를 미터와 같은 방식으로 기본상수를 기반으로 재정의하려고 한다. 미터의 재정의 과정을 이해하면 다른 단위들을 재정의하려는 이유와 그 원리를 이해할 수 있다.
제3장에서는 새로 정의된 기본단위와 기본상수와의 관계를 알아본다. 그리고 단위의 정의를 구현하는 방법에 대해서도 알아본다. 제4장에서는 SI 기본단위가 재정의됨으로써 과학기술분야에서 발생될 것으로 예상되는 활동과 변화를 예측해본다.
2. 미터의 재정의
2.1 미터 정의의 역사적 변천
국제미터원기(IPM)는 CGPM의 승인을 받은 후 BIPM 금고 속에 보관 되어 있었다. 세계에서 유일한 길이의 기준 잣대이기 때문에 보관과 유지 관리에 특별한 주의를 기울여야만 했다. 그런데 다른 여러 나라에서도 길이의 기준이 필요했기 때문에 IPM의 복제본을 여러 개 만들어 그 당시 미터협약국들에게 배포했다. 국제킬로그램원기(IPK)도 마찬가지로 복제본을 만들어 배포했다. IPM과 IPK는 인공물 자체가 ‘단위의 정의’이면서 ‘단위의 구현’ (Mise-en-Pratique)이다. 이것들이 예상치 못한 사고나 재난에 의해 사라지거나 망가지면 단위 자체가 없어지는 것이다. 그리고 복제본들은 세월이 지나면 그 값(길이 또는 질량 값)이 달라질 수 있는데, 그것들의 정확도는 이 원기(IPM 또는 IPK)와 직접 비교해야만 알 수 있다.
약 70년간 미터의 정의로 사용되던 IPM은 이런 문제로 인해 1960년에 그 당시의 과학기술의 발전에 힘입어 다음과 같이 재정의 되었다.
“미터는 크립톤 86 원자의 2p10과 5d5 준위간의 전이에 대응하는 복사선의 진공에서의 파장의 1 650 763.73 배와 같은 길이이다.”
가스의 방전관에서 발생하는 빛은 가스를 구성하는 원소의 종류에 따라 그 색깔(즉, 파장)이 다르다. 원소에서 발생하는 스펙트럼의 파장을 측정하고 분석하는 기술은 19세기 중엽에 분광분석법이 개발된 이후 지속적으로 발전되어 왔다. 크립톤 86 원자가 들어있는 램프에서 발생하는 빛은 주황색을 띄는데, 그 선 스펙트럼을 분광계로 측정하면 중심 파장이 605.7 nm이다. 따라서 이 파장을 약 165만배하면 1 미터가 된다. 이런 식으로 1 미터를 구현하는 것이 IPM과 같은 기준 잣대로 1 미터를 구현하는 것보다 더 정밀하고 편리하였기 때문에 미터의 정의가 바뀌게 된 것이다. 그 보다 더 중요한 이유는 크립톤 86 원자에서 발생하는 605.7 nm 빛은 실험 조건을 동일하게 만들면 언제 어디에서건 동일하다는 점이다. 이것이 망가지거나 훼손되더라도 복원하여 단위를 구현할 수 있다는 것은 IPM이 갖지 못한 최대의 장점이다.
이렇게 재정의된 미터는 1983년에 다시 현재와 같이 진공에서의 빛의 속력을 기반으로 바뀐다. 그 과정에는 빛의 속력을 정확히 측정하는 기술과 빛과 관련된 이론의 발전이 있었다. 빛의 속력을 측정하는 연구는 17세기 갈릴레오 갈릴레이 이후 약 400년 동안 많은 과학자들에 의해 시도되었다. 비교적 최근인 19세기에 마이켈슨(A. Michelson)은 일정 거리(최장 36.8 km)를 빛이 갔다가 오는데 걸린 시간을 측정하여 빛의 속력을 구했다.
전자기 이론을 종합하여 정립한 맥스웰(J. Maxwell)은 1864년에 빛은 전자파이며 그 전파 속력이 일정하다는 것을 이론적으로 증명했다. 그리고 아인슈타인은 1905년에 특수상대성 이론에서 진공에서의 빛의 속력은 어느 관성계에서나 일정하다는 것을 밝혔다. 진공에서의 빛의 속력은 항상 일정하다는 것이 이론으로 증명되었으므로 실험으로 그 값을 찾는 것이 그 당시 과학기술계에서 중요한 과제였다. 세계대전을 거치면서 레이더 개발을 통해 발전된 전자파 기술의 도움을 받아 빛의 속력 측정은 이전과는 전혀 다른 방식으로 시도되었다.
영국의 에센(L. Essen)은 1950년에 마이크로파 공진기에서 일어나는 공진 현상을 이용하여 전자파의 주파수(
f)와 파장(
λ)을 동시에 측정하고, 그 둘의 곱(
c =
fλ)으로부터 전자파의 전파 속력을 구했다. 이와 비슷한 방법이 주파수가 1000배 이상 높은 레이저에 적용되면서 그 정확도가 획기적으로 개선되었다. 즉, 미국의 이벤슨(K. Evenson) 등은 1972년에 메탄 분자에 안정화된 3.39 μm (88 THz) 헬륨-네온 레이저의 주파수와 파장을 동시에 측정했다.
3 파장은 레이저 간섭계를 이용하여 쉽게 측정할 수 있었다. 그러나 빛의 주파수를 측정하기 위해선 그 당시에 측정 가능했던 마이크로파 주파수에서 광 주파수(적외선) 영역으로 주파수를 높이는 작업이 필요했다. 이를 위해 파장이 다른 다섯 대의 레이저와 마이크로파를 발생하는 다섯 대의 클라이스트론(Klystron)을 사용했다. 이 기술을 요약하면, 서로 다른 마이크로파 및 광 주파수를 위상 잠금(Phase Locking)을 통해 조화파를 만드는 방법으로 주파수를 합성하여 X-밴드(대략 10 GHz)에서 88 THz에 이르는 주파수 체인을 구성한 것이다.
파장과 주파수는 1차 표준(Primary Standard)이 다르다. 파장의 차원은 길이이므로 앞에서 말한 605.7 nm를 발생하는 크립톤 표준램프가 1차 표준이었다. 이에 비해 주파수는 그 차원이 시간의 역수로서, 1차 표준은 세슘원자시계이다. 그 당시 시간 표준의 정확도는 길이 표준보다 10배 이상 높았다. 이벤슨의 실험에서 3.39 μm의 헬륨-네온 레이저 파장을 간섭계로 측정할 때 길이의 표준으로 크립톤 램프를 사용했다. 그런데 이 길이 표준의 상대불확도는 자체 불확도 평가에서 ± 3 × 10-9으로 알려져 있었다. 이 불확도의 주된 원인은 크립톤 램프에서 나오는 선 스펙트럼의 중심 파장을 결정하는 과정에 있었다. 결론적으로 3.39 μm 파장 측정의 상대불확도는 δλ/λ = ± 3.5 × 10-9이었다. 그런데 88 THz 주파수 측정의 상대불확도는 δν/ν = ± 6 × 10-10이었다. 이 둘의 곱(c = νλ)으로 구한 빛의 속력의 상대불확도는 전적으로 파장 측정 불확도에 의해 결정되어 δc/c = ± 3.5 × 10-9이었다. 이것은 곧 길이 표준이 빛의 속력을 구하기에 정확도가 충분하지 않다는 것을 의미한다. 그래서 미터 정의를 바꾸어야 한다는 필요성이 제기 되었고, 이를 위해 먼저 빛의 속력을 고정시키는 것, 즉 그 측정 불확도를 0으로 만드는 것이 필요했다.
1975년에 개최된 제15차 CGPM에서는 진공에서의 빛의 속력은 299 792 458 m/s라고 공식적으로 공고했다. 단 이 값은 불확도가 0인 상수(Constant)이다. 맥스웰이 빛의 속력은 일정하다는 이론을 정립한 후 111년만에, 아인슈타인이 광속 불변의 원리를 발표한지 70년만에 그 값이 확정된 것이다.
이에 따라 길이의 단위 미터는 1983년에 개최된 제17차 CGPM에서 다음과 같이 재정의되었다.
• 미터는 빛이 진공 중에서 1/299 792 458 초 동안에 진행한 경로의 길이이다.
2.2 빛의 속력에서 미터 정의 유도
양(Quantity)이란 수와 기준으로 표시될 수 있는, 크기를 갖는 현상, 물체 또는 물질의 성질이라고 정의 되어 있다.
4 여기서 말하는 기준의 하나로서 단위가 있다. 그러므로 수와 단위로 양의 크기를 표현할 수 있다. 진공에서의 빛의 속력이라는 양을 수와 단위로 나타내면 다음과 같다.
단, c는 진공에서의 빛의 속력을 의미하는 기호이다. 양을 나타내는 기호(여기서는 c)는 고정된 것이 아니다 (c0로 쓰기도 한다). 그렇지만 이 기호는 이탤릭 체(기울임 체)로 써야 한다. 숫자는 밑에서 3자리 마다 한 칸씩 띄우도록 되어 있다. 단위 m/s는 로만체(직립 체)로 쓴다. 단위를 나타내는 기호들은 임의로 변경할 수 없다(강제적인 것이다). 그래서 미터와 초의 기호들은 모두 알파벳 소문자로 써야 한다. (대문자로 쓰면, M은 메가(106)를 뜻하고, S는 전기전도도의 단위인 ‘지멘스’를 뜻한다.) 이런 내용은 모두 참고문헌 1에 나와 있다.
식(1)은 단순히 빛의 속력을 나타내기만 하는 것이 아니라 하나의 방정식이다. 그래서
식(1)을 m에 대해 다시 쓸 수 있다.
식(2)가 의미하는 것은 바로 앞에서 말한 미터의 정의이다.
c로부터 미터의 정의를 유도할 수 있는 것은 c에 포함된 숫자가 불확도 없이 고정된 값을 갖기 때문이다. 그 결과, m은 s에 의해서만 정의된다. 그런데 초(s)는 미터(m)보다 훨씬 높은 정확도로 구현할 수 있다. 그래서 미터를 구현할 때 초는 미터의 불확도에 영향을 미치지 않는다.
초(s)의 정의는 1967/68년에 다음과 같이 정의되었다.
• 초는 세슘 133 원자의 바닥상태에 있는 두 초미세 준위 사이의 전이에 대응하는 복사선의 9 192 631 770 주기의 지속시간이다.
이것을 쉽게 설명하면, 세슘원자가 갖는 에너지 준위 중 바닥 상태에 있는 두 초미세 준위 사이의 주파수는 약 9.2 GHz이다. 이 마이크로파가 위의 숫자만큼 정확히 진동하는데 걸린 시간이 1 초라는 뜻이다. 그런데 이 초의 정의를 구현하는 세슘원자시계는 다른 SI 기본단위들을 구현하는 1차 표준들보다 훨씬 정확하다. 오늘날은 세슘원자 분수시계(Fountain Clock)가 가장 정확한데 그 정확도는 10-16 수준에 이른다. 그래서 다른 SI 단위를 정의하거나 구현할 때 가능하면 시간이나 주파수와 연관시키려고 노력한다. 이런 현상은 이번 SI 기본단위 재정의에서 더욱 심화되어 나타난다.
3. SI 기본단위
3.1 기존 SI 기본단위의 정의
앞에서 말한 미터와 초 외에 나머지 SI 기본단위들의 현재 정의는 다음과 같다.
· 킬로그램은 국제킬로그램원기의 질량과 같다.
· 암페어는 무한히 길고 무시할 수 있을 만큼 작은 원형 단면적을 가진 두 개의 평행한 직선 도체가 진공 중에서 1 미터 간격으로 유지될 때, 두 도체 사이에 매 미터 당 2 × 10-7 뉴턴의 힘을 생기게 하는 일정한 전류이다.
· 켈빈은 물의 삼중점의 열역학적 온도의 1/273.16이다.
· 몰은 탄소 12의 0.012 킬로그램에 있는 원자의 개수와 같은 수의 구성요소를 갖는 어떤 계의 물질량이다. 몰을 사용할 때는 구성요소를 반드시 명시해야 하며, 이 구성요소는 원자, 분자, 이온, 전자, 기타 입자, 혹은 이러한 입자들의 특정한 집합체가 될 수 있다.
· 칸델라는 진동수 540 × 1012 헤르츠인 단색광을 방출하는 광원의 복사도가 어떤 주어진 방향으로 1 스테라디안 당 1/683 와트일 때 이 방향에 대한 광도이다.
이 기본단위 정의들의 특징을 살펴보자.
우선, 기본단위 정의들에서 과학적 일관성을 찾아볼 수 없다. 현재의 SI 단위들은 전체를 아우르는 원리나 원칙보다는 산업이나 상거래, 과학기술 분야 등에서 그 단위들이 필요했기 때문에 각각 별도로 채택되었다.
과학기술의 발전에 따라 단위의 정의가 바뀌어 온 것이 있는 반면, 킬로그램의 경우 1889년에 채택된 이후 오늘날까지도 계속 사용되고 있다. 그래서 킬로그램의 재정의가 갖는 의미가 다른 단위들에 비해 훨씬 크다고 할 수 있다.
암페어는 아주 이상적인 실험 조건에서 정의된 것이다. 실제로 암페어는 이 정의와 무관한 방법으로 구현되고 있다. 즉, 1990년에 CIPM에서 결정된 조셉슨 상수 값과 폰클리칭 상수 값을 기준으로, 조셉슨 전압과 양자홀 저항을 각각 전압과 저항의 표준으로 사용하고 있다. 전류는 이 두 값에서 옴의 법칙으로 구한다.
켈빈은 물의 삼중점이라는 물질의 성질로 정의된다. 그런데 높은 온도에서는 금속의 녹는점을 기준으로 1990년에 만든 국제온도눈금 ITS-90이 실제로 사용된다.
몰은 탄소 12 원자의 질량을 먼저 정의한 후 그 속에 든 탄소 원자의 개수로 정의된다. 따라서 몰의 정의에는 킬로그램 단위가 들어 있다.
칸델라의 현재 정의는 사람 눈이 빛의 파장에 따라 느끼는 감도를 모델로 먼저 정해놓았다. 즉 녹색광인 540 × 1012 헤르츠(=555 nm) 빛에 대해 시감 효율을 1로 정했다. 광도는 사람 눈이 느끼는 광량을 기준으로 하기 때문에 가시광선 영역에서만 적용된다. 광도는 조명과 밀접한 연관이 있다. 그래서 1937년 이전에는 국제조명위원회(CIE)가 주도적인 역할을 했다. 하지만 나라들마다 그 정의가 일치하지 않았다. 1946년에 CIPM은 CIE와 합의하여 백금 응고점 온도의 흑체의 광휘도에 기초를 둔 ‘신촉광’ 단위를 도입하여 공고했다. 1948년 CGPM에서 이것을 비준했지만 광도 단위에 대한 새 국제명칭으로 칸델라(기호: cd)를 채택했다. 1967년에 칸델라의 정의를 수정했는데, 1979년 CGPM에서 폐기하고 현재의 정의를 채택했다.
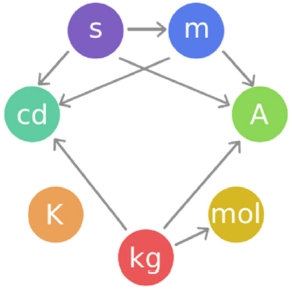
이 기본단위들 사이의 관계가
Fig. 1에 나와 있다. 그림에서 켈빈(K)은 유일하게 아무런 화살표가 없다. 즉 다른 단위들과 무관하게 독립적으로 정의된다. 이에 비해 초(s)와 킬로그램(kg)은 나가는 화살표만 3개씩 있다. 이 두 단위는 화살표가 가리키는 단위의 정의에 포함되어 있다. 암페어(A), 칸델라(cd), 몰(mol)은 들어오는 화살표만 있다. 즉 이 단위들은 그 정의에서 다른 단위의 영향을 많이 받는다. 미터(m)는 유일하게 나가고 들어오는 화살표를 모두 가지고 있다.
Fig. 1Relationships among the current SI base units
3.2 SI 기본단위의 재정의
3.2.1 재정의를 위한 준비와 조건
1999년 CGPM은 킬로그램이 갖는 문제점으로 인해 이를 재정의하기 위한 연구를 수행해야 한다는 권고안을 채택했다. 2007년에는 여러 나라의 측정표준연구기관(NMI)들과 BIPM, CIPM이 킬로그램뿐 아니라 암페어, 켈빈, 몰의 단위를 기본상수에 기반하여 재정의할 것을 요구했다. 2011년에는 플랑크 상수(
h), 기본전하(
e), 볼츠만 상수(
k), 아보가드로 상수(
NA)로부터 각각 킬로그램, 암페어, 켈빈, 몰을 유도하는 구체적인 방법의 초안이 제시되었다. 그리고 나머지 3개 단위(초, 미터, 칸델라)도 이와 같은 형식으로 정의를 바꾸는 안이 제시되었다. 2014년 CGPM은 각 기본상수들이 단위 재정의에 필요한 조건, 즉 충분히 낮은 상대불확도를 갖도록 NMI 들이 연구를 지속해나갈 것을 격려하는 결의안을 채택했다.
5
이와 함께 국제단위계(SI)에 대한 상세한 내용을 담고 있는 SI Brochure(제9판)의 초안(Draft)이 만들어져 세계 여러 나라의 NMI들을 포함하여 CIPM 산하의 여러 CC(자문위원회), IUPAP(국제 순수 및 응용물리 연합), IUPAC(국제 순수 및 응용 화학연합) 등에 배포되어 의견을 수렴했다.
과학기술분야에서 생산되는 여러 종류의 데이터를 취급하는 국제기구는 CODATA이다. 거기에 속한 TGFC (Task Group on Fundamental Constants)는 전 세계에서 발표된 기본상수와 관련된 이론 및 실험 데이터를 모아서 가장 최적의 값을 정하고, 매 4년마다 CODATA 권고 값을 미국 NIST 웹사이트를 통해 발표한다.
6
SI 기본단위 재정의는 기본상수에서 유도되기 때문에 재정의에 앞서 그 상수 값을 고정시키는 것이 필요하다. 이것은 미터 재정의를 위해 빛의 속력 값을 고정시킨 것과 동일한 과정이다. 그런데 기본상수 값의 불확도를 0으로 만들기 위해서는 전제 조건이 따른다. 예를 들면, CIPM 산하에 있는 CCM (질량및관련량자문위원회)은 2013년에 킬로그램 재정의를 위해 플랑크 상수 측정 값의 상대불확도는 다음 두 조건을 만족시켜야 한다고 발표했다.
(1) 키블 저울 및 XRCD 실험을 포함한 독립적인 3개 이상의 실험으로 구한 플랑크 상수 값들이 5 × 10-8 이내에서 일치하고,
(2) 그 중 최소한 하나의 결과는 2 × 10-8 이하의 상대 불확도를 가질 것.
여기서 키블(Kibble) 저울은 단위 재정의 전에는, IPK(즉, 킬로그램 단위)에 소급성(Traceability)을 갖는 표준 분동을 기준으로 플랑크 상수값을 구하는데 사용된다. 다른 말로 하면, 현재의 킬로그램 단위를 기준으로 플랑크 상수 값을 결정한다. 킬로그램 재정의 후에는 플랑크 상수(즉, 재정의된 킬로그램)를 기준으로 다른 물체의 질량을 재는데 사용된다. 그 기준과 역할이 모두 바뀐다는 뜻이다.
XRCD 실험은 1 kg 실리콘 구를 만들어 아보가드로 상수(
NA)를 구하는 실험이다. 아보가드로 상수를 알면 플랑크 상수를 알 수 있고, 그 역도 성립한다. 그래서 두 기본상수의 상대 불확도는 항상 같다. 이 실험에서도 실리콘 구의 질량 1 kg은 IPK에 소급성을 갖는 표준분동으로 측정한다. 그리고 실리콘 구의 질량과 플랑크 상수와의 관계식에서 상수 값을 구한다.
7 이 때 플랑크 상수는 평균 값과 함께 측정 불확도를 가진다. 그 상대불확도가 위의 두 조건을 만족시키면 플랑크 상수의 불확도는 0으로 둘 수 있고, 킬로그램의 재정의가 가능해진다.
위와 같은 조건을 내 건 이유는 서로 다른 측정 방법 또는 서로 다른 연구기관에서 측정하더라도 신뢰성 있는 결과가 나와야만 킬로그램 재정의가 가능하다는 것을 의미한다. 그리고 두 개의 상대불확도 조건, 5 × 10
-8 이하와 2 × 10
-8 이하를 제시한 것은 다음 두 가지 이유 때문으로 추정된다. 하나는 IPK와 6개 복제본들이 지난 130년 동안에 약 50 μg 차이가 났다는 것이다(뒤에 나오는 김동민 등의 논문 참조). 이 질량의 상대적 변화량은 5 × 10
-8이다. 그러므로 새로 정의되는 킬로그램은 적어도 이보다 상대불확도가 작아야 할 것이다. 다른 하나는, 여러 나라의 NMI에서 사용하고 있는 국가킬로그램원기(1차 표준분동)들을 서로 비교한 결과 그 상대 정밀도가 약 3 × 10
-8 수준이었다. 이것은 이보다 더 정확하게 질량을 측정할 수 없다는 뜻이다. 만약 키블 저울이나 XRCD 실험에서 이 보다 낮은 불확도로 플랑크 상수를 얻을 수 있다면 그 불확도를 0으로 둘 수 있다는 것이다. 참고로, 앞의 두 조건이 제시되었던 2013년에 CODATA가 권고한 플랑크 상수 값의 상대불확도는 4.4 × 10
-8이었다.
8
위 두 조건을 만족시키기 위해 선진국 NMI 들과 국제 아보가드로 공동 연구팀(IAC)은 1990년부터 연구를 수행해왔다. 세월이 흐름에 따라 그 값들이 수렴되어 왔으나, 2015년까지도 위에서 제시된 두 조건을 완전히 만족시키지 못했다. 그 주 원인은 미국 NIST가 만든 키블 저울(NIST-3)의 불확도가 컸기 때문이다. 다행히 새로 만든 저울(NIST-4)은 불확도가 줄어들어 킬로그램 재정의가 가능하게 되었다.
2018년 11월에 개최될 제26차 CGPM을 위해 매 4년마다 열리던 CODATA TGFC가 2017년에 특별히 개최되었다. 2017년 7월 1일 이전까지 출판되었거나 출판이 승인된 기본상수 관련 자료들을 모아서 TGFC는 4개의 기본상수들의 조정된 값을 발표했다.
Table 1은 플랑크 상수(
h), 기본전하(
e), 볼츠만 상수(
k), 아보가드로 상수(
NA)의 조정된 값과 상대불확도(
ur)를 보여준다.
9
Table 1The CODATA 2017 adjusted values of h, e, k, and NA
Table 1
|
Quantity |
Value |
u
r
|
|
h
|
6.626 070 150(69) 10-34 J s |
1.0 × 10-8
|
|
e
|
1.602 176 6341(83) 10-19 C |
5.2 × 10-9
|
|
k
|
1.380 649 03(51) 10-23 J K-1
|
3.7 × 10-7
|
|
N
A
|
6.022 140 758(62) × 1023 mol-1
|
1.0 × 10-8
|
플랑크 상수의 경우, 단위 재정의를 위해 CCM이 제시했던 두 가지 조건을 만족시키는 실험 결과가 참고문헌 9의
Fig. 1에 나와 있다. 키블 저울을 이용하여 3개 기관(NRC, NIST, LNE)이 구한 플랑크 상수의 불확도가 5 × 10
-8 이하로 일치했다. 또한 국제아보가드로 공동연구팀(IAC)이 발표한 세 번의 결과가 모두 이 조건을 만족했다. 그리고 이들 중 총 4개의 결과가 (2)번 조건을 만족했다. 결론적으로, 플랑크 상수값을 불확도 없이 고정시키는 조건들이 모두 만족되었다. 그 결과, 4개의 기본상수는
Table 2와 같이 불확도가 없는 값으로 고정되었다.
9
Table 2The CODATA 2017 values of h, e, k, and NA for the revision of the SI
Table 2
|
Quantity |
Value |
|
h
|
6.626 070 15 × 10-34 J s |
|
e
|
1.602 176 634 × 10-19 C |
|
k
|
1.380 649 × 10-23 J K-1
|
|
N
A
|
6.022 140 76 × 1023 mol-1
|
3.2.2 정의 상수로부터 SI 기본단위 유도
상기 4개의 기본상수와 연결된 기본단위 외에 나머지 3개의 기본단위들도 기존 단위의 정의에 이미 상수를 포함하고 있다. 이처럼 기본단위를 정의하는 상수를 ‘정의 상수’(Defining Constants)라고 부른다. 이들의 명칭, 기호 및 단위가
Table 3에 나와 있다. 정의 상수의 단위를 SI 기본단위로 표현한 것이 맨 오른쪽에 나와 있다.
Table 3Seven defining constants, their symbols, and their units
Table 3
|
Defining constant |
Symbol |
Unit |
|
Hyperfine transition frequency of Cs |
Δν
|
Hz = s-1
|
|
Speed of light in a vacuum |
c
|
m s-1
|
|
Planck constant |
h
|
J s = kg m2 s-1
|
|
Elementary charge |
e
|
C = A s |
|
Boltzmann constant |
k |
J K-1
|
|
Avogadro constant |
N
A
|
mol-1
|
|
Luminous efficacy |
K
cd
|
lm W-1 = cd sr W-1
|
세슘의 초미세 전이 주파수 Δν는 Hz 단위를 가진다. 그런데 Hz와 초(s)는 서로 역수의 관계가 있다. 시간의 기본단위는 초(s)이므로 Hz를 s로 바꾸는 과정이 필요하다. 이것을 수식으로 표현하면 다음과 같다. 이 관계 식은 몰을 제외한 다른 기본단위의 정의에 모두 사용된다.
Δν = 9 192 631 770 HzHz = s-1 = Δν / 9 192 631 770s = 9 192 631 770 / Δν
초의 정의(초안)는 Δν에 대한 수식과 동일한데, 풀어 쓰면 다음과 같다.
“초(기호: s)는 시간의 SI 단위이다. 초는 세슘 133 원자의 섭동이 없는 바닥상태의 초미세 전이 주파수 Δν의 값을 주기적 현상에 대해서는 s-1과 동일한 Hz 단위로 나타낼 때, 9 192 631 770으로 고정함으로써 정의된다.”
기존의 초의 정의와 표현이 다소 달라졌지만 세슘원자의 초미세 전이 주파수가 기준이 된다는 점에서는 동일하다.
미터(m)를 c로 표현하면 m = c / 299 792 458 × s이다. 여기서 s 대신에 앞에서 구한 식을 대입하면 다음과 같이 된다.
m = c / 299 792 458 × 9 192 631 770 / Δν≈ 30.663 319 c / Δν
이 식은 미터(m)가 진공에서의 빛의 속력(c)과 세슘의 초미세 전이 주파수(Δν)에 의해 정의된다는 것을 나타낸다. 미터 정의(초안)는 다음과 같다.
“미터(기호: m)는 길이의 SI 단위이다. 미터는 진공에서의 빛의 속력 c의 값을 m s-1 단위로 나타낼 때 299 792 458로 고정함으로써 정의된다. 여기서 s는 세슘의 초미세 전이 주파수 Δν로 정의된다.”
미터의 정의도 기존의 정의와 표현은 달라졌지만 진공에서의 빛의 속력이 기준이 된다는 점에서는 동일하다.
플랑크 상수의 단위는 J s이다. 여기서 에너지의 단위 줄(J)을 기본단위로 풀어 쓰면 kg m2 s-2이다. 따라서 플랑크 상수의 단위는 kg m2 s-1이다. 이 단위 속에 kg이 있고, m와 s는 앞에서 이미 정의되었다. 그러므로 kg을 다음과 같이 플랑크 상수로부터 유도할 수 있다.
h = 6.626 070 15 × 10-34 kg m2 s-1kg = h m-2 s / 6.626 070 15 × 10-34≈ 1.475 5214 × 1040 h Δν / c2
킬로그램의 정의(초안)는 다음과 같다.
“킬로그램(기호: kg)은 질량의 SI 단위이다. 킬로그램은 플랑크 상수 h의 값을 kg m2 s-1 와 동일한 J s 단위로 나타낼 때 6.626 070 15 × 10-34으로 고정함으로써 정의된다. 여기서 m과 s는 각각 c와 Δν 로 정의된다.”
나머지 기본 단위들도 같은 방식으로 유도할 수 있다.
기본 전하 e의 단위는 쿨롬(C)이고 이것은 A s와 동일하다. 따라서 e로부터 암페어(A)를 유도하면 다음과 같다. 단, s는 Δν로 정의된 식을 사용한다.
e = 1.602 176 634 × 10-19 A sA= e / 1.602 176 634 × 10-19× s-1≈ 6.789 687 × 108 e Δν
볼츠만 상수 k의 단위는 J K-1이므로 켈빈(K)을 유도해 낼 수 있다. J은 kg m2 s-2이므로 K의 정의 속에는 다음과 같이 h Δν가 포함된다.
k = 1.380 649 × 10-23 J K-1K = 1.380 649 × 10-23 / k × kg m2 s-2≈ 2.266 6653 × h Δν / k
아보가드로 상수 NA의 단위는 몰(mol)의 역수이므로 다음과 같이 쉽게 유도된다.
NA = 6.022 140 76 × 1023 mol-1mol = 6.022 140 76 × 1023 / NA
시감 효능
Kcd는
Table 3에 나온 다른 정의 상수와 달리 사람의 눈이 느끼는 감각을 상수화한 것이다. 이것은 상수로부터 단위를 유도하려는 재정의 형식에 맞추기 위해 도입한 기술 상수(Technical Constant)이다. 미래에 광자의 개수를 기반으로 광도의 단위를 재정의하려는 연구가 진행 중이지만 아직 극복해야 할 기술적 난제가 많이 남아있다.
Kcd의 단위는 lm W-1이다. 여기서 루멘(lm)은 광선속의 단위이고, 와트(W)는 복사선속의 단위이다. 광도의 단위 칸델라(cd)는 단위 입체각(sr) 당 광선속(lm)으로 정의된다. 그런데 W = J s-1 = kg m2 s-3이므로 cd는 다음과 같이 표현된다.
Kcd = 683 lm W-1 = 683 cd sr W-1cd = Kcd / 683 × sr-1 × kg m2 s-3
여기서 kg, m, s 대신에 앞에서 유도한 식들을 대입하면 다음과 같이 된다.
cd ≈ 2.614 830 × 1010 × h (Δν)2 Kcd
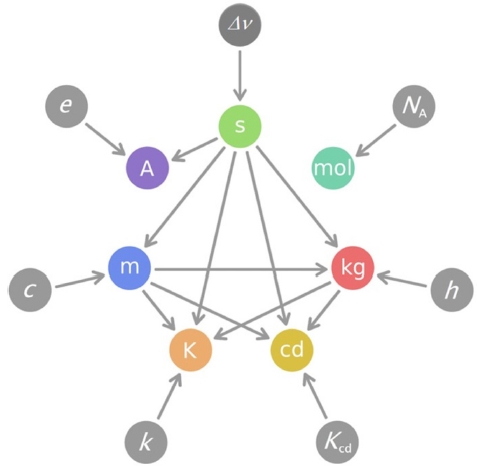
Fig. 2는 앞에서 설명한, 새로 정의되는7개 기본단위 사이의 관계를 보여준다. 기본단위들이 각각의 정의 상수로부터 유도된다는 것을 화살표로 나타내었다. 기본단위에서 나가는 화살표는 그 기본단위가 다른 기본단위의 정의에 포함되어 있음을 나타낸다. 예를 들면, 초(s)는 몰(mol)을 제외한 나머지 5개 단위에 모두 포함되어 있다. 미터(m)는 켈빈(K), 칸델라(cd)와 킬로그램(kg)에 포함되어 있다. 이에 비해 몰(mol)은 다른 기본단위들과 아무 관계가 없다. 기존의 정의에서 독립적으로 존재하던 켈빈(K)이 다른 단위들과 관계를 가진 반면, 몰(mol)은 기존의 정의와 달리 킬로그램(kg)을 포함하지 않는다.
Fig. 2Relationships among the revised SI base units, which are defined by their own defining constants
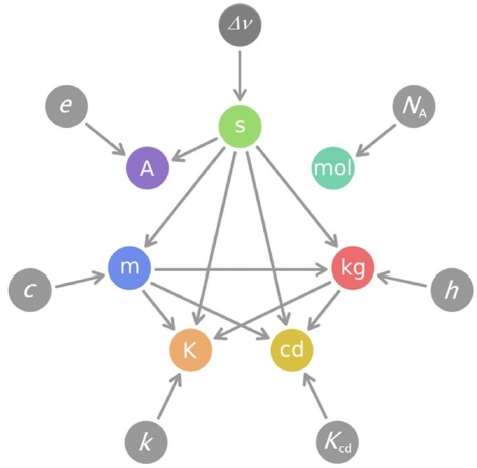
Fig. 1의 기존 정의보다 초(s)를 포함한 기본단위가 더 많아졌다. 이런 현상은 기본단위에서뿐 아니라 유도단위에서도 나타나고 있다. 예를 들면, 압력(=단위 면적당 힘)을 레이저 주파수로부터 구하는 것이다.
10 이런 연구는 기본단위 재정의 후에 더욱 많아질 것으로 예상된다.
3.2.3 개정 SI 기본단위의 구현
“단위를 구현한다”는 것은 단위의 정의에 부합하는 양의 값 및 불확도를 확정하는 일련의 작업을 말한다. 또는 이것에 관한 상세한 안내서를 말한다. 이것을 프랑스 말로 “Mise-en-Pratique”라고 하는데, 이를 줄여서 단순히 MeP라고도 한다. 영어로는 “Practical Realization”으로 번역되어 있다.
단위 구현의 가장 높은 단계, 즉 최고 수준의 구현 방법을 ‘1차 방법’(Primary Method) 라고 한다. 개정 SI가 갖는 큰 장점 중 하나는 MeP를 어떤 특정 방법에 국한시키지 않고, 새로 발견되거나 발전된 과학 법칙과 기술을 적용할 수 있다는 것이다. 다시 말하면, 물리학 법칙과 SI 기본단위의 정의에 부합하는 것이면 어떤 방법도 단위 구현에 사용할 수 있다. 이에 따라 기본단위를 해당 기본상수와 연결시키는 법칙과 방법을 찾는 연구가 앞으로 많이 진행될 것이다.
새로 정의되는 4개 기본단위에 대한 MeP는 이 논문 뒤에 이어 나오는 다른 논문들에서 자세히 설명할 것이다. 이것은 모두 1차 구현방법들이다. 간단히 소개하면 다음과 같다.
킬로그램의 MeP는 현재 키블 저울이 가장 널리 개발되어 있다. 암페어의 MeP는 조셉슨 효과와 양자 홀 효과를 이용하여 전위차 V와 전기 저항 R을 측정하고, 이 사이의 관계식인 옴의 법칙 I = V/R에서 전류(I)의 단위 암페어를 구현할 수 있다. 그리고 단일 전자전송(SET) 소자를 이용하여 단위 시간당 전송된 전자의 개수로부터 암페어를 구현할 수 있다. 이것이 완성되면 양자 측정 삼각체계를 구성하여 양자 수준에서 옴의 법칙을 검증할 수 있을 것이다. 켈빈의 MeP로서 음향기체온도계(AGT)가 가장 널리 개발되어 있다.
4. 개정 SI의 영향 및 전망
개정 SI에서 관련 기본상수들의 불확도는 0이다. 4개의 기본상수(
h,
e,
k,
NA)뿐 아니라 이것들로 구성된 기본상수들도 불확도가 0이 된다. 그리고 불확도 전파 법칙에 의해 4개 기본상수 중 일부를 포함한 기본상수들은 불확도가 줄어든다. 이에 반해 기존에 불확도가 0이었던 것들은 불확도를 가지게 되는 경우도 생긴다.
11
Table 4는 불확도가 0이 되는 일부 기본상수들과 그 관계식을 보여준다. 맨 오른쪽 칸에서 보는 것처럼 이 기본상수들은 모두
h,
e,
k,
NA로 구성되어 있다.
Table 4 Fundamental constants and conversion factors whose uncertainties are to be zero by the revision of the SI
Table 4
|
Quantity |
Symbol |
Relation |
|
Molar gas constant |
R
|
= NA k
|
|
Faraday constant |
F
|
= NA e
|
|
Stefan-Boltzmann constant |
σ = (8π5/60) k4/h3 c2
|
|
Stefan-Boltzmann constant |
K
J
|
= 2e/h
|
|
von Klitzing constant |
R
K
|
= h/e2
|
|
Magnetic flux quantum |
Φ
0
|
= h/2e
|
|
Conductance quantum |
G
0
|
= 2e2/h
|
|
Molar Planck constant |
N
A
h
|
|
|
First radiation constant |
c
1
|
= 2πhc2
|
|
Second radiation constant |
c
2
|
= hc/k
|
|
E = mc2 Energy equivalent |
J↔kg |
|
|
E = hc/λ Energy equivalent |
J↔m-1
|
|
|
E = hν Energy equivalent |
J↔Hz |
|
|
E = kT Energy equivalent |
J↔K |
|
|
1 J = 1(C/e) eV Energy equivalent |
J↔eV |
|
한편, 불확도가 당초 0이었지만 불확도를 갖게 되는 기본상수와 양은
Table 5에 나와 있다. 자기상수
μ0는 미세구조상수
α와 다음과 같은 관계가 있다:
μ0= 2
hα/
ce2. 여기서
α를 제외한 나머지 기본상수들은 불확도가 0이므로
μ0의 상대불확도는
α와 동일해진다. CODATA 2014에서
α의 상대불확도는 2.3 × 10
-10인데, 2018년에는 이와 비슷하거나 좀 줄어들 것으로 예상된다. 전기상수
ε0는
μ0와
ε0= 1/
μ0 c2의 관계가 있다. 따라서
ε0와
μ0의 상대불확도는 동일하다.
Table 5 Quantities which have new uncertainties by the revision of the SI
Table 5
|
Quantity |
Symbol |
ur
|
|
Magnetic constant |
μ
0
|
ur(μ0) = ur (α) |
|
Electric constant |
ε
0
|
ur(ε0) = ur (α) |
|
Molar mass of carbon-12 |
M(12C) |
ur = ur (NAh) |
|
IPK |
m(K) |
1.0 × 10-8
|
|
Triple point of water |
T
TPW
|
3.7 × 10-7
|
국제킬로그램원기와 물의 삼중점은,
Table 1에 나와있는 것처럼 불확도가 0이 되기 직전, 즉 SI 개정 직전의 플랑크 상수와 볼츠만 상수의 상대불확도를 가지게 될 것이다.
탄소-12의 몰 질량은 다음과 같은 과정에서 결정된 상대불확도를 갖게 된다.
NA가 고정되기 전과 후의 비를 나타내는 몰 질량 인자(1 +
κ)가 미세구조상수
α의 제곱과 리드베리(Rydberg) 상수
R∞에 의존한다.
12 그 결과,
ur(
α)의 2배 보다 좀 큰 상대불확도를 가질 것이다. 엄밀하게 말하면, 몰 플랑크 상수
NAh의 SI 개정 직전의 상대불확도를 가질 것이다.
13
개정 SI에서 초(s)와 칸델라(cd)는 다른 기본단위와 달리 보편적인 상수가 아니다. 특정 원자 또는 기술 상수를 기반으로 정의되어 있다. 그런데 초의 경우 가장 정확한 세슘원자분수시계 보다 더 상대불확도가 작은 광원자시계들이 개발되었다. 스트론튬(Sr) 또는 이트븀(Yb) 원자를 이용한 광격자시계는 그 불확도가 10
-18에 이른다.
14 즉 세슘원자분수시계보다 약 100 배 우수하다. 그래서 CIPM 산하 CCTF(시간주파수자문위원회)에서는 미래에 초의 정의를 광원자시계로 바꾸는 계획을 수립하였다.
15 이렇게 바뀐다 하더라도 보편적 기본상수가 아닌 특정 원자의 에너지 준위 사이의 주파수가 기준이 된다. 원자에서 발생되는 광주파수와 가장 연관성이 높은 기본상수는 리드베리(Rydberg) 상수
R∞이다. 그런데 이 상수의 상대불확도는 2010년 CODATA에서는 5.9 × 10
-12 으로 광원자시계의 상대불확도에 비해 너무 나쁘다. SI 개정 후에는
R∞ (=
α2mec/2
h) 속에 포함된
h의 불확도가 0이 되기 때문에 그 불확도는 개선되겠지만
α2me가 갖는 불확도 때문에 광원자시계의 불확도에는 미치지 못한다. 그래서 미래 초의 정의는 특정 원자나 원자들을 기반으로, 지금과 같은 방식으로 재정의 될 것으로 예상된다.
기본단위의 재정의에 따라 이들을 구현하는 1차 측정표준을 개발하는 연구가 활발해질 것으로 전망된다. 특히 이런 일을 임무로 수행하고 있는 각 나라의 국가측정표준기관(NMI)에서 활발한 연구가 진행될 것이다. 이와 함께 기본단위의 정의가 바뀌었다는 사실을 국내 과학기술계 및 국민들에게 널리 알리고, 또 교과서 등에 실린, 단위 관련 내용을 수정하는 일을 해야 한다. 이런 일을 세계적으로 추진하기 위해 CIPM 산하에 Task Group을 만들어 일반인을 대상으로 홍보 및 교육 자료를 만들고 있다.
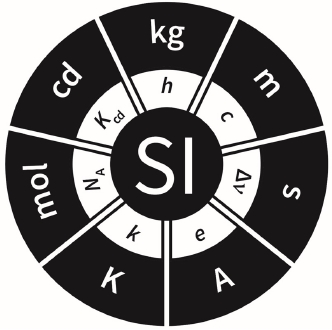
Fig. 3은 새로 만든 SI 도해 중 하나이다. 흑백과 칼러 등 여러 가지 도해를 만들어 일반인들도 다운로드 받을 수 있도록 BIPM 홈페이지(
www.bipm.org)에 공개하고 있다.
Fig. 3 SI illustration
5. 결론
SI가 출범한지 58년만에 기본단위 재정의라는 큰 변화가 생긴다. 지금까지 인공물에 의존해왔던 킬로그램 단위가 마침내 플랑크 상수라는 기본상수를 기반으로 재정의된다. 물의 삼중점을 기준으로 정의되었던 열역학적 온도 단위 켈빈은 볼츠만 상수를 기반으로 재정의된다. 전류의 단위 암페어는 양성자의 전하에 해당하는 기본 전하로 재정의되고, 물질량의 단위 몰은 아보가드로 상수로부터 재정의된다. 측정학계에서는 엄청난 변화이며 역사적인 사건이고, 과학기술계 전반에 큰 영향을 끼칠 것으로 전망된다. 그러나 단위의 정의가 바뀌었다 하여 상거래나 제조업, 안전, 건강, 환경 보호와 같은 국민들의 일상 생활에서 특별한 변화가 생기지 않을 것이다. 단지 측정분야에서 더욱 정확하고 안정적인 기준을 마련했다는데 큰 의의가 있다. 이 새 기준을 바탕으로 새로운 과학 법칙과 기술의 탄생을 기대해본다.
SI 기본단위의 재정의는 2018년 11월, 제26차 CGPM에서 확정될 것이다. 그리고 2019년 5월20일, 세계측정의 날부터 실제 적용될 것이다.
REFERENCES
- 1.
- 2.
Davis, R., “The Si Unit of Mass,” Metrologia, Vol. 40, No. 6, pp. 299-305, 2003.
10.1088/0026-1394/40/6/001
- 3.
Evenson, K., Wells, J., Petersen, F., Danielson, B., Day, G. W., et al., “Speed of Light from Direct Frequency and Wavelength Measurements of the Methane-Stabilized Laser,” Physical Review Letters, Vol. 29, No. 19, Article No. 1346, 1972.
10.1103/PhysRevLett.29.1346
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
Lee, H. S., “Fundamental Constants and System of Units,” Cheong Moon Gak, p. 165, 2016.
- 8.
Mohr, P. J., Taylor, B. N., and Newell, D. B., “CODATA Recommended Values of the Fundamental Physical Constants: 2010,” Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, Vol. 84, No. 4, Article No. 1527, 2012.
- 9.
Newell, D., Cabiati, F., Fischer, J., Fujii, K., Karshenboim, S., et al., “The CODATA 2017 Values of h, e, k, and NA for the Revision of the SI,” Metrologia, Vol. 55, No. 1, 2018.
10.1088/1681-7575/aa950a
- 10.
Hendricks, J. H., Ricker, J. E., Stone Jr, J. A., Egan, P. F., Scace, G. E., et al., “Measuring Pressure and Vacuum with Light: A New Photonic, Quantum-Based, Pressure Standard,” Proc. of the XXI World Congress, 2015.
- 11.
Newell, D. B., “A More Fundamental International System of Units,” Physics Today, Vol. 67, No. 7, pp. 35-41, 2014.
10.1063/PT.3.2448
- 12.
Mills, I. M., Mohr, P. J., Quinn, T. J., Taylor, B. N., and Williams, E. R., “Redefinition of the Kilogram, Ampere, Kelvin and Mole: A Proposed Approach to Implementing CIPM Recommendation 1 (CI-2005),” Metrologia, Vol. 43, No. 3, p. 241, 2006.
10.1088/0026-1394/43/3/006
- 13.
Fischer, J. and Ullrich, J., “The New System of Units,” Nature Physics, Vol. 12, No. 1, pp. 4-7, 2016.
10.1038/nphys3612
- 14.
Ludlow, A. D. and Ye, J., “Progress on the Optical Lattice Clock,” Comptes Rendus Physique, Vol. 16, No. 5, pp. 499-505, 2015.
10.1016/j.crhy.2015.03.008
- 15.
Riehle, F., “Towards a Redefinition of the Second Based on Optical Atomic Clocks,” Comptes Rendus Physique, Vol. 16, No. 5, pp. 506-515, 2015.
10.1016/j.crhy.2015.03.012