ABSTRACT
Water spraying work to prevent the dust from scattering during building dismantling operation has usually been done manually. Since it is very risky and often causes fatal accidents due to unexpected collapse, a few countries have adopted mechanical water spaying machines. However, these machines are still operated by human laborer, specifically in orienting the spraying direction, which induces low dust suppression efficiency. In this research, an automated fine dust tracking system was suggested to identify and track the dust generating position accurately. A GPS is installed on the secured body of the excavator which contains a crusher as an end-effector for building dismantlement. Assuming the position of the crusher is the dust generating spot, a forward kinematics analysis is performed to identify the crusher position from the body origin on which the GPS sensor is placed. With another GPS on the water-spraying robot, its relative position to the dust generating spot and its heading angle for tracking can be calculated consequently. Tracking experiments were conducted with a miniature excavator and a reduced size water spraying robot. The results showed a sufficient tracking performance enough to be applied to the water spaying machines.
-
KEYWORDS: Position tracking, Field robot, Dust suppression, Construction robot, Kinematics analysis
-
KEYWORDS: 위치추적, 필드 로봇, 미세먼지 억제, 건설 로봇, 기구학 해석
1. 서론
현재 우리나라에서 건물 철거 작업 시 발생하는 미세먼지는 별도의 처리 기술이 없어
Fig. 1(a)와 같이 인력살수 작업을 통해 억제되고 있다.
1 그러나 인력살수 작업 중 붕괴사고로 인해 작업하던 근로자들이 사망 및 부상을 당하는 재해 사건이 빈번히 발생하고 있어 인력살수 작업은 근로자들의 안전이 보장받지 못한다는 큰 문제점을 가지고 있다. 재래적인 인력살수 방법을 통해 미세먼지 처리를 하고 있는 우리나라의 경우와는 달리, 유럽을 비롯한 미국, 일본, 호주 등의 선진외국에서는
Fig. 1(b)와 같이 수동 물 분사 장치를 개발하여 각종 산업현장에서 사용하고 있다.
2-4 하지만 해외 미세먼지 억제 시스템 또한 물을 분사하는 기계를 사람이 직접 움직여주어야 하고 미세먼지 발생원과 물을 분사하는 기계의 분사 방향의 불일치로 인해 미세먼지의 처리 효율이 떨어지는 문제가 발생한다. 따라서 이 연구에서는 앞서 언급한 바와 같이 우리나라의 재해사건과 해외기술의 문제점을 해결할 수 있으며, 또한 다양한 산업 현장에서 발생하는 미세먼지를 제거하기 위한 새로운 미세먼지 억제 시스템 기술을 제안하고자 한다. 이에 따라 미세먼지 발생원의 위치를 인식하고 자동으로 위치를 정확하게 추적하는 기술이 필수적이다.
Fig. 1 Conventional dust suppression work

따라서 본 연구에서는 다양한 환경에서 발생하는 미세먼지 중에서 건설현장에서 발생하는 미세먼지 억제에 초점을 맞춰 시스템을 개발하고자 한다. 공사 현장의 먼지를 억제하기 위해서는 먼지 발생원의 위치를 파악하고 그 위치를 정확히 추적하는 전략이 필수적이다. 본문에서는 개발된 시스템의 소개와 미세먼지 발생원 위치의 인식과 추적에 대한 알고리즘이 제시된다. 개발된 시스템을 통해 작업자의 안전문제를 해결하고 기존 시스템을 보완함으로써 보다 효율적인 살수 작업을 진행할 수 있는 성능을 검증하고자 한다.
2. 미세먼지 발생원 위치인식 알고리즘
2.1 미세먼지 발생원 위치인식을 위한 기구학 방정식
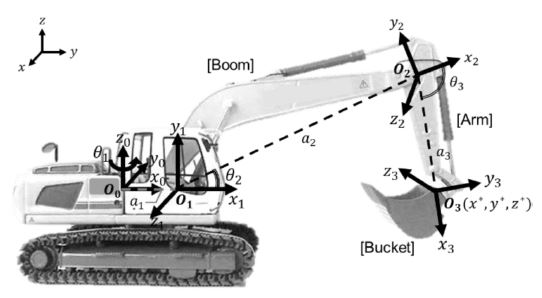
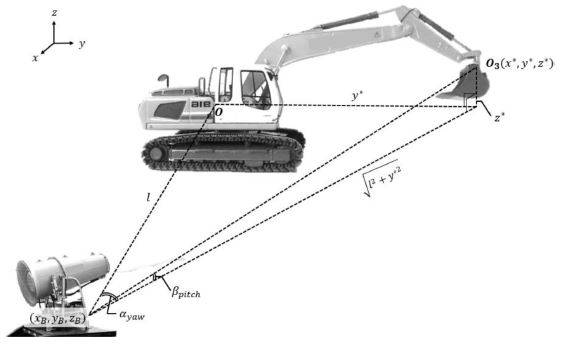
Fig. 2는 먼지 발생원인 굴삭기의 버킷(Bucket) 부분의 위치(
x*,
y*,
z*)를 구하기 위한 굴삭기의 좌표계 설정을 보여준다. 실제 건설현장에서 이용되는 굴삭기의 말단 장치는 크러셔(Crusher)를 이용하지만, 이 연구에서는 굴삭기에 일반적으로 사용되는 버킷을 이용하였다. 굴삭기 버킷의 위치를 알기 위해서 버킷 부분에 바로 GPS (Global Positioning System) 센서를 장착하는 것이 해당 부분의 위치 정보를 알아내기 쉽다. 하지만 실제 산업현장에서 운용되는 굴삭기는 현장에서 발생한 먼지를 비롯하여 철거 시 생성되는 건물 잔해와 접촉하면서 다양한 불순물이 직접적으로 닿을 가능성이 커 버킷 부분에 직접 센서를 부착할 수 없다. 따라서 GPS 센서를 굴삭기 몸체의 중심부에 부착 후, 원점으로부터 말단 장치의 위치와 방향을 알아낼 수 있는 순기구학 방정식(Forward Kinematics Equation)을 통하여 굴삭기의 버킷 부분의 위치를 계산하고자 하였다.
Fig. 2Excavator’s coordinate system
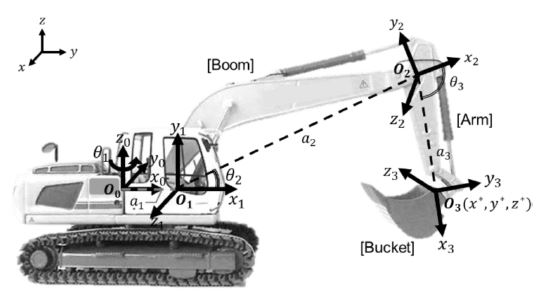
원점
O0에서 굴삭기가 회전하는 각도와 붐(Boom), 암(Arm) 부분이 기울어지는 각도인
θi (
i = 1,2,3)는 IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) 센서를 통해 얻을 수 있다. 인접한 두 좌표계의 관계를 설명하는 동차행렬(Homogeneous Matrix)인
식(1)을 통해
O0에서 부터
O3까지의 좌표변환을 계산할 수 있으며, 계산된 각 동차변환행렬은
식(2)를 통해 원점으로부터 버킷까지의 변환이 계산된다. 굴삭기의 원점인
O0의 위치는 굴삭기에 부착된 GPS 센서를 통해 알 수 있다. 이 때
ai (
i = 1, 2, 3)는 각 링크의 길이를,
ϕi (
i = 1, 2, 3)는 회전이 반시계 방향일 때
xi (
i = 0, 1, 2, 3)축에 대한
zi-1 (
i = 1, 2, 3)과
zi (
i = 1, 2, 3) 축 사이의 각도를 의미하며,
di (
i = 1, 2, 3)는 각 링크의
i (
i = 1, 2, 3)번째 조인트 사이의 오프셋 길이로 본 연구에서는 0으로 계산된다. 계산된 전체 변환은
식(3)과 같이 나타낼 수 있으며,
R03은 끝 점의 회전행렬(Rotation Matrix)을 표기한 것이고
d03는 위치를 벡터로 나타낸 것을 의미한다.
d03는 식(4)로 표현되어 굴삭기의 버킷 부분의 위치(
x*,
y*,
z*)를 계산할 수 있다.
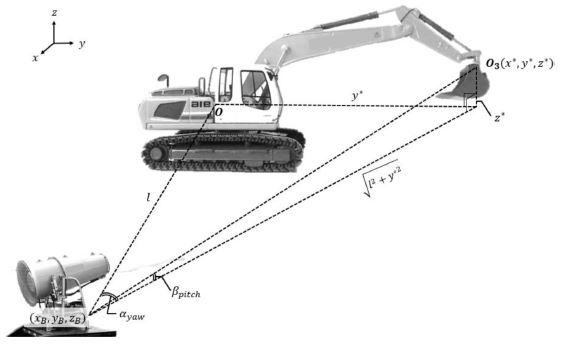
Fig. 3은 물 분사 로봇의 구동 각도를 계산하기 위한 각 변수를 도식화한 것이다. 물 분사 로봇은 물 분사구를 수직방향과 수평방향으로 움직여 굴삭기 버킷의 위치를 추적한다.
5 먼지 발생원의 위치를 추적하기 위해서, 먼지 발생원인 굴삭기 버킷 부분의 위치 (
x*,
y*,
z*)와 물 분사 로봇의 상대위치(Relative Position)를 계산한다.
6-8 물 분사 로봇의 위치는 장착된 GPS 센서를 통해 측정할 수 있으며, 물 분사 로봇과 굴삭기 버킷 부분의 상대위치는 위도 차인
l과 경도 차인
y*로 표현된다. 계산된 위치 차이값은 역탄젠트(Arctangent)를 이용하여 계산되는
식(5)와
식(6)에 대입되어 물 분사 로봇이 향해야 할 각도
αyaw,
βpitch를 계산한다.
αyaw는 수평방향으로 회전하는 각도이며
βpitch는 수직방향으로 회전하는 각도로 나타낼 수 있다. 계산된 각도로 물 분사 로봇의 구동 방향이 결정되고, 굴삭기 버킷의 위치를 추적 후 물을 분사하여 먼지를 억제시킨다.
Fig. 3Calculation of rotational angel for water spraying robot to rotate
3. 미세먼지 발생원 위치추적 자동화 시스템 구성
3.1 위치추적 알고리즘 기반의 자동화 시스템 구성
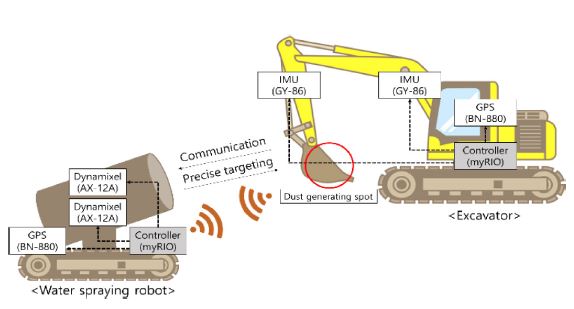
Fig. 4는 본 연구에서 다루는 위치추적 자동화 시스템의 구성 및 하드웨어 구성도를 보여준다. 본 시스템은 굴삭기에 적용된 버킷 위치의 정보와 물 분사 로봇의 버킷 위치 추적 알고리즘으로 구성된다. 굴삭기 버킷 부분이 미세먼지가 발생하는 위치이고, 물 분사 로봇이 굴삭기의 버킷을 추적하여 먼지를 억제할 수 있게 하는 자동화 시스템이 구현된다.
Fig. 4System configuration of water spraying robot and excavator hardware
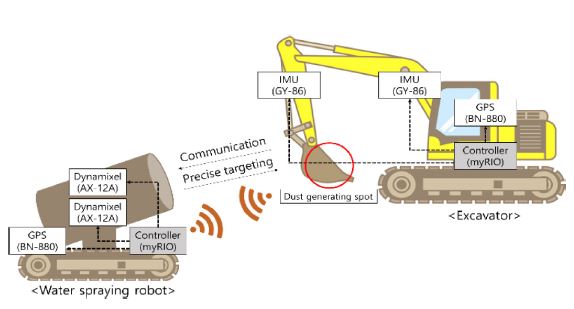
먼지의 발생원과 물 분사 로봇의 위치를 알아내기 위해 굴삭기와 물 분사 로봇의 중앙부에 BN-880 GPS를 설치하여 각 시스템의 절대위치(Absolute Positon)를 얻는다. 먼지 발생원인 굴삭기의 끝점 위치를 얻기 위해 굴삭기 GPS 위치를 원점으로 하는 순기구학 방정식을 이용한다. 굴삭기 몸체의 회전 각도와 붐, 암 부분이 기울어지는 각도는 GY-86 IMU센서를 이용하여 얻어낸다. 이 후, 계산된 굴삭기의 버킷 위치와 물 분사 로봇 위치를 통해 둘 사이의 상대 위치를 계산할 수 있으며, 이를 통해 물분사 로봇의 AX-12A Dynamixel 모터를 이용하여 물 분사 로봇이 향해야 할 방향을 가리키게 된다. 최종적으로 물 분사 로봇이 굴삭기의 버킷 위치를 추적하게 된다. 이 연구에서 제안한 먼지 발생원 위치추적 알고리즘을 구현하기 위한 소프트웨어로는 National Instrument 사의 LabVIEW가 사용되었다. 본 연구에 사용된 부품들에 대한 상세 정보는
Table 1에 정리되어 있다.
Table 1Specification of the position tracking control system
Table 1
|
Component |
Model |
Manufacturer |
Specification |
|
Controller |
myRIO |
National
Instrument |
Resolution : 12 bits
Overload protection : ±16V |
|
Actuator |
Dynamixel
AX-12A |
ROBOTIS |
Resolution : 0.2930
Angle [degree] : 300 |
|
IMU |
Gy-86 |
GY SENSOR |
Communication : I2C |
|
GPS |
BN-880 |
Beitian |
UART Interface : UART |
3.2 위치추적 자동화 시스템의 제어 알고리즘
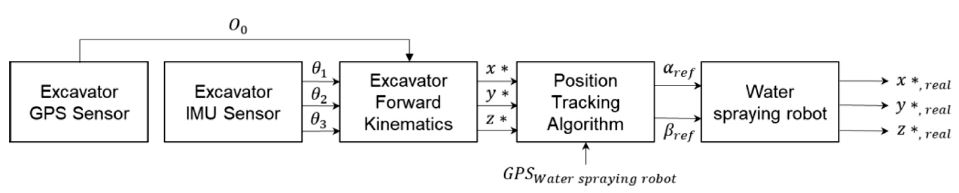
Fig. 5는 위치추적 자동화 시스템의 전체 제어 과정을 보여준다. 굴삭기에 부착된 GPS 센서로부터 굴삭기 중심부의 위치
O0값을 얻게 되고, 굴삭기에 장착된 IMU 센서를 통해 획득된 굴삭기의 붐, 암의 기울어진 각도와 함께 굴삭기 순기구학 방정식에 대입된다. 굴삭기 붐, 암의 기하학적 정보와 함께 계산된 순기구학 방정식을 통해 먼지 발생원인 굴삭기 버킷의 좌표 (
x*,
y*,
z*)가 계산된다. 굴삭기 버킷의 위치와 물 분사 로봇에 부착된 GPS 센서로부터 구한 상대위치를 통해 물 분사 로봇이 향해야 할 방향으로 모터 구동 각도가 정해지고, 입력되는 구동 각도에 의해 물 분사 로봇이 굴삭기의 버킷 위치를 추적하여 물을 분사하게 된다.
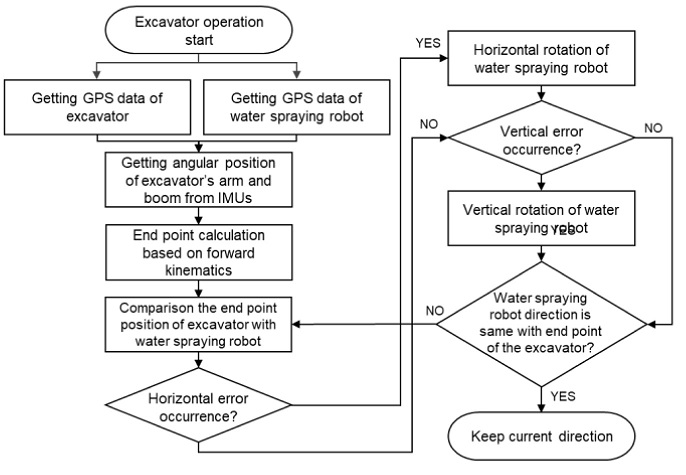
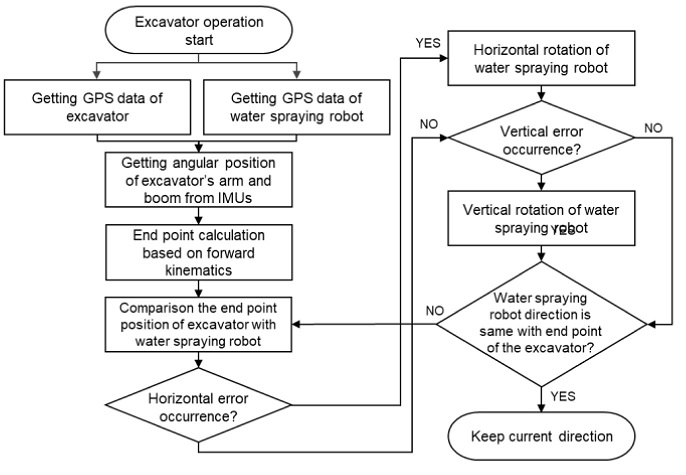
Fig. 6은 물 분사 로봇의 굴삭기 버킷 위치추적 과정을 설명한 순서도이다.
Fig. 5Control algorithm for the position tracking robot system
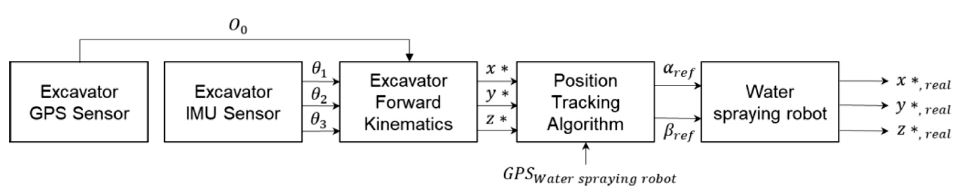
Fig. 6Operational procedure for the dust position tracking
4. 위치추적 알고리즘의 실험적 검증
4.1 관성 측정 장치(IMU)를 통한 각도 측정 실험
본 연구에서 사용되는 IMU 센서인 GY-86은 각도 변환 과정인
식(7)을 이용하여 굴삭기 붐, 암의 기울어진 각도를 계산한다. 이 때
acci (
i =
x,
y,
z)는 IMU 센서로부터 획득된
x,
y,
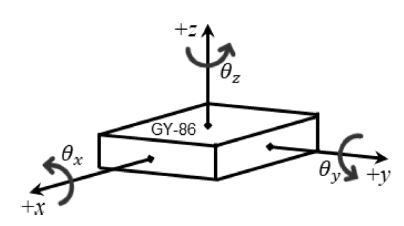
z축 방향의 가속도에 해당한다. 본 연구에서는 IMU 센서의 y축 방향 회전을 이용했기 때문에
Fig. 7의
θy를 이용하여 각도를 추출하였다. 그리고 진동에 다소 취약한 가속도 센서의 특성을 보완하기 위해 발생 노이즈를 감소시키는 저역 통과 필터(Low Pass Filter)를 이용하였다.
Fig. 7Coordinate system of IMU sensor (GY-86)
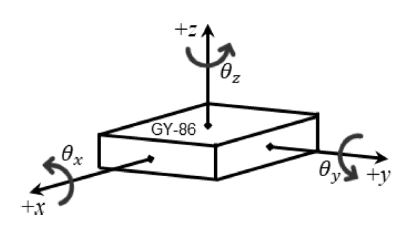
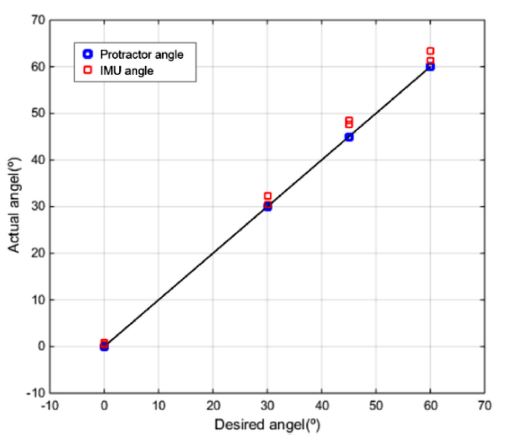
본 연구에서 사용되는 IMU 센서의 오차 범위를 측정하기 위한 실험을 진행하였다.
Fig. 8과
Table 2가 센서 내의 가속도센서의 제어환경을 고려하여 측정한 실험결과를 보여준다.
Fig. 8Angular position measuring experiment with protractor and IMU sensor
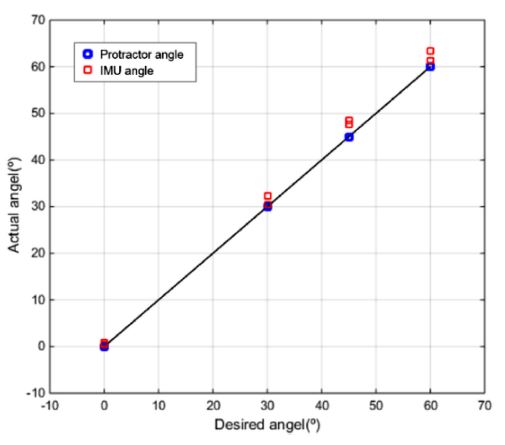
Table 2Angular position measuring experiment result: protractor, IMU sensor, and Max Error
Table 2
|
Protractor (°) |
0° |
30° |
45° |
60° |
|
IMU (°) |
0.4 - 0.76 |
30.46 - 32.39 |
47.6 - 48.43 |
61.28 - 63.38 |
|
Max Error (°) |
0.76 |
2.39 |
3.43 |
3.38 |
실제 측정하고자 하는 각도는 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°로 설정하였고, 이 각도를 IMU센서로 측정하여 정확한 값을 추출해내는지에 대한 실험을 진행하였다. 센서값의 최대 오차는 3.43°로, 비교적 정확한 각도가 추출됨을 알 수 있다.
4.2 GPS기반의 위치추적 실험
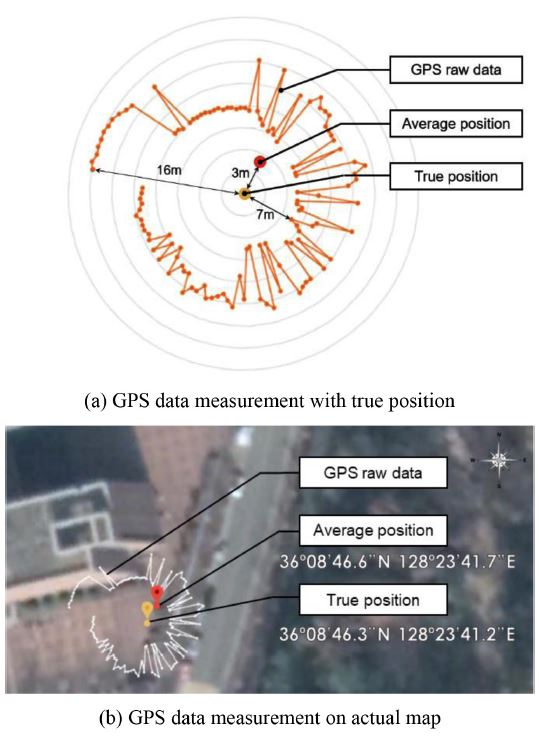
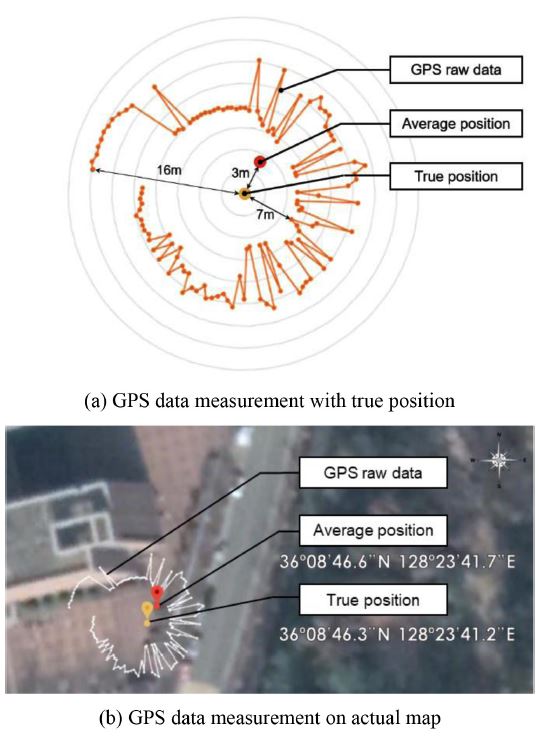
이 연구에 사용된 BN-880 GPS 센서를 사용하여 한 점의 위치를 반복적으로 측정하여
Fig. 9(a)와 같은 그래프로 나타냈다. 이 값을
Fig. 9(b)와 같이 지도에 입력하여 실제 측정한 위치와 비교해본 결과, 실제 위치와 센서로 측정한 값의 위치는 최소 7 m, 최대 16 m까지 차이가 발생하는 것을 확인했다. 이러한 오차를 줄이기 위해, 최근 1분 동안 반복적으로 측정한 센서 값들의 평균을 사용하였다. 이때 1분의 기준은 실제 굴삭기가 한 자리에 오래 머물러 철거작업을 진행하는 점을 고려하여 설정하였다.
9 그리고 평균값을 내어 실험한 결과, 실제로 측정한 위치와 실험의 평균값 위치의 차이가
Fig. 9(a)에서와 같이 3 m 이내로 확연히 감소한 것을 확인할 수 있다.
Fig. 9Comparison of position gap between experimental and average values
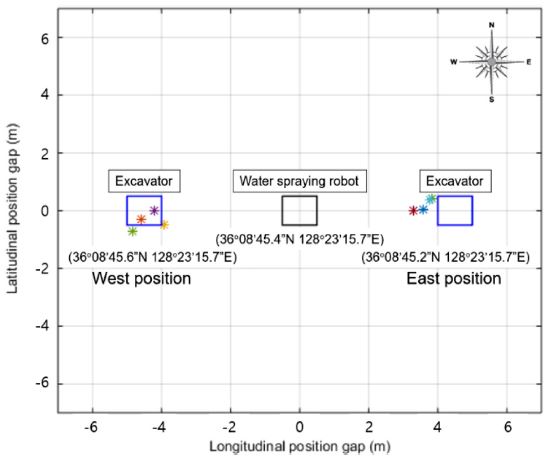
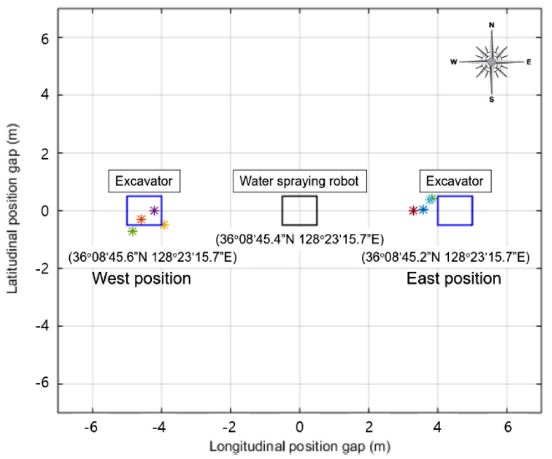
본 연구의 GPS 기반 위치추적 실험은 GPS의 정확도를 높임으로써 물 분사 로봇이 먼지 발생원을 정확하게 추적할 수 있도록 하는 것이다. 따라서 굴삭기와 물 분사 로봇 사이의 정확한 위치 차를 알아내는 것이 중요하다. 보정한 두 개의 GPS 센서를 굴삭기와 물 분사 로봇 상에 각각 하나씩 부착하고, 두 위치 사이의 위도와 경도를 측정하였다. 그리고 이 위치를 바탕으로 상대위치를 계산하는 실험을 진행하였다. 실험은 물 분사 로봇을 기준으로 굴삭기의 위치를 서쪽 4번, 동쪽 4번으로 실험했다. 이때 기준으로부터의 거리는 4.5 m이다.
Table 3과
Table 4는 굴삭기를 물 분사 로봇의 동쪽과 서쪽에 배치하여 실험하였을 때의 위치 계산값과 최대 오차값을 보여준다.
Fig. 10은
Table 3과
Table 4의 실험값을 그래프로 나타낸 것이다. 실험 결과, 최대 위치 오차는 약 1.2 m로 측정된다. 일반적인 물 분사 로봇은 반경 1 m 이상을 차지하는 물 분사 노즐을 사용하므로 실험으로 측정된 그래프 상의 오차는 실제 시스템을 구현하는데 허용되는 오차라 할 수 있다.
Table 3Relative position measuring experiment based on GPS sensor (east position)
Table 3
|
Relative position (m) |
Experiment |
Max Error (m) |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
Longitudinal position gap |
4.5 |
3.83 |
3.77 |
3.30 |
3.57 |
1.2 |
|
Latitudinal position gap |
0 |
0.39 |
0.36 |
0.008 |
0.05 |
0.39 |
Table 4Relative position measuring experiment based on GPS sensor (west position)
Table 4
|
Relative position (m) |
Experiment |
Max Error (m) |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
Longitude gap |
-4.5 |
-4.59 |
-3.92 |
-4.21 |
-4.85 |
0.58 |
|
Latitude gap |
0 |
-0.285 |
-0.47 |
0.01 |
-0.71 |
0.71 |
Fig. 10Comparison GPS of experimental and true values
4.3 굴삭기 구동 시 미세먼지 발생원 추적 정확성 실험
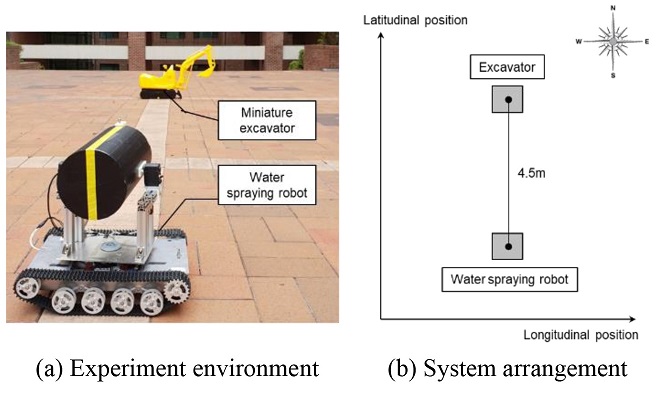
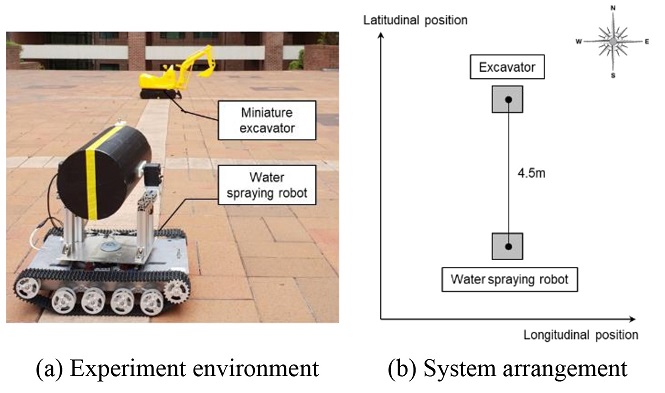
앞서 정확도를 높인 센서를 이용하여 위치추적 시스템의 정확성을 실험하기 위하여 실제 작업환경과 유사하게 구현하였다. 그러나 실제 굴삭기의 사용이 어려워 붐 길이가 47 cm, 암 길이가 20 cm인 소형 모형 굴삭기를 실험에 사용하였고, 물 분사 로봇의 직접적인 물 분사 구현이 어려워 중앙부에 분사 지점을 가리킬 수 있는 레이저 포인터를 장착하여 위치 추적하는 모습을 확인할 수 있도록 하였다. 물 분사 로봇의 위도 차는 4.5 m, 경도 차는 0 m로 설정하였다.
Fig. 11(a)가 구현한 실험 환경을 나타내며,
Fig. 11(b)가 실험 환경을 도식화 한 것이다. 실험 시 GPS의 측정 위치를 고정시켜 굴삭기가 한 자리에 멈춰 붐과 암을 구동하며 작업하는 상황을 가정하였다.
Fig. 11Position tracking experiment
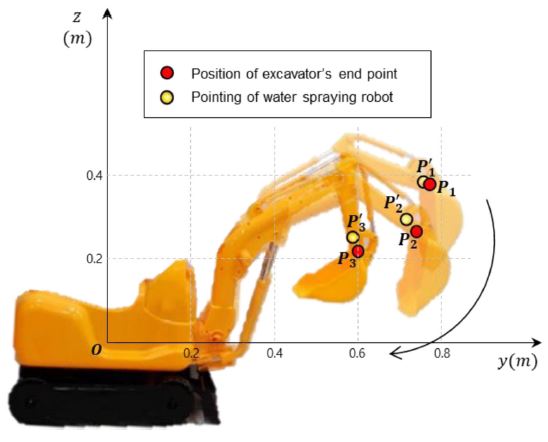
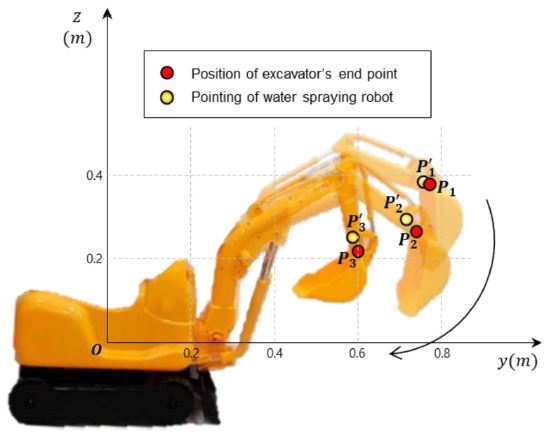
실험 환경 세팅 후, 실제 작업 모습과 유사하게 굴삭기의 팔을 움직여 팔이 작동되는 동시에 물 분사 로봇이 굴삭기의 버킷 부분을 제대로 추적하는지에 대한 실험을 진행하였다. 굴삭기 버킷 상의 한 점은
Fig. 12의
y -
z 그래프 상
Pi (
i = 1, 2, 3)와 같은 경로를 그리며 움직였으며,
Pi의 위치가 변경됨에 따라 물 분사 로봇에 설치된 레이저 포인터는
Fig. 12의
Pi' (
i = 1, 2, 3)의 위치를 가리켰다.
Fig. 12Position of excavator’s end point and water spraying robot
물 분사 로봇의 위치추적 정확성 파악을 위해
Fig. 12의
Pi점 과
Pi' (
i = 1, 2, 3)점의 위치의 좌표를 비교하여
Table 5에 나타내었다.
y값의 최대 오차는 0.025 m,
z값의 최대 오차는 0.035m로, 본 연구에서 사용한 굴삭기의 버킷 길이인 0.16 m의 4분의 1 길이인 0.04 m보다도 작다는 결과를 보여준다. 이는 물 분사 로봇이 분사하는 물의 위치가 먼지가 발생하는 굴삭기 버킷의 위치 범위에 안정적으로 포함된다는 것을 의미한다. 따라서 물 분사 로봇은 굴삭기의 버킷 부분이 움직일 때마다 정확한 위치추적을 하고 있다는 것을 알 수 있으며, 추후 실제 크기의 굴삭기를 이용하여 먼지 억제 작업을 진행할 경우에도 정확한 추적 모습을 보일 것으로 판단된다.
Table 5Position of excavator’s end point and water spraying robot
Table 5
|
a
|
Pa
|
Pa'
|
Error |
|
y*
|
z*
|
y*
|
z*
|
y*
|
z*
|
|
(m) |
(m) |
(m) |
(m) |
(m) |
(m) |
|
1 |
0.77 |
0.38 |
0.76 |
0.38 |
0.01 |
0 |
|
2 |
0.74 |
0.26 |
0.72 |
0.29 |
0.02 |
0.03 |
|
3 |
0.60 |
0.22 |
0.59 |
0.25 |
0.01 |
0.03 |
5. 결론
본 연구에서는 순기구학 해석을 통해 미세먼지 발생원의 위치를 추적하는 알고리즘이 소개되고 이를 실험적으로 검증하는 작업이 수행되었다. 굴삭기와 물 분사 로봇의 위치 정보를 얻기 위하여 GPS 센서가 사용되었고 굴삭기 버킷의 위치 정보를 계산하기 위한 순기구학 수식과 IMU센서가 사용되었다. 미세먼지가 발생하는 굴삭기 버킷의 위치를 계산하는 순기구학 수식이 전개되고 이를 바탕으로 물 분사 로봇이 버킷의 위치를 추적하는 알고리즘이 제안되었다. 개발된 위치추적 알고리즘을 검증하기 위한 실험을 수행하기 위하여 작은 크기의 굴삭기와 물 분사 로봇을 마련하였다. 굴삭기의 붐, 암, 버킷의 위치가 변할 때마다 물 분사 로봇이 굴삭기 버킷의 위치를 성공적으로 추적하는 모습을 확인하였다. 본 연구에서는 연구 환경이 제한되어 있어 작은 크기의 굴삭기와 물 분사 로봇을 사용하였다. 그러나 추후 실제 건설현장에 필요한 미세먼지 발생원 추적 및 억제 시스템이 적용되기 위해서, 실제 크기의 굴삭기와 실제 굴삭기에서 발생하는 미세먼지를 억제할 수 있는 크기의 물 분사 로봇을 이용하여 위치를 추적하는 추가 연구를 진행할 예정이다.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
본 연구는 금오공과대학교학술연구비에 의하여 연구된 논문임.
REFERENCES
- 1.
Leung, K. K., Liu, C., Wong, C. C., Lo, J. C. Y., and Ng, G. C. T., “On the Study of Ventilation and Pollutant Removal Over Idealized Two-Dimensional Urban Street Canyons,” Building Simulation, Vol. 5, No. 4, pp. 359-369, 2012.
10.1007/s12273-012-0085-4
- 2.
Michioka, T., Sato, A., Takimoto, H., and Kanda, M., “Large-Eddy Simulation for the Mechanism of Pollutant Removal from a Two-Dimensional Street Canyon,” Boundary-Layer Meteorology, Vol. 138, No. 2, pp. 195-213, 2011.
10.1007/s10546-010-9556-2
- 3.
Faschingleitner, J. and Höflinger, W., “Evaluation of Primary and Secondary Fugitive Dust Suppression Methods Using Enclosed Water Spraying Systems at Bulk Solids Handling,” Advanced Powder Technology, Vol. 22, No. 2, pp. 236-244, 2011.
10.1016/j.apt.2010.12.013
- 4.
Chavhan, M. V. and Mukhopadhyay, A., “Fibrous Filter to Protect Building Environments from Polluting Agents: A Review,” Journal of The Institution of Engineers: Series E, Vol. 97, No. 1, pp. 63-73, 2016.
10.1007/s40034-015-0071-3
- 5.
Bailer, C., Pagani, A., and Stricker, D., “A Superior Tracking Approach: Building a Strong Tracker Through Fusion,” European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 170-185, 2014.
10.1007/978-3-319-10584-0_12
- 6.
Koivo, A. J., Thoma, M., Kocaoglan, E., and Andrade-Cetto, J., “Modeling and Control of Excavator Dynamics During Digging Operation,” Journal of Aerospace Engineering, Vol. 9, No. 1, pp. 10-18, 1996.
10.1061/(ASCE)0893-1321(1996)9:1(10)
- 7.
Chang, P. H. and Lee, S., “A straight-Line Motion Tracking Control of Hydraulic Excavator System,” Mechatronics, Vol. 12, No. 1, pp. 119-138, 2002.
10.1016/S0957-4158(01)00014-9
- 8.
Nguyen, Q. H., Ha, Q. P., Rye, D. C., and Durrant-Whyte, H. F., “Force/Position Tracking for Electrohydraulic Systems of a Robotic Excavator,” Proc. of Decision and Control 39th Conference, pp. 5224-5229, 2000.
- 9.
Eryutin, V. N., “The Work Methods of a Leading Excavator Team,” Refractories and Industrial Ceramics, Vol. 17, No. 11, pp. 723-724, 1976.
10.1007/BF01319875
Biography
- Seolha Kim
M.Sc. candidate in the Department of Mechanical System Engineering, Kumoh National Institute of Technology. Her research interest is robotics.
- Minji Kim
B.Sc. in the Department of Mechanical System Engineering, Kumoh National Institute of Technology. His/Her research interest is robotics.
- Heeyun Jung
B.Sc. in the Department of Mechanical System Engineering, Kumoh National Institute of Technology. Her research interest is mechatronics.
- Baeksuk Chu
Associate Professor in the Department of Mechanical System Engineering, Kumoh National Institute of Technology. His research interest includes robotics, mechatronics, intelligent control and reinforcement learning.