ABSTRACT
The necessity for printing multi-materials has increased as the importance of 3D printing grew in various industries. Many studies have undertaken for printing multi-materials simultaneously. In ME (Material Extrusion) type 3D printers, the method of printing different materials using multi nozzles is generally commercialized. Polymers with different composition are hard-to-mix with each other, making it difficult to maintain the structural strength of printer parts. So the MJ type 3D printer uses a unique method that mixes multi-materials in a liquid state before printing. In the ME type 3D printer, there were also efforts to mix materials in a melted state, but they were mainly demonstrated for multi-colored parts. In this study, the effect of multi-material mixing on structural strength changes was tested. Multi-Materials were printed with the ME type 3D printer by using one nozzle with a multiple filament feeding system. The bending and tensile tests were conducted to verify the structural characteristics.
-
KEYWORDS: Multi-material specimen, Diamond hotend, Material extrusion, Concurrent printing, Property analysis
-
KEYWORDS: 다종 재료 시편, 다이아몬드 핫엔드, 재료 압출 방식, 동시 출력, 물성 분석
1. 서론
3D 프린팅 기술은 간단한 조작만으로도 복잡한 형태의 3차원 형상을 제작할 수 있어서 다양한 시제품 개발에 필요한 시간과 비용을 절감할 수 있어 많은 주목을 받고 있는 기술이다.
1 이에 3D 프린팅 기술은 기계, 건축, 전자, 의료 등 다양한 산업 분야에서 그 중요성을 더해가고 있다.
2-6 이러한 3D 프린팅 기술의 적용 범위가 점차 늘어감에 따라 다기능성 복합 형상을 제작하기 위해 다종 소재 출력에 대한 요구도 늘어나고 있다. 다종 소재 출력은 비단 동일 소재에 기반한 컬러 구현 뿐만 아니라 출력 형상의 위치별로 다양한 강도 및 특성을 지니는 소재를 혼합 출력함으로써 출력물의 기계적 특성을 조형 위치에 따라 다양하게 변화시킬 수 있다. 특히 소재의 혼합 비율을 연속적으로 변화시킴으로써 기계적 물성이 연속적으로 변화하는 FGM(Functional Graded Material) 구조도 많이 연구되고 있다.
7
액상 소재에 기반하여 재료를 출력하는 MJ (Material Jetting) 방식의 3D 프린터를 활용하여 이러한 FGM 구조물을 출력하는 것과 관련된 많은 연구가 진행 중이다.
8 이는 MJ방식의 소재 특성상 출력 전 액상 상태에서 혼합이 용이하기 때문에 비교적 이종 소재 혼합을 통한 동시 출력 연구가 다양하게 이루어진 것이다. 하지만, MJ방식의 경우 비교적 장비 가격과 소재 가격이 높기 때문에 다양한 분야에 활용하기가 어렵다. 또한, 광경화 액상 수지의 종류에도 제한이 있어서 다양한 소재 개발에 한계가 있다는 단점을 지니고 있다.
7
반면, ME (Material Extrusion)방식 3D 프린터의 경우 가열된 노즐을 이용하여 열가소성 필라멘트를 녹여서 출력하는 방식이므로 그 구조가 간단하고 대부분의 열가소성 수지 재료에 적용 가능하다는 장점을 지니고 있다. 그래서, 비교적 저렴한 가격에 다양한 소재에 대한 출력이 가능하다. 하지만, 기본 고체 상태의 폴리머 필라멘트를 녹여서 출력하는 방식이므로 조형 중 소재 변경이나 혼합이 어려워 대부분의 경우는 단일 소재로 출력하거나 다수의 노즐을 통해 각각의 소재를 번갈아 가면서 출력하는 것이 대부분이다.
9,10 이 경우 출력 중 다른 색상이나 강도의 소재를 각각 출력하는 것은 가능하나 고상화된 상태에서 서로 다른 물성의 소재 간 접합력은 일반적으로 현저히 낮은 경우가 많아서 실제 원하는 기계적 물성을 얻지 못하게 된다. 이러한 이유로 ME방식으로 다종 재료를 출력하여 구조적 강도를 보인 사례가 드물었다.
최근 ME방식 3D 프린터에서도 다양한 소재 및 컬러에 대응하기 위해 2, 3종의 필라멘트 소재를 하나의 노즐에 공급 후 동시에 녹여서 출력하는 다이아몬드 핫엔드 노즐(Diamond Hotend Nozzle)과 같은 형태의 제품들이 소개되었다. 이러한 기술을 바탕으로 노즐의 개조나 G-Code 변화를 통해 색상이 다른 동일 소재 필라멘트를 혼합하여 다양한 색상이 구현된 출력물에 대한 연구 시도들도 있었다.
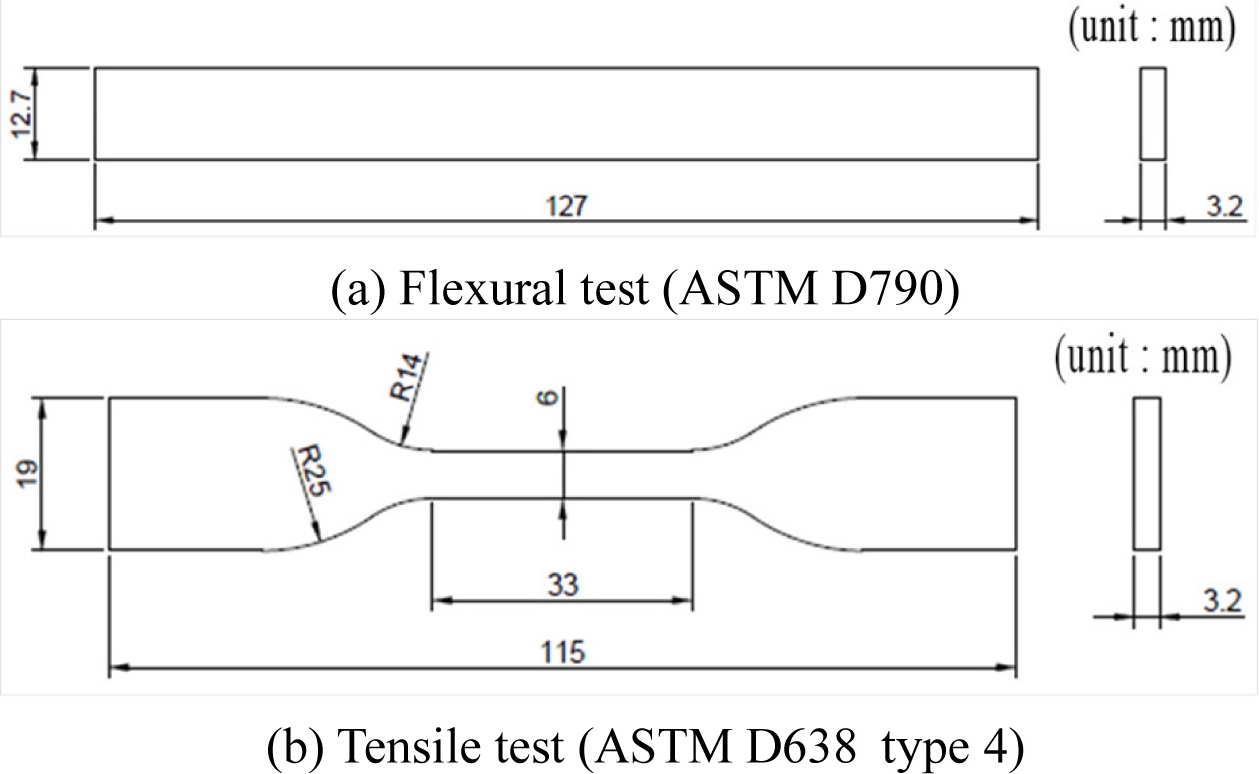
11-13 또한, 이러한 구조의 노즐은 동시에 다종 필라멘트를 녹인 상태로 혼합 출력이 이루어지므로 소재 간 접합력을 조금 더 개선할 수 있을 가능성이 존재한다. 하지만, 현재까지는 다른 기계적 물성을 지니는 이종 소재 간 혼합에 의한 ME방식 시편 출력 및 물성 검증에 대한 연구가 거의 없었다. 이에 본 연구에서는 다양한 소재를 출력할 수 있을 뿐만 아니라 상대적으로 비용이 적게 드는 ME방식의 프린터를 기반으로 하여 다종 소재 출력 시 기계적 물성 변화가 가능한지에 대한 실험을 진행하였다. 이를 위해 상용화되어 판매되는 다이아몬드 핫엔드 노즐을 활용하여 다종 소재 필라멘트의 혼합 출력을 진행하였으며 명확한 기계적 특성 분석을 위해 순수 소재, 50% 혼합 소재 등에 기반한 시편 제작과 분석을 진행하였다. 이종 소재 간 혼합 출력된 시편의 기계적 물성 변화 여부를 판단하기 위하여 굽힘과 인장 시험을 진행하여 특성을 분석하였다. 각 시험은 공인 시험 방법을 따랐으며 굽힘 시험은 ASTMD790, 인장 시험은 ASTM D638을 기준으로 측정을 진행하였다.
2. 실험 구성
2.1 사용 소재
혼합 출력 시편의 물성 변화가 가장 극명하게 드러나도록 하기 위해 기계적 강도가 크게 차이나는 두 종류의 상용 필라멘트 소재를 대상 소재로 선정하였다. 고강성 소재로는 강도와 인성이 높은 고강성 PLA (Poly Lactic Acid)인 ZNY TECH사의 FILATINUM PLA-T를 사용하였다. 반면에 상대적으로 강도는 낮지만 유연하여 탄성이 뛰어난 소재로는 TOP 3D사의 Topflex 제품을 사용하였다. 해당 제품은 Butylene/Poly (Alkylene Ether) Phthalate 화합물 99%로 이루어진 TPEE (Thermoplastic Polyester Elastomer) 소재이다. 이에 본 연구에서는 위 두 소재를 각각 고강성 소재(A 소재)와 탄성 소재(B 소재)로 지칭하여 사용하였다. 다만, 각 제조사에서 정확한 재료의 조성이나 기계적 물성치를 제공하지 않아서 각 사용 소재의 기계적 물성치에 대한 측정도 함께 진행하였다.
2.2 시험 시편 규격
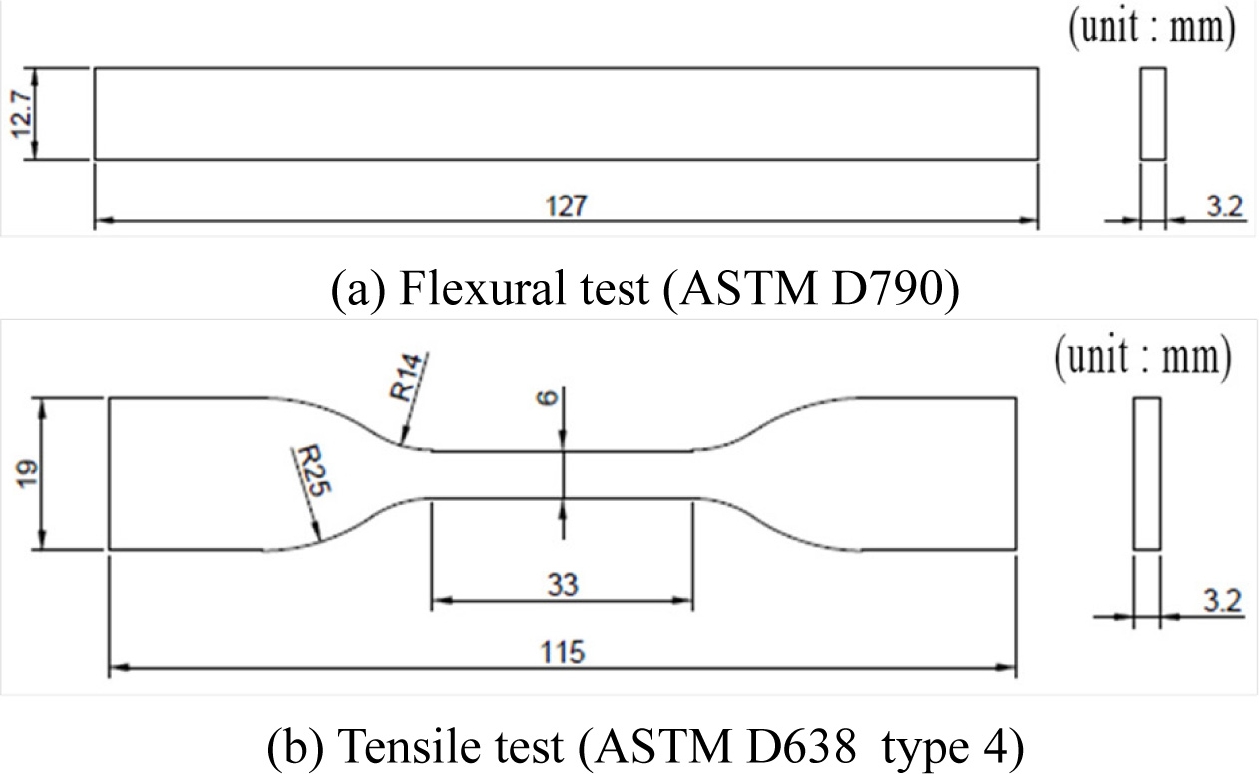
굽힘 시험과 인장 시험은 국제 시험 규격에 맞도록 ASTM 시험을 기준으로 진행하였다. 굽힘 시험은 일반적인 폴리머 시험에 흔히 적용되는 ASTM D790 시험법을 적용하기 위해
Fig. 1(a)에 보인 바와 같이 두께 3.2mm를 지니는 막대형 시편으로 제작하였다.
14 인장 시험의 경우 일반적인 폴리머 시험에서 많이 사용되는 ASTM D638 시험법을 적용하였다.
15 D638 시험법의 경우 재료의 특성 및 시험 목적에 따라 다시 Types 1부터 5로 세분화된다. 본 실험의 경우 일반 폴리머 재료 시험도 진행하지만 탄성 변형이 큰 고탄성 재료에 대한 시험도 동시에 진행하므로 고탄성 소재 시험에 적절한 Type 4 시편을 기준으로
Fig. 1(b)와 같이 제작하였다.
Fig. 1Design of ASTM standard specimens
2.3 사용 장비
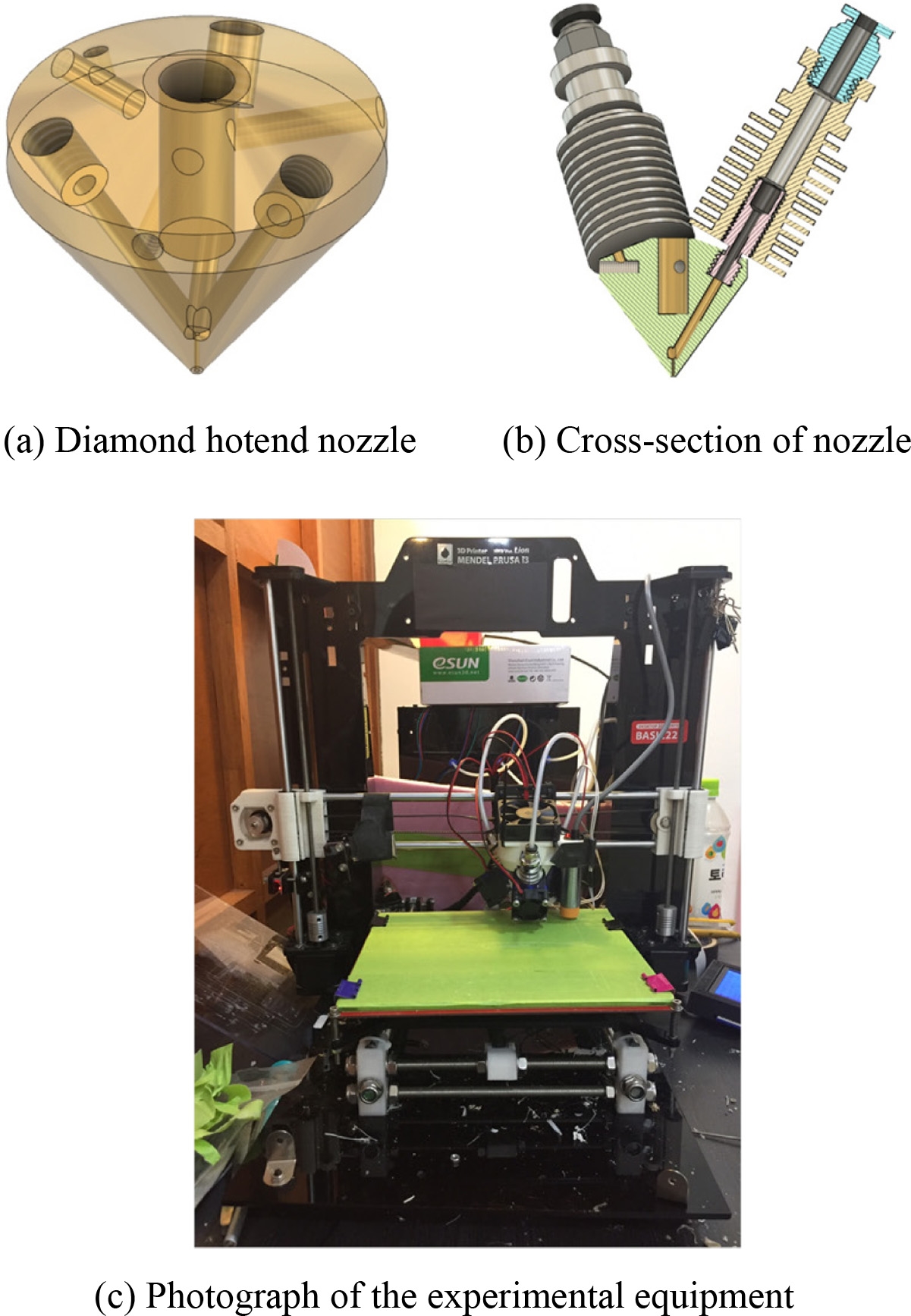
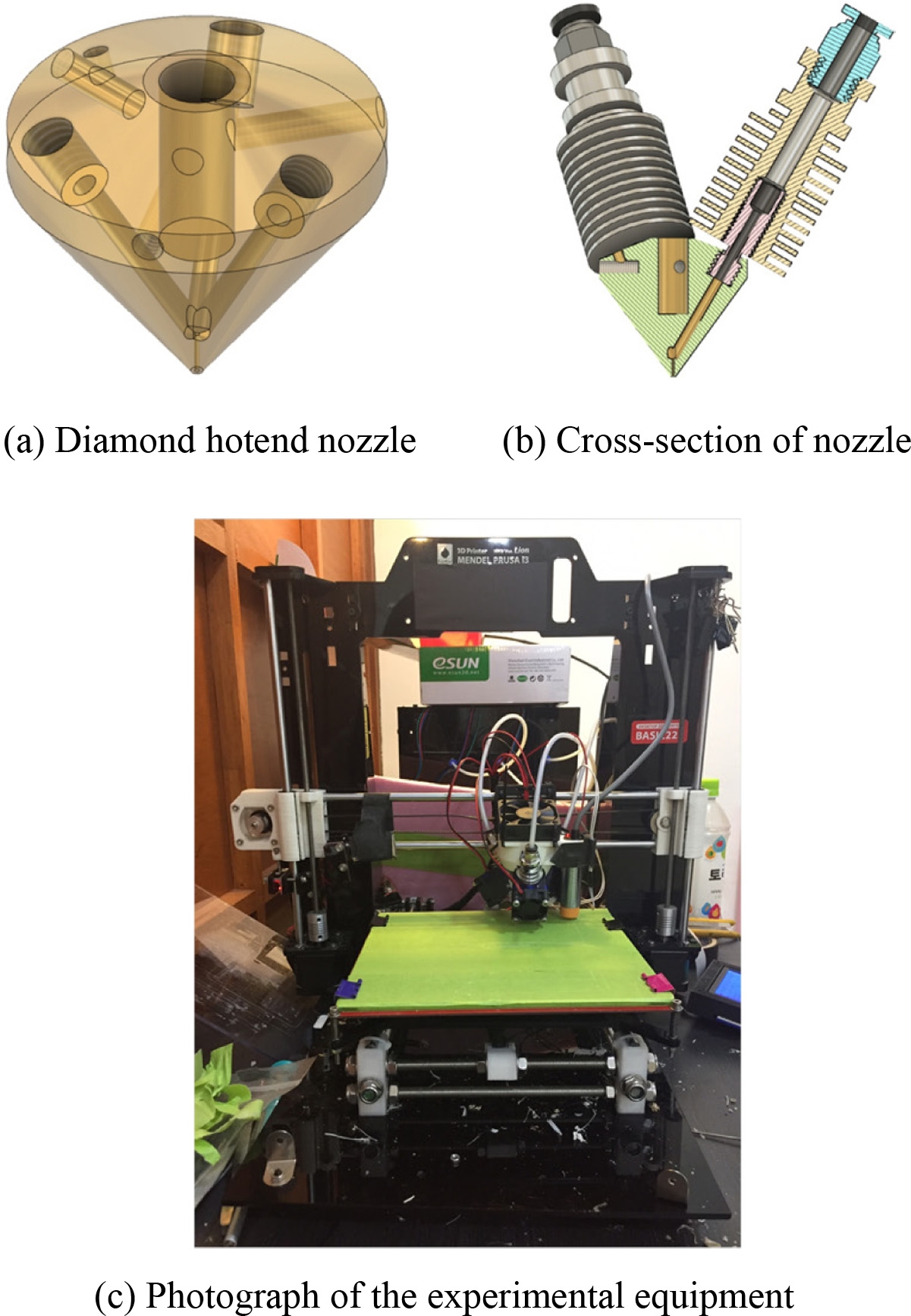
본 연구에서 사용한 3D 프린터는 오픈 소스 기반으로 제작되어 다양한 개조 및 변형이 용이한 RepRap사의 Prusa i3이다. 기본 구조는 기성품을 사용하여 출력 가능한 최대 크기는 215 × 210 × 180이다. 다종 재료 압출 및 X, Y, Z축 구동을 위해 총 7개의 Nema 17 스텝 모터를 사용하였다. 기존 상용 장비와 달리 다종 소재 출력을 위해 제어해야할 압출 모터 수가 증가하였으나 기본적으로 제공되는 제어보드에서는 제어 가능한 모터 포트가 제한적이어서 제어보드를 Geeetech Inc.사의 Rumba 3D Printer Controller Board ATmega2560으로 교체하여 사용하였다. 기존 상용품과 기본적으로는 흡사한 CPU에 기반하고 있으므로 제어 프로그램은 기존 장비와 호환이 가능하여 오픈 소스인 Repetier Firmware를 사용하였다. 다종 소재 재료를 상호 혼합하여 동시 출력을 진행하기 위하여
Fig. 2(a)에 보인 바와 같이 3가지 소재 입력을 받아서 하나의 노즐로 출력이 가능한 RepRap사의 다이아몬드 핫엔드 노즐을 사용하였다. 입력된 3개의 소재는 노즐 가운데 위치한 히터에 의해 가열되어 용융되며 0.4 mm 직경을 지니는 출구 노즐 직전에서 상호 혼합되어 압출된다. 이때, 고온의 노즐 열이 필라멘트 공급부에 미치는 영향을 최소화하기 위하여
Fig. 2(b)에 보인 바와 같은 알루미늄핀 방열 구조가 각 필라멘트 공급부에 위치하게 된다. 이러한 구조를 기반으로
Fig. 2(c)에 보인 것과 같은 장비를 제작하여 실험을 진행하였다.
Fig. 2Experimental equipment
제작된 복합 시편의 기계적 물성을 분석하기 위하여 대표적 시험법인 굽힘 시험과 인장 시험을 진행하였다. 인장 시험을 위해 사용한 시험기는 상용 만능 시험기인 AMETEK사의 EZ20모델을 사용하였다. 시험기의 최대 허용 하중은 20 kN이고 분해능은 1 N이다. 인장 속도는 0.001-508 mm/min의 범위에서 설정이 가능하다. 본 실험에서는 ASTM 시험법에 따라서 5 mm/min의 속도로 실험을 진행하였다. B 소재로 제작된 시편의 경우 장비의 최대 시험 길이를 초과한 경우에도 완전 파단이 발생하지 않아서 시험 길이는 인장 응력이 수렴하기 시작하는 시점까지 진행하였다.
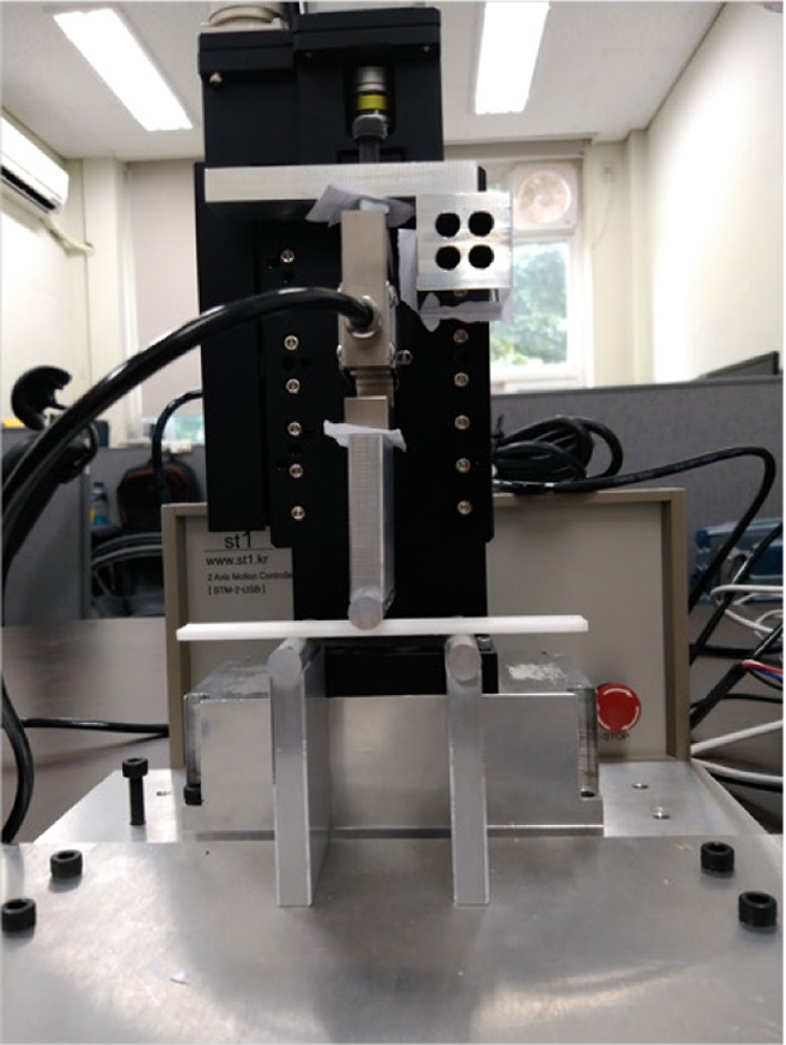
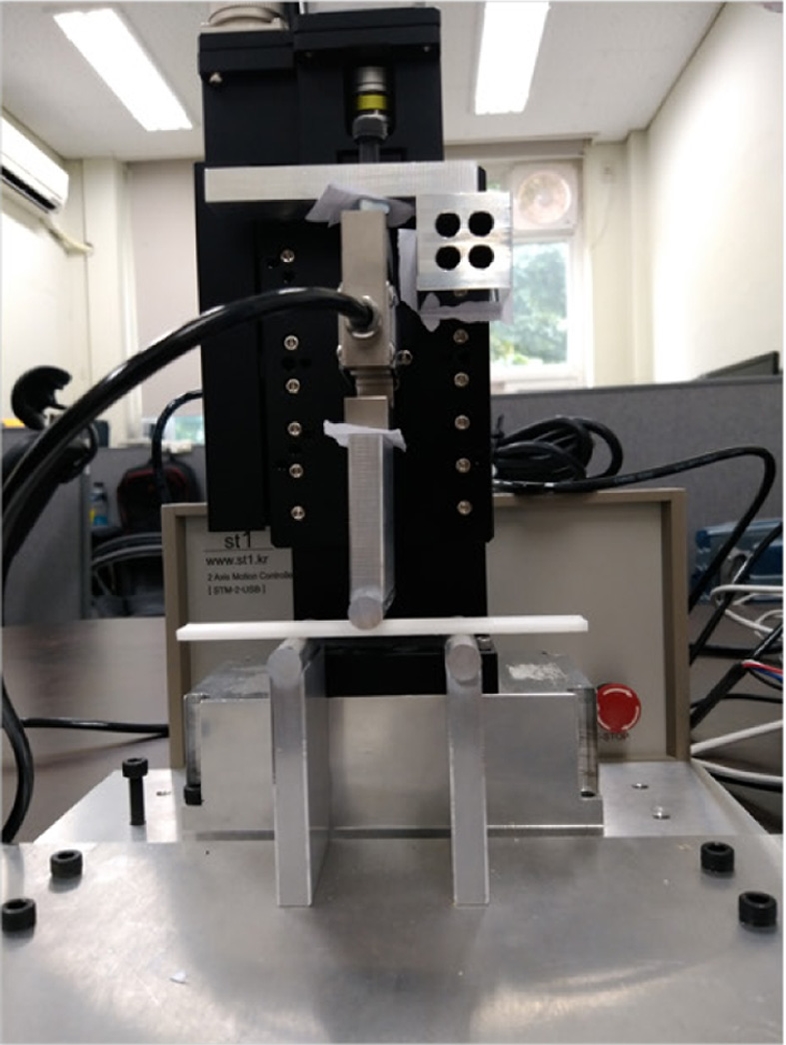
굽힘 시험의 경우 고강성 A 소재는 약 50MPa 이상의 굽힘 응력을 지녔지만 탄성 B 소재의 경우에는 이보다 훨씬 낮은 5MPa 미만의 응력으로 측정되었다. 이에 인장 시험에서 사용한 만능시험기 로드셀의 정밀도가 1 N 이상임을 감안하여 굽힘 시험을 위해서는 별도의 소용량 시험기를 자체 제작하였다. 제작된 굽힘 시험기는 S형 로드셀, 일축 정밀스테이지 등의 장치를 이용하여
Fig. 3과 같이 제작하였다. 3점 굽힘 시험을 진행하기 위한 시편 지지대와 로딩 노즈(Loading Nose)는 굽힘 하중이 매우 작으므로 가공이 용이한 알루미늄 60재료를 이용하여 제작하였다. 정밀 측정을 위해 로드셀은 최대 하중은 250 N으로 낮으나 반복 정밀도가 1 mN 수준으로 우수한 CAS사의 SBA-25L을 사용하였다. 최종적으로 24 bit A/D 보드를 사용하여 값을 기록하였다. 굽힘 시험기의 이송 속도는 ASTM 시험법에 따라 1.37 mm/min로 설정하였다. 로딩 노즈의 이송 거리는 ASTM 시험법에 표기된 아래
식(1)에 근거하여 결정하였다.
Fig. 3Photograph of the flexural test equipment
여기에서 L은 지지 간격, d는 시편의 두께를 의미하며 r은 변형률이다. 굴곡 시험 중 각 소재의 시편 파단 및 변형 정도가 다르므로 r은 시험 규격에서 권장하는 최대 변형률 이내인 0.02 수준으로 고정하였다. 이를 토대로 계산된 D값은 지지 간격 중간에서의 변형량을 의미하므로 로딩 노즈의 이송 거리는 약 3mm로 설정하였다.
2.4 시편 제작 조건
시편 제작을 위해 대표적 오픈 소스인 Slic3r을 사용하여 슬라이싱을 진행하였다. 기본 출력 조건은 일반적으로 사용되어지는 기본값을 사용하였으며 주요 출력 조건은
Table 1에 표기하였다. A 소재의 제조사 추천 출력 노즐 온도는 200-220°C인 반면 B 소재의 추천 온도는 220-240°C이므로 사용한 노즐 온도는 모든 실험에서 일정한 조건을 유지하기 위하여 공통적으로 출력 가능한 온도 값인 220°C로 설정하였다. 일반적인 ME방식 3D 프린팅 구조물의 경우 라인 간 간격과 적층 두께가 소재 간 밀착력 및 중첩률에 영향을 미치게 되어 인장 강도가 변화하게 된다.
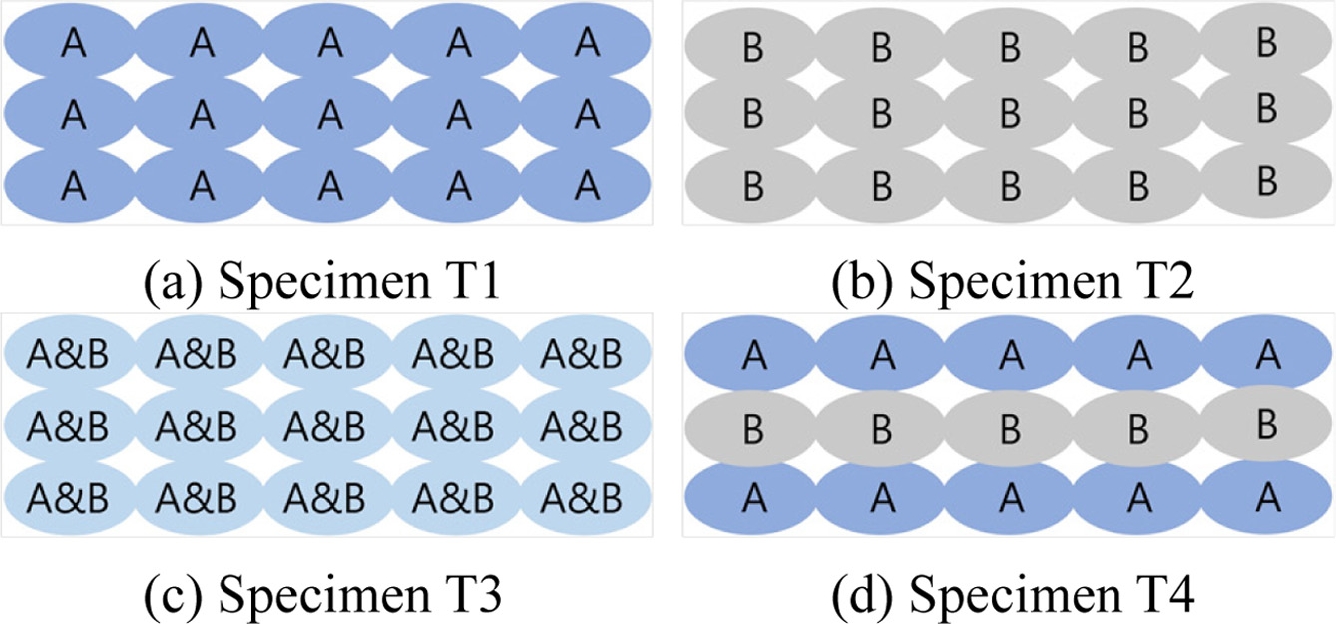
16 이에 본 연구에서는 이러한 영향을 배제하기 위하여 라인 간 간격과 적층 두께를 모든 실험에서 일정하게 고정하여 진행하였다. 시편 출력 시 이송 방향과 접합력에 따른 영향도 최소화하기 위하여 모든 시편은 인장 시험 길이 방향으로 노즐을 이송하여 출력하였다. 테스트 시편은
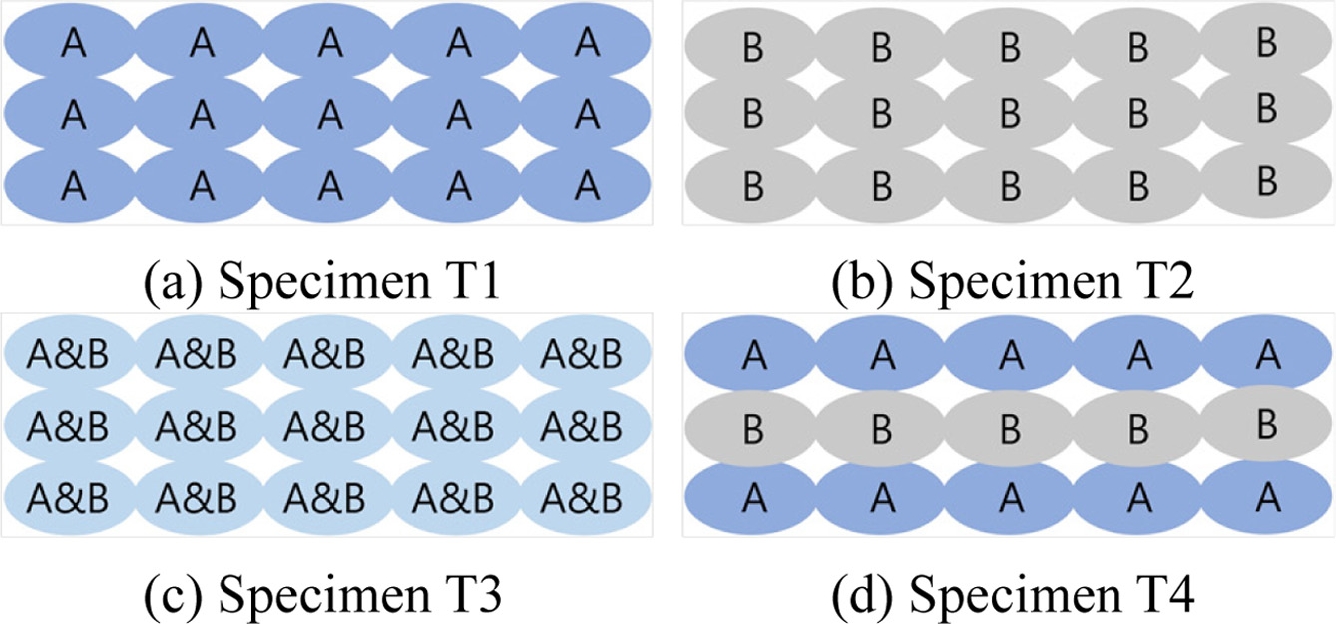
Fig. 4에 보인 바와 같이 사용 소재들의 출력 방법에 따라 시편 T1-T4의 4종류로 구분하여 제작하였다. 이때, A 소재는 고강성 소재인 FILATINUM PLA-T를 의미하며 B 소재는 탄성 소재인 Topflex를 의미한다. 이를 통해 시편 T1과 T2는 각각 개별 소재만을 사용하여 출력하였으며 시편 T3는 A 소재와 B 소재를 1 : 1 비율로 혼합 동시 출력, 시편 T4는 A 소재만으로 한 층을 적층한 후 이어서 B 소재만으로 다음 층을 적층하는 형태로 각 소재를 한 층씩 번갈아가면서 격층 형태로 출력하여 제작하였다. 즉, 시편 T3와 T4를 구성하고 있는 A 소재와 B 소재의 전체 비율은 동일하게 1 : 1로 이루어져 있으나 시편 제작 시 소재 압출 중 혼합 여부가 다르게 진행되었다. 모든 시편은 동일하게 3개씩 제작하여 측정을 진행하였다.
Table 1Printing condition of experimental specimen
Table 1
|
Layer thickness |
0.2 mm |
|
Nozzle diameter |
0.4 mm |
|
Line spacing |
0.25 mm |
|
Nozzle temp. |
220℃ |
|
Bed temp. |
60℃ |
Fig. 4Printing method according to specimen
3. 실험 결과 및 고찰
3.1 컬러 출력
이종 소재의 출력 시험에 앞서 제작된 장비의 출력성 검증을 위해 상용 PLA 소재에 기반한 3가지 색상의 필라멘트를 활용하여 단일 출력 및 혼합 출력을 진행하였다. 사용된 필라멘트의 색상은 감산 혼합인 색의 3원색에 기반하여 시안(Cyan), 마젠타(Magenta), 엘로우(Yellow)를 사용하였다. 출력 시 전체 압출량을 유지한 채 각 색상 필라멘트의 공급 비율을
Fig. 5(a)에 표기된 바와 같이 조정하여 3가지 필라멘트로 16색상 이상의 혼합 컬러 구현이 가능함을 확인하였다. 또한, 각각의 필라멘트로 개별 출력한 경우와 이를 동시 출력한 경우 모두 모델링된 형태대로 출력이 원활히 이루어졌다. 이를 기반으로 출력 중 필라멘트 공급 비율을 연속적으로 변경하여
Fig. 5(b)에 보인 바와 같이 16색상으로 이루어진 컵 형상의 출력도 가능하였다. 이를 통해 제작되어진 장비의 동일 소재에 기반한 단일 및 동시 출력성이 원활함을 확인하였다.
Fig. 5Results of the color printing test

3.2 인장 시험
이종 소재의 출력 방법에 따른 기계적 물성 차이를 확인하기 위하여 인장 시험을 수행하였다. 사용된 각 소재의 제조사에서 정확한 기계적 물성을 제공하지 않고 있으므로 A 소재와 B 소재에 대한 시험도 함께 진행하였다.
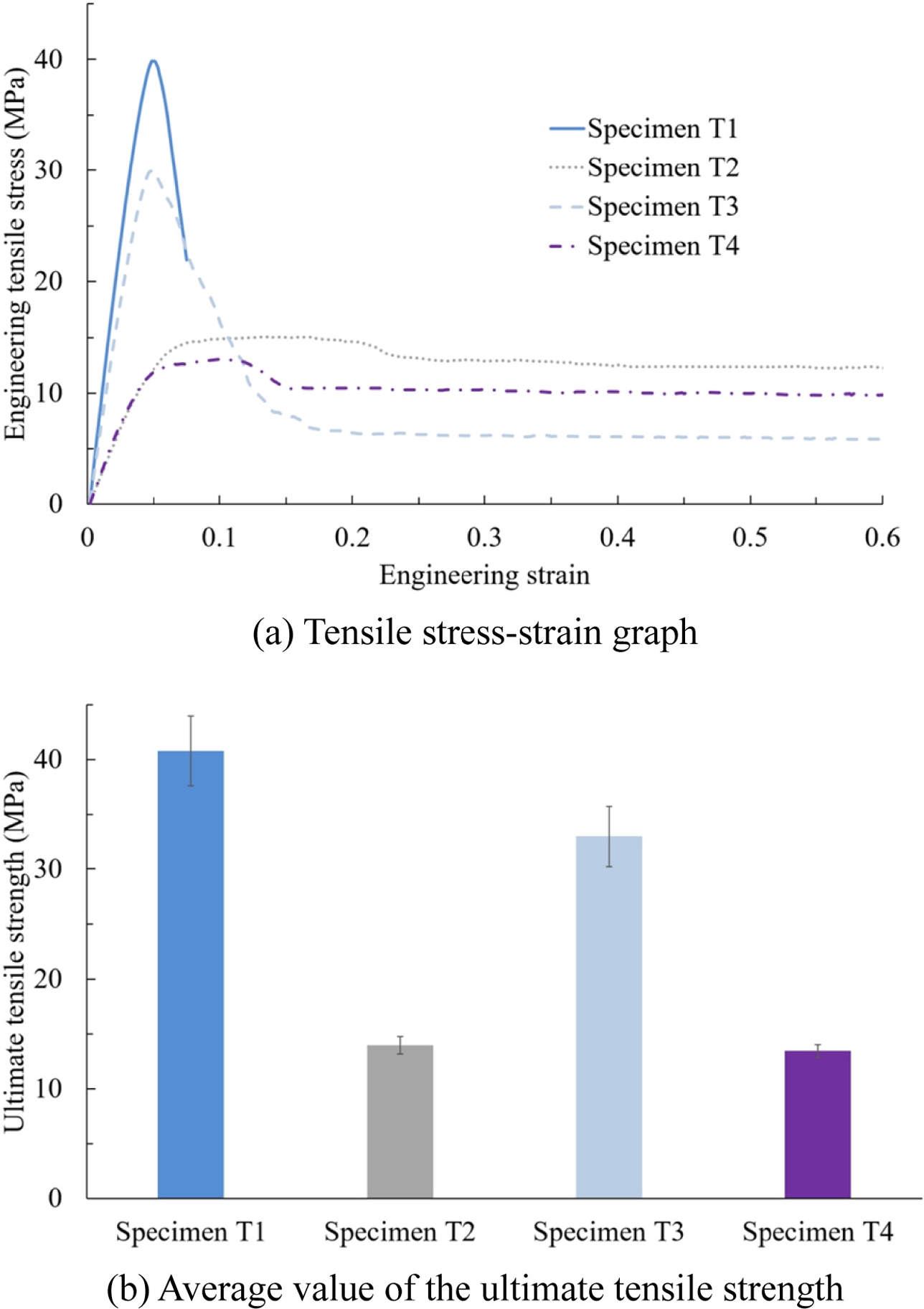
Fig. 6(a)에 보인 바와 같이 A 소재만으로 출력한 시편 T1의 경우 변형률이 0.05를 초과하면서 넥킹이 발생하였으며 그 이후 파단이 되었다. 반면, B 소재만을 사용한 시편 T2의 경우 연성이 매우 우수하여 장비에서 시험 가능한 최대 이송에서도 파단이 발생하지 않았다. 변형률 0.15 근방에서 최대 응력을 보였으며 그 이후에는 인장 응력이 조금 감소한 상태로 큰 변화없이 수렴되는 양상을 보였다. 이에 소재의 최대 인장 강도값을 지난 후 안정적으로 값이 충분히 수렴하는 시점인 변형률 0.6까지 모든 시험을 진행하였다. 기존 듀얼 노즐 시스템에서와 유사하게 A 소재와 B 소재를 한 층씩 격층으로 출력한 시편 T4 경우에는 시편 T2와 유사하게 최대 인장 강도를 지난 시점 이후에 인장 응력이 소폭 감소하며 수렴되는 경향을 보였다. 하지만, 두 소재를 함께 용융하여 동시 출력한 시편 T3 경우에는 시편 T1의 넥킹 지점과 유사한 지점에서 최대 인장 강도를 보인 후 상대적으로 가파르게 인장 응력이 감소하였다. 그 이후에는 시편 T2가 수렴한 인장 응력 값의 약 50%정도 수준으로 유사하게 수렴되는 경향을 보였다.
Fig. 6Results of the tensile test
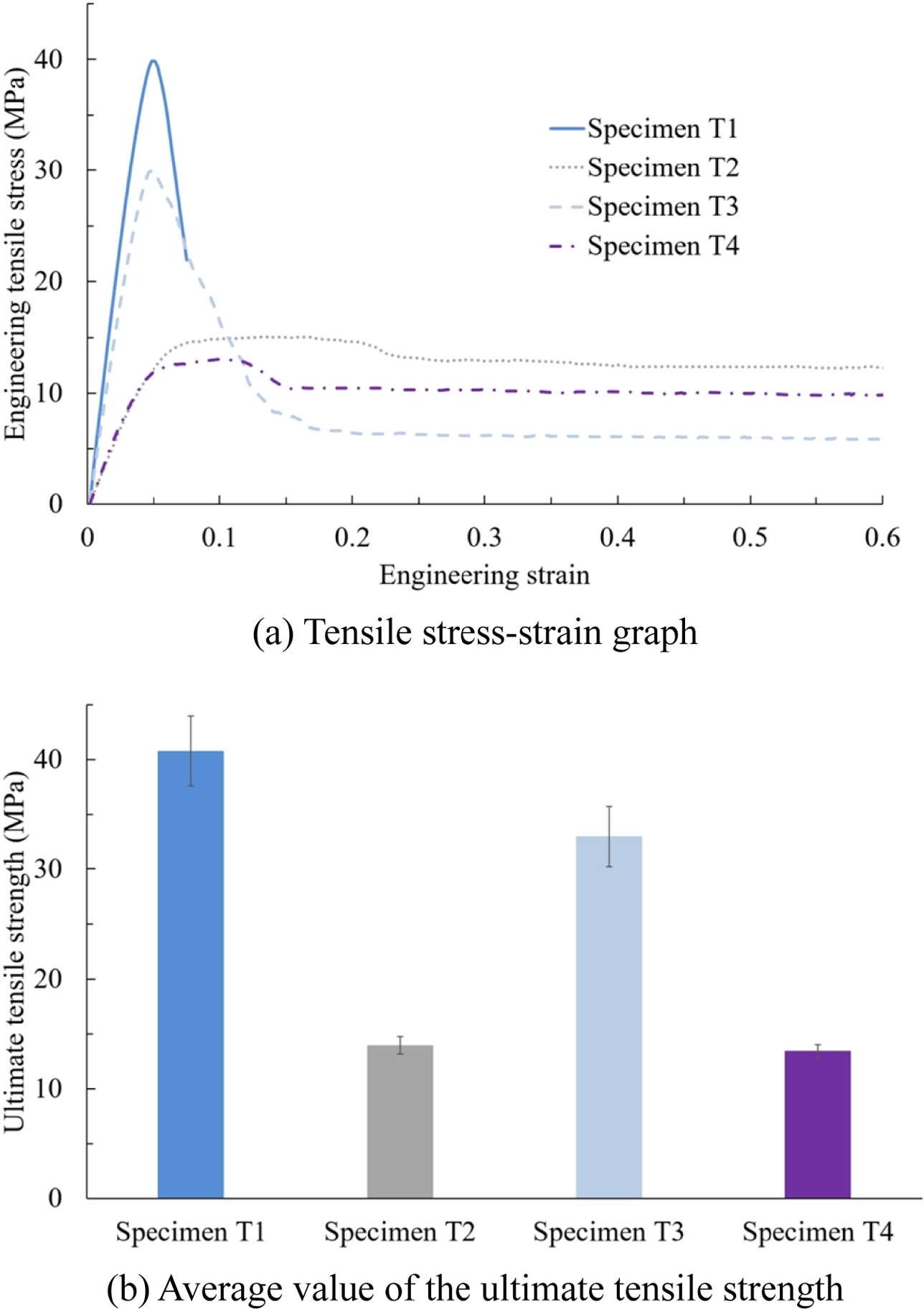
각 시험 시편별 최대 인장 강도의 3회 평균값과 표준편차는
Fig. 6(b)와 같이 얻어질 수 있었다. 시편 T1의 최대 인장 강도 평균값은 40.80 MPa로 측정되었으며 표준편차는 3.16이다. 시편 T2의 최대 인장 강도 평균값은 13.99 MPa로 측정되었으며 표준편차는 0.80이다. 이종 소재를 동시 출력한 시편 T3의 경우에는 시편 T1과 T2의 최대 인장 강도의 중간 값인 27.40MPa보다 높은 32.97 MPa로 나타났다. 반면, 두 소재를 격층 출력한 시편 T4의 경우에는 최대 인장 강도가 13.45 MPa로 시편 T2와 거의 유사하나 조금 낮게 측정되었다.
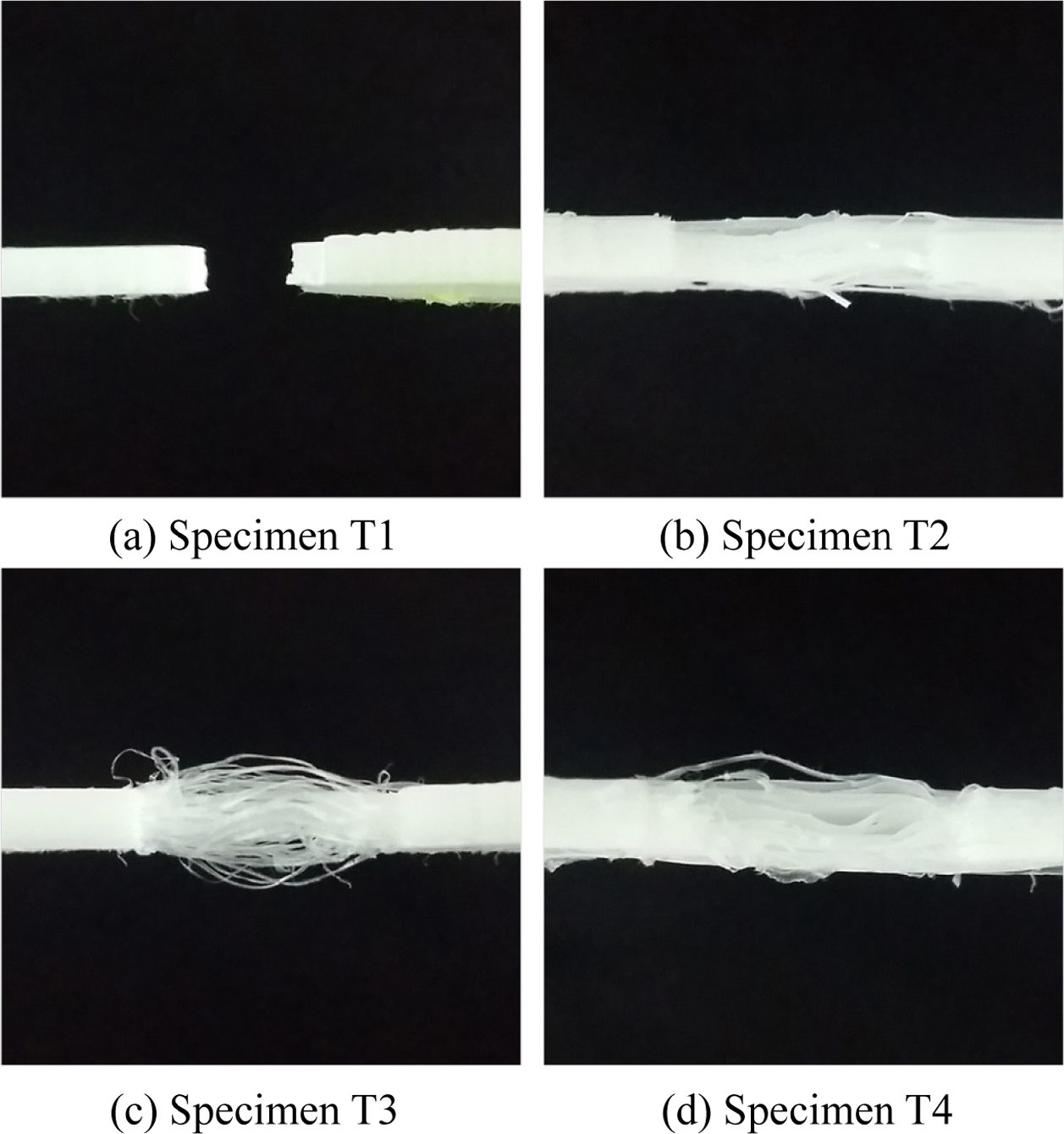
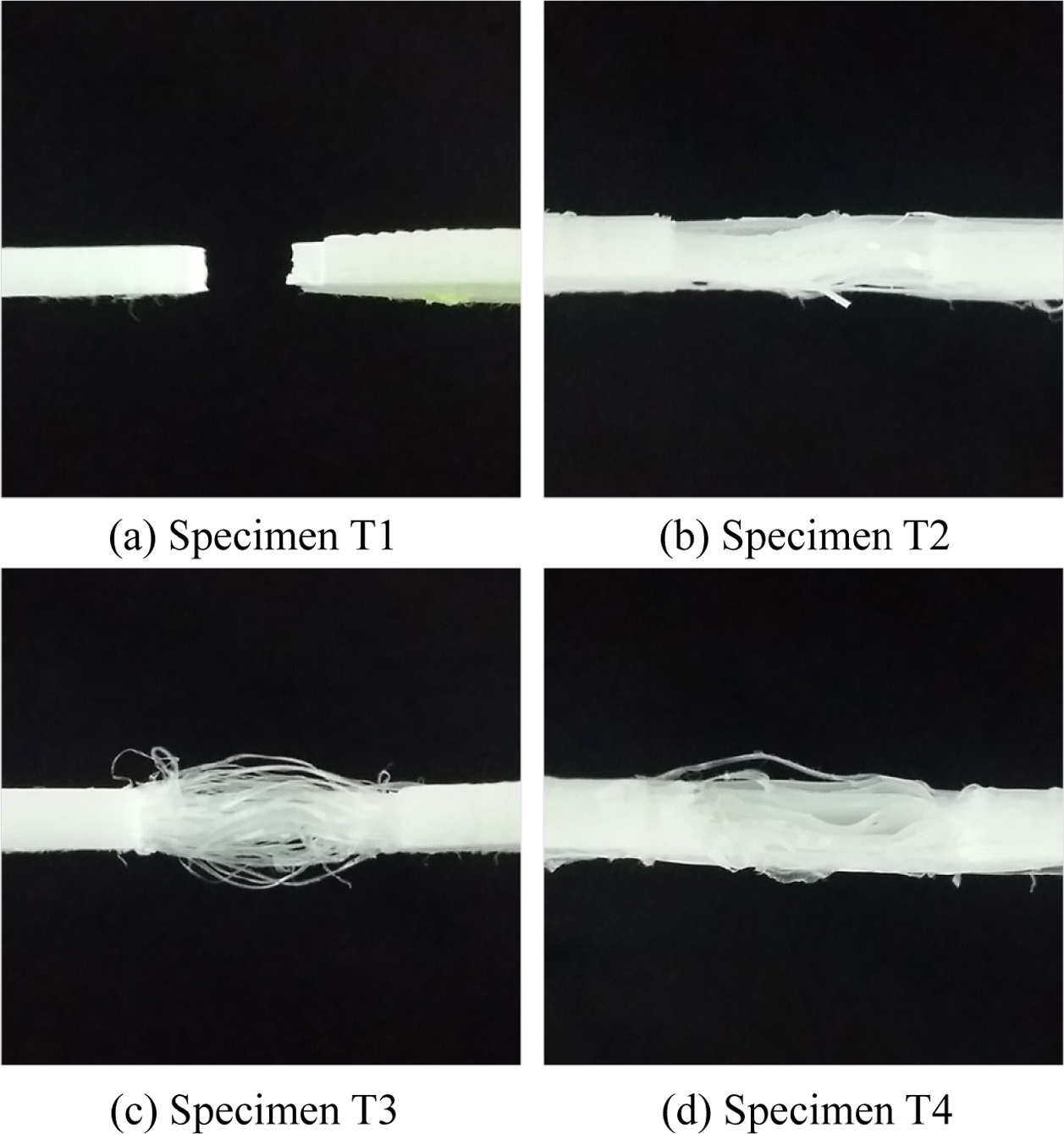
Fig. 7은 각 시험 시편의 인장 시험 후 사진이다. 앞선 실험 결과에서 알 수 있듯이 시편 T1의 경우에만 완전 파단이 발생하였으며 나머지 시편은 모두 파단되지 못하였다. 시편 T2의 경우에는 극히 일부 출력층에서 파단 및 층간 박리가 관찰되었으나 전체적으로는 각 출력층이 시험 후에도 접합된 상태를 유지하면서 변형이 발생하였음을 볼 수 있다. 시편 T3의 경우에는 사진에서 볼 수 있듯이 여러 개의 가느다란 실타래 가닥들이 파단되지 않고 남아있음을 볼 수 있었다. 즉, A 소재와 B 소재가동시 출력되었지만 소재 간에 완벽히 용융 혼합된 것이 아니라 동시 용융되면서 하나의 다발처럼 뭉쳐져 있었음을 알 수 있다. 그 결과 앞선 인장 시험에서 볼 수 있듯이 시편 T1과 유사한 변형 시점에서 A 소재 부분만 파단이 발생하게 되었으며 그 이후 급격히 인장력이 감소하는 결과가 발생한 것이다. 그 이후 서로 독립적으로 존재하는 얇은 실타래의 B 소재에 의해 낮은 인장 응력 값으로 수렴하게 되었다. 반면 이종 소재를 격층 출력한 시편 T4의 경우에는 격층으로 존재하는 A 소재 부분만 파단이 일어나면서 B 소재 부분이 얇은 판재 형태로 남아있음을 볼 수 있다. 즉, 이종 소재가 층간에 번갈아 가면서 적층되어 있으므로 소재 간 상호 접합력이 매우 낮아 하나의 인장 시편이 아니라 상호 구속되지 않은 얇은 다층 박판의 인장인 경우로 볼 수 있다. 이로 인해, 인장 시험 시 적층면 간의 상호 구속력 부재로 쉽게 슬립이 발생하여 얇은 다층 박판의 A 소재 부분이 낮은 하중 영역에서 불규칙하게 쉽게 파단이 발생한 것이다.
Fig. 7Photograph of the specimen after tensile test
3.3 굽힘 시험
앞선 인장 시험 결과를 고려해보면 출력 형태에 따라 이종 소재의 접합력이 다를 것으로 예상되었다. 이에 이종 소재 간접합력 및 연성을 정량적으로 테스트하기 위하여 ASTM 시험법에 근거한 굽힘 시험을 진행하였다. 자체 제작한 굽힘 시험기의 로드셀에서 굽힘 시 가해지는 하중 값을 얻을 수 있으므로 이를 각 시편의 상대 비교가 용이한 굽힘 응력으로 변환하여 표기하기 위해 아래
식(2)를 사용하였다.
14
여기에서
σf는 시험점에서의 굽힘 응력을 의미하며,
P는 하중-변형 곡선상의 임의의 지점에서의 하중을 의미한다.
L은 굽힘 시편의 지지 간격이므로 사용된 시험기의 규격인 51.2 mm를 적용하였고, 시편의 폭
b와 시편의 두께
d는 매번 개별 측정하여 사용하였다. 각 시편의 굽힘 시험 결과
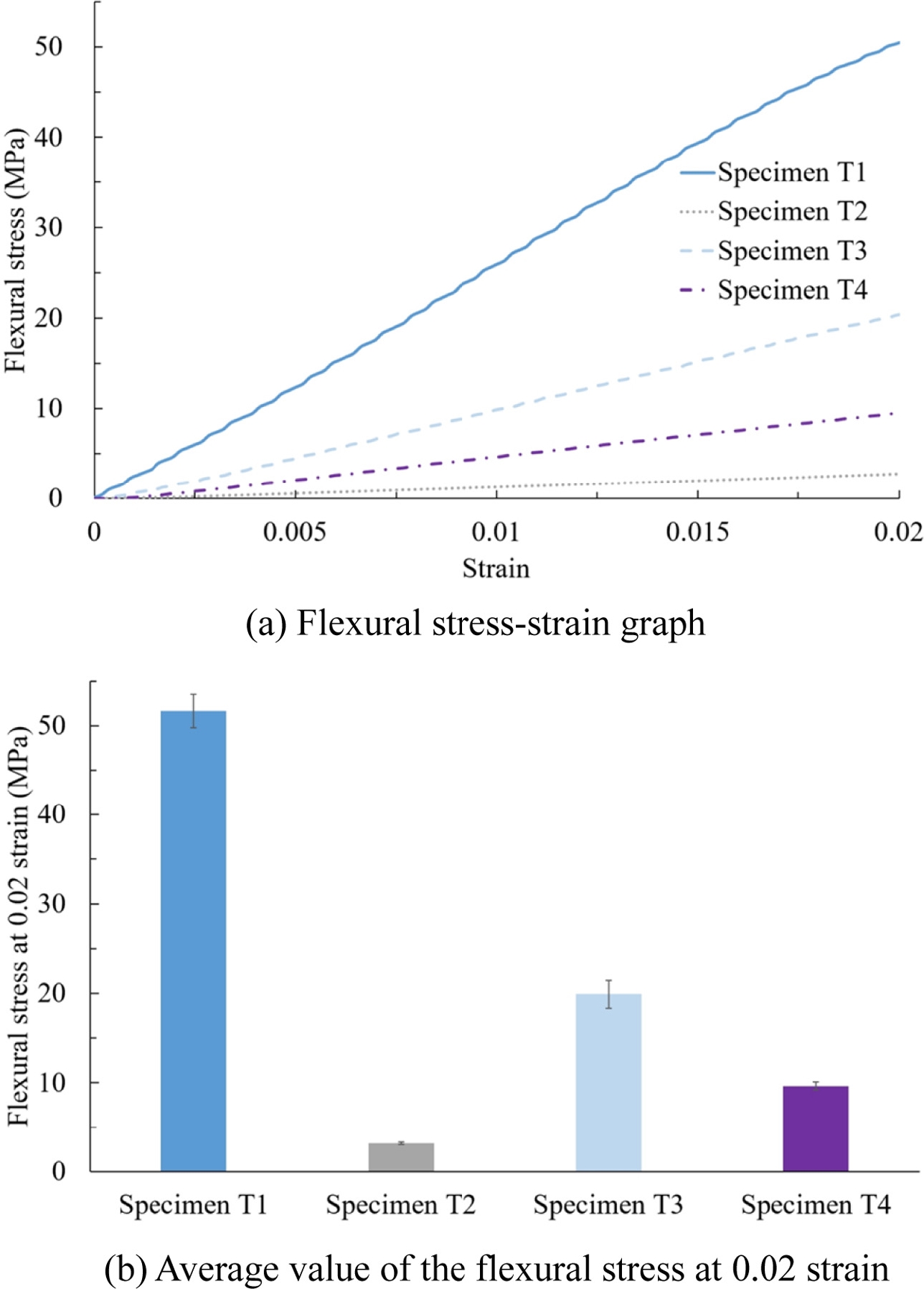
Fig. 8(a)에 보인 바와 같이 변형률 0.02 수준에서는 모든 시편에서 파단이 발생하지 않았으며 변형률과 굽힘 응력이 선형적으로 비례하는 탄성 영역에서 시험이 이루어졌음을 볼 수 있다. 앞선 인장 시험과 동일하게 각 시험 시편 종류별로 3개의 시편을 제작하여 변형률 0.02 지점에서의 굽힘 응력 평균값과 표준편차를 측정하면
Fig. 8(b)와 같다.
Fig. 8Results of the flexural test

A 소재 단독으로 출력한 시편 T1의 0.02 변형률에서의 굽힘 응력 평균값은 51.68 MPa이었으며 표준편차는 1.86이다. B 소재 단독으로 출력한 시편 T2의 동일한 지점에서 굽힘 응력 평균값은 3.15MPa로 측정되었으며 표준편차는 0.13이다. 두 소재를 1 : 1 비율로 동시에 출력한 시편 T3는 평균 19.92 MPa의 굽힘 응력을 보였다. 반면 각각의 이종 소재를 격층으로 교차 출력한 시편 T4의 굽힘 응력은 9.62MPa로 시편 T2보다는 높으나 동시 출력한 시편 T3에 비해서는 상대적으로 낮게 측정되었다.
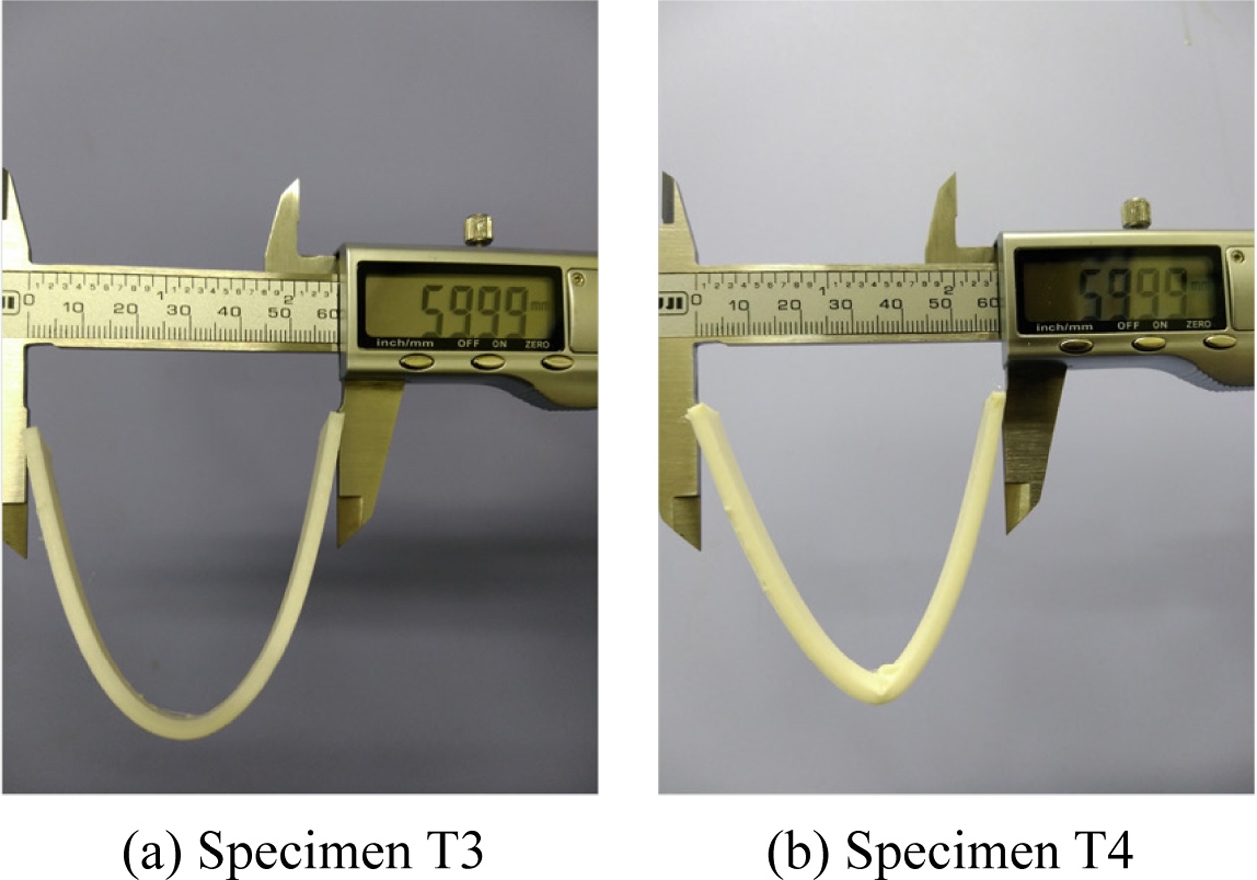
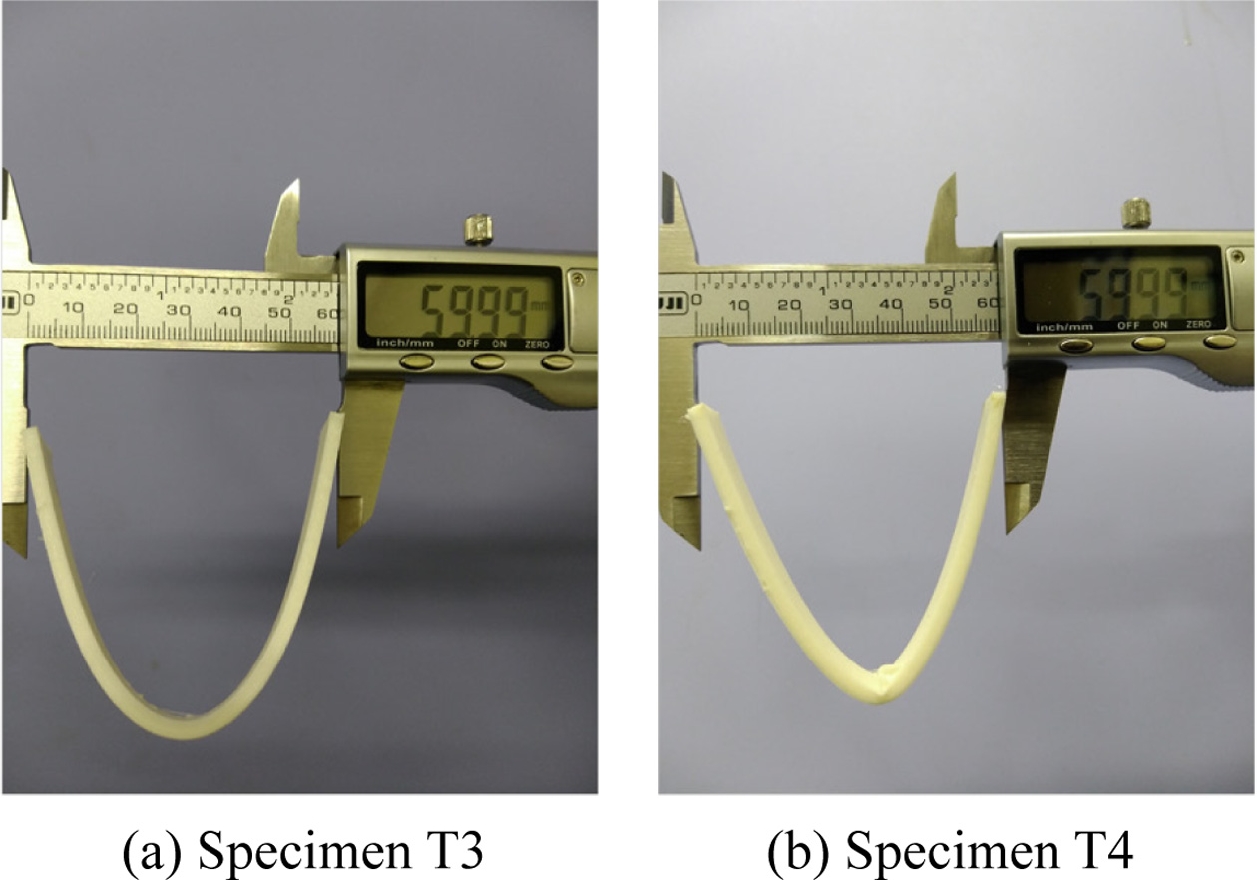
앞서 진행한 굽힘 시험에서 시편 T3와 시편 T4의 강도 차이의 원인을 좀 더 명확히 구분하기 위하여 가운데 부분에서의 변형률이 약 0.4에 도달하는 시점까지 과도 굽힘 변형을 진행하였다. 하지만, 굽힘 시험 장비에서는 지지대 등의 시험 구조물로 인해 일정 이상의 변위에 대한 시험이 불가능하였다. 이에 변형 형상을 2차원 곡선 형태로 가정하면 대략 시편 길이 방향으로 60 mm 지점까지 변형이 발생한 경우가 변형률 0.4에 해당하게 된다. 그러므로,
Fig. 9와 같이 버니어 캘리퍼스를 이용하여 60 mm가 될 때까지 시편을 변형시키는 과도 굽힘을 진행하였다. 그 결과 시편 T3에서는 별다른 특이 현상 없이 굽힘이 이루어졌으며 균일한 2차원 곡선 형태의 굽힘이 발생하였다. 하지만, 격층 출력한 시편 T4에서는 소재 간 접합력 및 기계적 물성 차이에 의해 중앙부에서 박리 현상이 발생하면서
Fig. 9(b)에 보인 것처럼 V형태로 과도하게 꺾인 형상이 관찰되었다.
Fig. 9Results of the excessive bending test
이는 시편 T3의 경우 두 소재를 동시에 녹여서 하나의 노즐로 출력하므로 소재 간 경계면에서 일부 혼합이 이루어진 상태에서 고화가 발생한데다가 서로 물성이 다른 재료 간 교차가 미소 영역에서 발생하여 기계적 물성이 전체적으로는 중간적 성격을 띄게 되었으며 소재 간 접합력도 개선되어 과도한 박리가 관찰되지 않았다. 하지만, 서로 다른 물성과 조성을 지니는 두 소재를 번갈아 가면서 격층으로 출력한 시편 T4의 경우 화학적으로 소재 간 접합력이 매우 낮은데다가 소재 층간에 급격한 물성 변화로 인해 변형이 발생 시 쉽게 층간 박리 현상이 관찰되었다. 즉, 이러한 소재 간 혼합과 물성 변화 차이로 인해 굽힙 시험에서 서로 다른 강도 차이를 보인 것이라 할 수 있다.
3.4 시편 단면 관찰
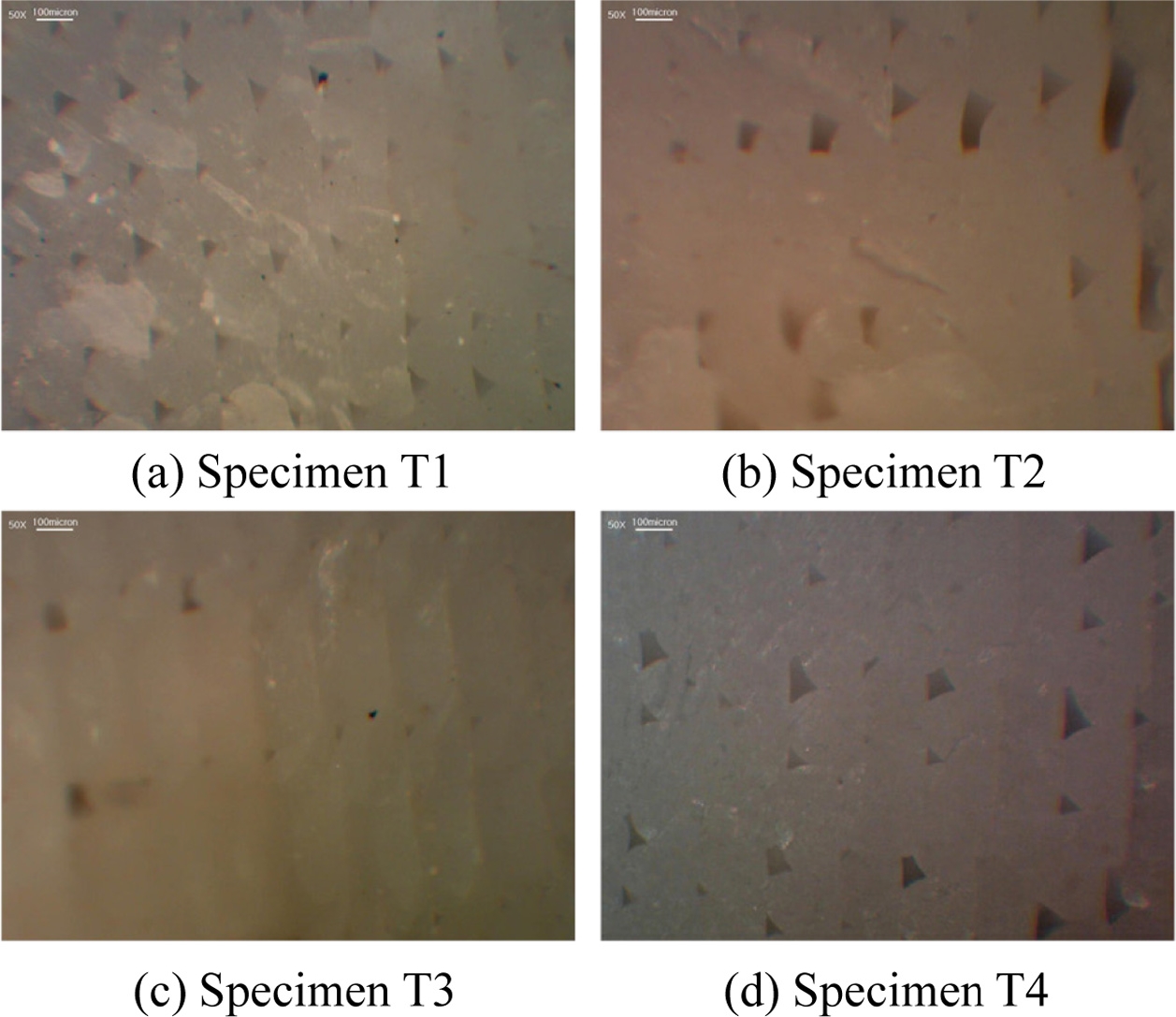
각 출력 시편에 노치를 새긴 후 액화 질소에 담궈 급냉하여 부러뜨린 후 단면을 광학현미경으로 관찰한 모습은
Fig. 10과 같다. 시편 T1의 경우 필라멘트 모습은 반원의 형태로, 상당히 뚜렷하고 일정한 편이다. 시편 T2의 경우 시편 T1에 비해 공극과 적층 형상이 일정하지 않은 모습을 보인다. 이는 ME방식으로 출력 시 노즐이 용융되어 나오는 폴리머 필라멘트를 눌러주면서 출력이 이루어지는데 이때 A 소재에 비해 B 소재의 경우에는 변형이 크게 발생하면서 생기는 현상이다.
Fig. 10Cross section of each specimen
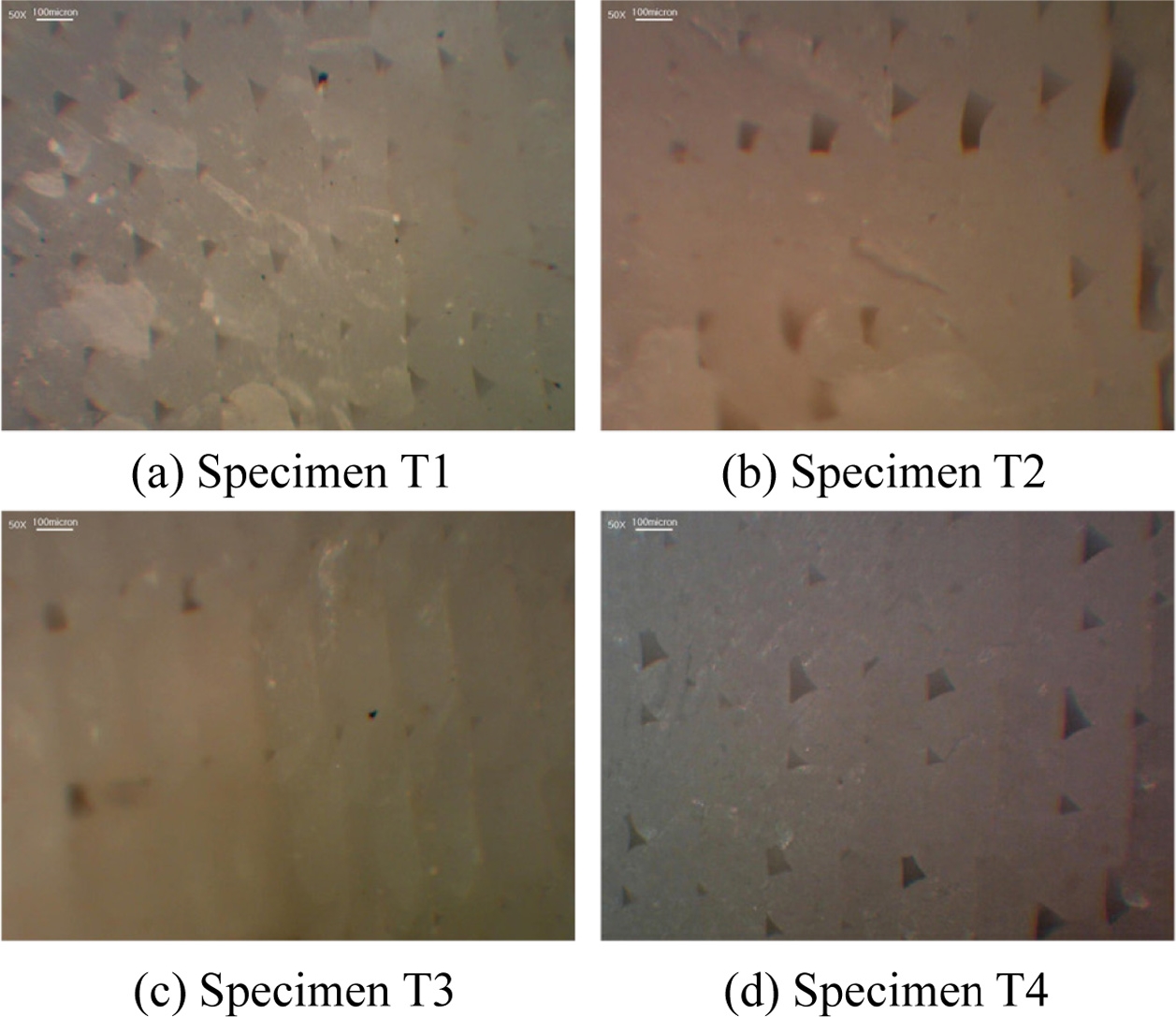
두 소재를 동시 출력한 시편 T3의 경우 한 필라멘트 가닥에서도 두 소재가 서로 감싸고 있는 모습을 볼 수 있다. 즉, 두 소재가 동시 출력되었지만 완전 용융되어서 혼합된 것이 아니므로 두 소재의 경계면이 관찰되나 동시 용융으로 인해 두 소재간 밀착이 비교적 잘 이루어져있으며 균일한 형태로 적층이 되었음을 볼 수 있다. 반면, 두 소재를 격층 출력한 시편의 경우 반원 형태를 가진 A 소재 필라멘트 층과 형태가 뭉개진 B 소재 필라멘트층이 반복되어 적층되어 있는 것이 관찰된다. 즉, 서로 다른 물성을 지닌 필라멘트가 각 층에 번갈아가면서 출력되다보니 각 소재 간 변형량 차이로 인해 매 층간 형상이 다르게 적층된 것이다. 뿐만 아니라, 각 소재의 화학 조성 차이로 인한 소재 간 접합력도 낮으므로 앞선 인장 시험이나 굽힘 시험과 같이 외력에 의한 변형이 발생 시 소재 층간의 박리가 매우 쉽게 발생하게 된 것이다.
4. 결론
본 연구에서는 ME방식 프린터에서 다종 소재의 혼합 출력을 할 수 있는 다이아몬드 핫엔드 노즐을 이용하여 서로 다른 기계적 물성을 지니는 두 소재를 하나의 노즐을 통해서 동시 출력 시 기계적 강도 변화가 가능한지를 확인하였다. 이를 위해 기계적 물성이 크게 다른 이종의 소재에 기반하여 출력 방식을 달리함으로써 각 시편 간 물성 변화를 살펴보았다.
기계적 물성 시험의 가장 기본이 되는 인장 시험에서는 이종 소재를 동시 출력한 시편 T3의 경우 하나의 소재가 항복점에 도달하는 시점에서 최대 인장 강도를 보였으며 이때 강도는 두단일 소재 시편의 최대 인장 강도 중간 값보다 조금 높은 수준을 보였다. 반면 이종 소재를 번갈아가면서 격층 출력한 시편 T4의 경우에는 동시 출력한 시편 T3의 최대 인장 강도 값의 절반에도 미치지 못하는 낮은 강도를 보였다.
출력 방식별 소재 간 접합력 및 시편의 연성을 확인하기 위하여 굽힘 시험도 진행하였다. 모든 시료의 탄성 변형 영역 내에서 실험을 진행하기 위하여 변형률 0.02 수준에 도달했을 때의 굽힘 응력을 상호 비교하였다. 그 결과 이종 소재를 동시 출력한 시편 T3의 굽힘 응력은 두 단일 소재 시편 측정값의 중간값보다 조금 낮지만 근접한 수준을 보였다. 반면 두 소재를 번갈아가면서 격층 출력한 시편 T4의 경우에는 인장 시험에서와 유사하게 동시 출력한 시편 T3의 굽힘 응력의 절반 정도밖에 되지 않는 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 이를 좀 더 명확하게 관찰하기 위하여 변형률 0.4정도 수준으로 과도 굽힘을 진행하였으며 그 결과 출력 방식에 따라 소재 간 접합력 차이가 크게 발생함을 관찰할 수 있었다. 또한 출력된 시료의 단면을 절단하여 관찰한 결과 동시 출력한 시편 T3 경우에는 이종 소재가 잘 어우러져서 출력된 반면 격층 출력한 시편 T4 경우에는 소재 종류에 따라 층간에 적층 형상이 다르게 생성됨으로써 소재 간 접합력 저하 및 불규칙한 층간 강도 변화로 외력에 의한 박리가 쉽게 발생됨을 볼 수 있었다.
앞선 실험 결과로 미루어 볼 때 하나의 노즐에서 서로 다른 화학 조성과 물성을 지니는 이종 소재를 동시 출력하는 것이 완전한 혼합을 통한 중간 물성을 만드는 것은 아니지만 비교적 미소 영역에서 이종 소재가 서로 어우러져 있음으로써 단일 소재의 항복 변형이 발생하는 직전 시점까지는 중간적인 물성에 가까운 특성을 가질 수 있음을 확인하였다. 특히 기존에 흔히 사용되는 다중 노즐을 이용한 소재별 개별 출력 방식에 비해서는 월등히 우수한 소재 간 접합력 및 물성을 가짐을 확인하였다. 이를 통해 기존 저가 ME방식 3D 프린터에서도 간단한 노즐 구조 변경만으로 물성이 다른 소재 간 동시 혼합 출력을 통해 FGM과 같은 물성이 다양하게 변하는 구조를 제작할 수 있을 것으로 판단된다.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
이 연구는 서울과학기술대학교 교내연구비의 지원으로 수행 되었습니다.
REFERENCES
- 1.
Shin, Y. M., “Types and Applications of 3D Printers,” Polymer Science and Technology, Vol. 26, No. 5, PP. 404-409, 2015.
- 2.
Lim, Y. E. and Park, K., “Investigation of Bending Stiffness of Porous Shell Structures Fabricated by 3D Printing,” Transactions of the Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers A, Vol. 41, No. 6, pp. 491-497, 2017.
- 3.
Lee, M. J., “Inkjet Printing Technology Still in Progress,” Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society, Vol. 48, No. 6, pp. 543-548, 2011.
10.4191/kcers.2011.48.6.543
- 4.
Chu, W. S. and An, S. H., “Introduction of Bio Printing Technology,” CDE Review, Vol. 14, No. 1, pp. 5-11, 2008.
- 5.
Ryu, B. H. and Choi, Y. M., “The Role of Functional Materials and Inkjet Printing Technology for Printable Electronics,” Proc. of the Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers Conference, pp. 446-450, 2007.
- 6.
Choi, S. K., “3D Printing Technology and Architectural Application,” Review of Architecture Building Science, Vol. 58, No. 2, pp. 17-25, 2014.
- 7.
Lee, W. H., Han, S. C., and Park, W. T., “Bending, Vibration and Buckling Analysis of Functionally Graded Material Plates,” Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial Cooperation Society, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp. 1043-1049, 2008.
10.5762/KAIS.2008.9.4.1043
- 8.
Kim, H. S. and Kang, I., “Study on Status of Utilizing 3D Printing in Fashion Field,” Journal of the Korea Fashion and Costume Design Association, Vol. 17, No. 2, pp. 125-143, 2015.
- 9.
Kim, T. Y. and Lee, Y. G., “A Method for Optimizing Building Position of Model to Minimize Interference between Nozzles in FDM with Dual-Nozzles,” Korean Journal of Computational Design and Engineering, Vol. 22, No. 1, pp. 37-43, 2017.
10.7315/CDE.2017.037
- 10.
Pascale, D. and Simion, I., “Multi-Material 3D Printer Extruder Concept,” Journal of Industrial Design and Engineering Graphics, Vol. 13, No. 1, pp. 25-28, 2018.
- 11.
Kim, J. Y., Hong, D., and Kwon, O., “Concept Design of Nozzle for 3D Printer Using Color Dot Painting Method,” Proc. of the Spring Conference on Korean Society of Precision Engineering, pp. 909-910, 2016.
- 12.
Noh, K. S., Seo, H. W., Kim, T. Y., and Lee, Y. G., “Development of a G-Code Generator for Color Gradation Generations in a Mixing Chamber FDM 3D Printers,” Korean Journal of Computational Design and Engineering, Vol. 22, No. 1, pp. 10-17, 2017.
10.7315/CDE.2017.010
- 13.
Han, S., Xiao, Y., Qi, T., Li, Z., and Zeng, Q., “Design and Analysis of Fused Deposition Modeling 3D Printer Nozzle for Color Mixing,” Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, Vol. 2017, pp. 1-12, 2017.
10.1155/2017/2095137
- 14.
ASTM D790-17, “Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials,” 2017.
- 15.
ASTM D638-14, “Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics,” 2014.
- 16.
Kang, Y. G., Kweon, H. K., and Shin, G. S., “Strength Variation with Inter-Layer Fill Factor of FDM 3D Printer,” Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers, Vol. 18, No. 3, pp. 66-73, 2019.
10.14775/ksmpe.2019.18.3.066
Biography
- Sohyang Lee
M.Sc. candidate in the Graduate School of Nano IT Design Fusion, Seoul National University of Science & Technology. Her research interest is UX design and HCI.
- Chaeeun Shin
Bachelor in the Department of Mechanical System Design Engineering, Seoul National University of Science & Technology. Her research interest is mechanical design.
- Minji Jung
Bachelor in the Department of Mechanical System Design Engineering, Seoul National University of Science & Technology. Her research interest is mechanical design and reverse engineering.
- MinSoo Park
Professor in the Graduate School of Nano IT Design Fusion, Seoul National University of Science & Technology. His research interests are metal / ceramic 3D printing, laser processing and micro machining.