ABSTRACT
The controller for the power assist robot that is in constant contact with the user requires to be sensitively controlled as per the user's intention and maintain control stability to ensure the user's safety. Admittance control is generally used for human intention-based force control. By setting the parameters of the admittance control at a low level it is possible to sensitively control according to the user's intention. However, too sensitive settings make the system unstable. Therefore, it is difficult to set a fixed admittance parameter in a power assist robot in which dynamics change with an increase in load mass. Consequently, we propose a variable admittance control strategy according to the load mass. The proposed method responds sensitively to the user's intention by setting the admittance parameters at low during no-load action and ensures stability by setting the admittance parameter high when transmitting high loads. In simulation with a carrying load of 30 kg, the proposed method requires half the interaction force compared with a fixed admittance control when decelerating and has twice faster settling time when stopped. In addition, through experimental verifications, the variable admittance control was proven to reduce the user's load by 70% compared to load mass.
-
KEYWORDS: Admittance control, Power assist robot, Wearable robot, Human robot interaction
-
KEYWORDS: 어드미턴스 제어기, 힘 증강 로봇, 착용형 로봇, 인간-로봇 상호 작용
NOMENCLATURE
Desired Mass of Admittance Control
Desired Damper of Admittance Control
Desired Stiffness of Admittance Control
Current End-Effector Position of Robot
1. 서론
오늘날 의료기술의 발달과 산업 환경 패러다임의 변화로 고령자 혹은 신체적 약자를 포함한 고용 안정성과 산업 근로자의 장기 근로에 따른 산업재해 문제가 주요 이슈가 되고 있다.
1 따라서 자연스럽게 이들을 대상으로 작업을 지원하고 산업재해를 예방하기 위한 착용형 힘 증강 로봇이 다양한 산업 현장에서 기대되고 있다.
2 착용형 힘 증강 로봇에는 두 가지 제어 목표가 있다. 첫 번째는 무거운 물체를 다루기 위해 근력을 지원하는 것이다.
3 이를 위해 힘 증강 로봇은 높은 기어비의 역구동성이 낮은 시스템으로 설계된다.
3,4 두 번째로 힘 증강 로봇은 사용자의 동작 의도에 순응하여 안정적이며 민감하게 제어되어야 한다. 이를 위해 힘 증강 로봇과 같이 역구동성이 낮은 시스템에서는 어드미턴스 제어 방법이 일반적으로 사용되고 있다.
5-7
어드미턴스 제어기는 매니퓰레이터의 비선형 동역학을 선형화시키기 위하여 말단을 가상의 질량-댐퍼를 갖는 시스템으로 모델링한다. 일반적으로 착용형 로봇에서는 질량-댐퍼와 같은 어드미턴스 파라미터를 고정된 비율로 낮게 설정하여 사용자와 민감하게 상호 작용하도록 구성된다.
8 하지만 어드미턴스 파라미터가 낮게 설정될 경우 외부 환경 변화에 쉽게 불안정해지는 단점을 가지게 된다. 힘 증강 로봇은 부하 무게에 의해 전체 시스템의 물성 정보가 변하는 특성을 갖는다. 따라서 무부하 상태를 기준으로 민감하게 설정된 어드미턴스 제어기가 무거운 물체를 핸들링할 때에도 제어 안정성을 유지하는 것은 기대하기 어렵다. 시스템의 물성 변화에도 안정성을 유지하기 위해서는 어드미턴스 파라미터가 높게 설정되어야 하지만 이는 사용자에게 높은 상호 작용력을 요구하는 단점을 갖게 된다.
이와 같이 어드미턴스 파라미터 설정은 민감도와 안정성 사이에 상충 관계를 가지므로 다양한 운영 환경을 만족하는 고정된 어드미턴스 파라미터를 설정하는 것에는 어려움이 존재한다. 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 운영 환경에 따라 어드미턴스 파라미터를 조절하는 가변 어드미턴스 제어기가 연구되어왔다.
9,10 Laval 대학의 Alexandre Lecours는 사용자 동작 의도에 민감하게 중량 물체를 이송하기 위하여 사용자의 가감속 의도 추론 기반 가변 어드미턴스 제어기를 제안하였다.
11 이 연구에서 제안된 제어기의 성능을 보이기 위해 고정된 베이스를 갖는 3축 리니어 로봇이 이용되었다. 이 로봇의
x축 자중은 500 kg이고, 탑재 가능한 물체의 질량은 최대 113 kg으로 자중 대비 약 0.22배에 해당하는 상대적으로 가벼운 물체를 이송한다. 이처럼 이전의 가변 어드미턴스 제어 연구들은 탑재된 물체의 무게가 전체 로봇 물성에 미치는 영향이 미비하기 때문에 부하 무게에 따른 제어 성능을 고려하지 않았다. 하지만 착용형 로봇의 경우 시스템의 자중이 곧 사용자에게 가해지는 부담이 되기 때문에 가능한 가볍게 제작하는 것을 목표로 하는 반면 로봇이 지원하는 힘 성능은 높기를 기대한다. 따라서 착용형 힘 증강 로봇의 제어기는 부하 무게에 따른 시스템의 물성 변화로 인한 제어 불안정성에 대해 노출되어 있다.
이에 본 연구에서는 무부하 운동 시 사용자의 동작 의도에 민감하면서도 부하 무게 증가에 강인한 제어 방법을 구성하기 위하여 부하 무게에 따른 가변 어드미턴스 제어기법을 제안한다. 이를 위해 본 논문의 2장에서는 1자유도 모델을 이용하여 부하 무게에 따른 어드미턴스 제어기의 안전성 변화를 분석하고, 이를 기반으로 한 가변 어드미턴스 제어기법을 제안한다. 3장에서 제안 제어기의 성능 평가를 하기 위해 자중 대비 약 4배 무거운 물체를 이송하도록 설계된 착용형 힘 증강 로봇을 소개하고 제안된 제어 방법을 적용한다. 4장과 5장에서는 시뮬레이션 및 실험 검증을 수행한다. 마지막으로 6장에서는 본 연구의 결론을 정리하고 추후 연구 방향을 논의한다.
2. 가변 어드미턴스 제어 전략
2.1 어드미턴스 모델
어드미턴스 제어 모델은 매니퓰레이터가 외부 환경과 접촉이 발생하기 전 그리고 후로 나누어 로봇의 상태를 자유 공간에서의 제어 상태와 접촉 공간에서의 제어 상태로 정의하게 된다. 그리고 각 상태에 따라 제어기법을 서로 다르게 하는 것이 일반적이다.
12 로봇의 목표 궤적이 존재하고 말단에서 힘 피드백을 받아 조립 공정을 수행하는 공장형 로봇은
식(1)과 같이 자유 공간에서의 어드미턴스 모델이 적용된다.
x는 매니퓰레이터의 말단 위치를 의미하고,
x0는 목표 위치를 의미한다. 그리고
md, dd, kd는 어드미턴스 파라미터들로 각각 목표 무게, 댐퍼 그리고 강성을 의미한다.
fext는 로봇 말단에 인가되는 모든 힘으로
식(2)와 같이 상호 작용 힘
fh와 목표 힘
f0로 구성된다. 착용형 로봇에서는 사용자의 손과 매니퓰레이터의 말단이 항상 접촉 상태에 있기 때문에
식(3)과 같이 로봇의 목표 궤적
x0, 속도
x˙0, 가속도
x¨0그리고
kd를 0으로 하는 접촉 공간에서의 어드미턴스 제어 환경이 만들어진다.
8 그리고 힘 증강 로봇에서는 사용자 부담을 최소화하기 위해 목표 힘
f0는 0 N으로 설정된다.
2.2 어드미턴스 제어기의 선형 모델 기반 안전성 분석
어드미턴스 제어기의 안정성 평가는 일반적으로 선형 다이나믹스로 구성된 1자유도 모델을 기반으로 진행된다.
7,8,13 하지만 이와 같은 1자유도 모델 기반은 모델링의 불확실성 및 비선형성에 대한 고려가 부족하기 때문에 본 논문에서는 인간-로봇 시스템의 주파수 응답에 대한 정성적 평가를 위해서만 사용된다.
13
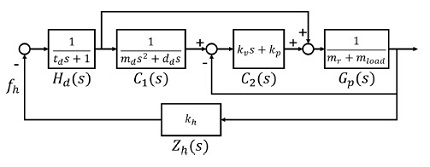
Fig. 1은 어드미턴스 제어기의 안정성 평가를 위한 블록선도이다.
식(3)을 기반으로 구성된 어드미턴스 모델
C1은
식(4)와 같이 외부 힘에 대한 말단 위치
xref를 결정한다. 그리고 폐루프 위치 제어기
C2를 통하여 이를 추종한다. 이 내부 위치 제어기는
식(5)와 같이 비례 게인
kp와 미분 게인
kv를 갖는 비례-미분 제어기로 구성되어
xref를 추종하기 위한 힘
fout을 출력한다.
Fig. 1Block diagram of admittance control for stability analysis
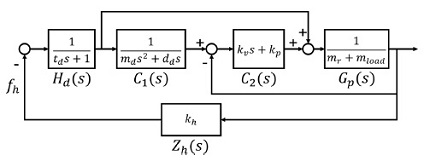
안정성 분석을 위한 단순화된 1자유도 모델
Gp는
식(6)과 같이 로봇의 무게
mr과 부하물의 무게
mload를 포함한다. 사용자 임피던스
Z는
식(7)과 같이 스프링 모델
kh로 구성되었다. 그리고 시간 지연 함수
Hd는
식(8)과 같이 전체 시스템을
td만큼 선형 1차 지연시킨다.
식(4)에서
식(8)을 따라 인가된 외부 힘에 대한 어드미턴스 제어기의 전달함수
Cadm은
식(9)와 같다.
1자유도 모델에서 어드미턴스 제어기의 안정성을 분석하기 위해 mr은 1 kg 그리고 td는 1 ms로 설정하였다. md와 dd는 각각 1 kg과 15 Ns/m로 설정하였다. 그리고 내부 위치 제어기의 kp와 kv는 임계 감쇠 조건을 만족하도록 각각 100 N/m와 20 N/s로 설정되었다. 또한, 부하 무게에 따른 어드미턴스 제어기의 특성을 보이기 위해 mload는 0에서 4 kg의 서로 다른 무게를 갖도록 구성하고 비교 평가하였다.
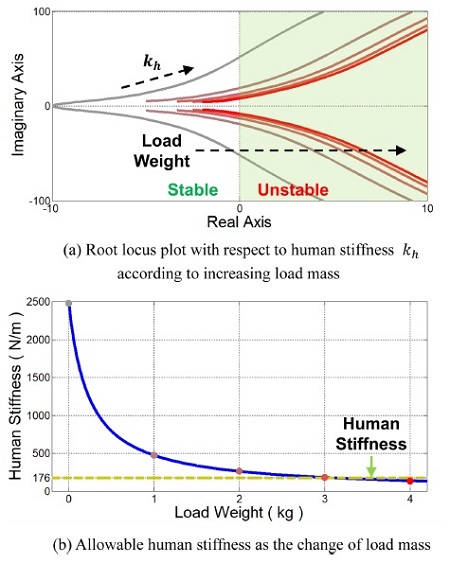
Fig. 2(a)는
식(9)로부터 구해진 사용자 강성 증가에 따른 근궤적 선도이고,
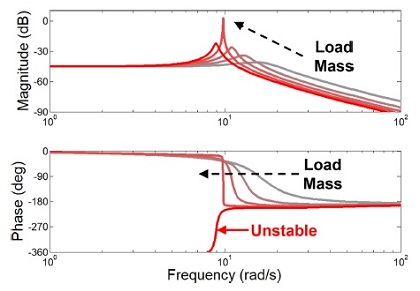
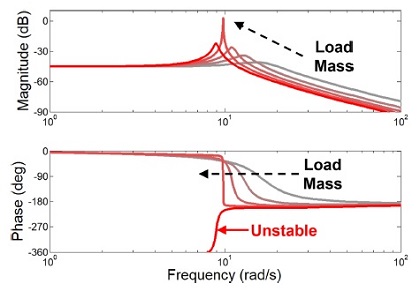
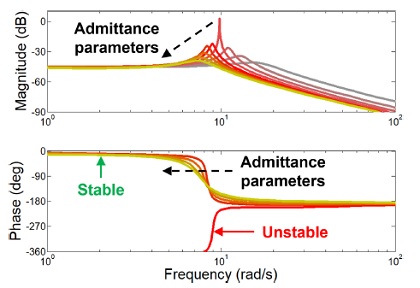
Fig. 3은 보드 선도이다. 두 그래프에서 회색에서 빨간색까지의 각 선은 0에서 4 kg의 서로 다른 부하 무게를 갖는 어드미턴스 모델의 제어 특성을 표현한다. 이를 통해 어드미턴스 제어기는 사용자의 강성과 부하 무게가 증가할수록 불안정해짐을 알 수 있다.
Fig. 2(b)의 파란선은 부하 무게에 따른 각각의 근궤적 선이 실수축과 맞닿아 한계 안정(Marginally Stable)할 때의 강성을 표현한 것이다.
Fig. 2(b)의 초록 점선은 실험적으로 측정된 사람 상지의 강성 평균값으로서 176.39 N/m 의 값을 갖는다.
14 이를 통해 부하 무게가 증가할수록 허용 가능한 사용자의 동작 의도가 점점 줄어들고, 부하 무게가 3 kg을 초과하면 사용자의 작은 동작 의도에도 시스템이 불안정해짐을 알 수 있다.
Fig. 2Stability analysis of the admittance controller
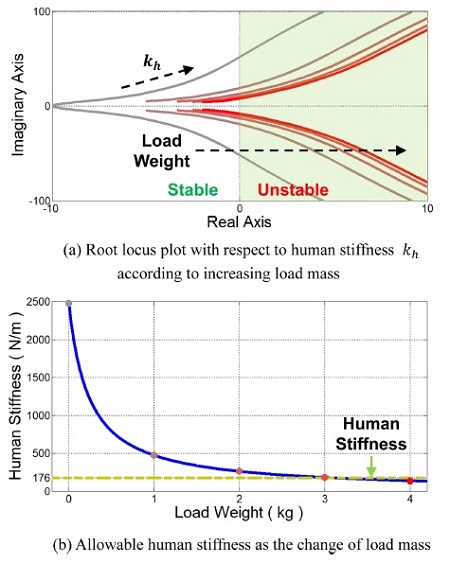
Fig. 3Frequency response plot of the admittance controller with fixed control parameters when the load mass increases
2.3 부하 무게에 따른 가변 어드미턴스 제어 전략
시스템의 불안정을 야기하는 다양한 운용 환경에 대응하기 위하여 어드미턴스 파라미터를 조절하는 제어기법들은 다양한 방식으로 연구되어왔다. 일반적으로 불안정 상태의 시스템을 안정화하기 위하여 목표 무게
md를 고정시키고, 목표 댐퍼
dd를 증가시켜 과도 감쇠(Overdamped)를 유도하는 가변 어드미턴스 제어기법이 사용되어왔다.
15,16 하지만 이와 같이 댐퍼만 조절하는 것은 진폭의 크기는 줄일 수 있더라도 진동 주파수는 낮출 수 없는 성능 한계를 갖게 된다. 사용자와 로봇이 상시 접촉 상태에 있는 착용형 로봇에서는 사용자에게 의도하지 않은 고진동으로 인한 불안감을 유발시킬 수 있다.
5 이를 해결하기 위하여
md와
dd를 고정된 비율로 증가시키는 가변 어드미턴스 제어 기법이 제안되었다.
8 제안된 제어기에서는 진동 주파수 및 진폭 모두를 효과적으로 낮추어 사용자가 느낄 불안감을 예방할 수 있었다.
md와
dd가 고정된 비율을 갖고 증가하였을 때 어드미턴스 제어기의 특성은
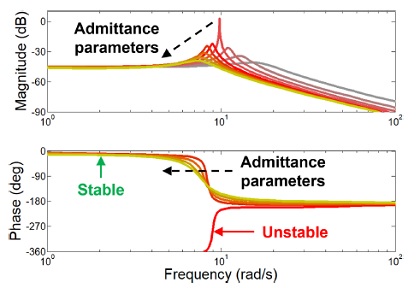
Fig. 4의 보드 선도와 같다.
Fig. 4의 보드 선도를 구하기 위한 파라미터 및 게인들은
Fig. 3에서의 설정과 동일하며 부하 무게
mload는 3 kg으로 고정되게 설정되었다. 따라서 부하 무게가 3 kg일 때 시스템이 불안정하였던
Fig. 3의 붉은 선과
Fig. 4의 붉은 선은 동일하다.
Fig. 4의 보드 선도를 통해 불안정하였었던 제어기가 어드미턴스 파라미터를 고정된 비율로 증가함으로서 초록선과 같이 진동주파수 및 진폭을 감소시켜 안정화됨이 확인된다.
Fig. 4Frequency response plot of the admittance controller when the desired mass and damper increase at a fixed rate with 3 kg of the load mass
본 논문에서는 안정성 분석을 통해 구해진 어드미턴스 제어기 특성을 활용하여 부하 무게에 강인한 착용형 힘 증강 로봇의 제어를 위해
식(10) 그리고
식(11)과 같이 목표 무게 및 댐퍼를 고정된 비율로 조절하는 가변 어드미턴스 제어기법을 제안한다.
md,0와 dd,0는 md와 dd의 초기값으로 무부하 상태에서 사용자 동작 의도에 순응한 제어를 하기 위하여 민감하게 설정된다. α는 부하 무게에 따라 어드미턴스 파라미터의 변화율을 조절하기 위한 가중치 변수이다. 이를 통해 제안된 가변 어드미턴스 제어기의 파라미터 md와 dd는 고정된 비율을 가지고 무부하 상태에서는 민감하게 그리고 부하 무게가 증가할수록 둔감하게 설정된다.
3. 착용형 힘 증강 로봇
이전 장에서 제안된 부하 무게에 따른 가변 어드미턴스 제어기의 성능을 검증하기 위하여
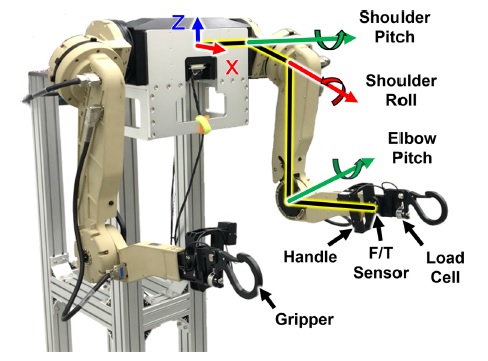
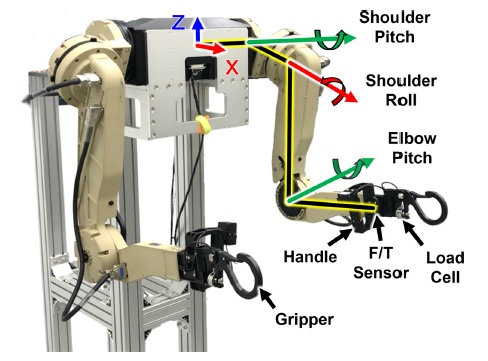
Fig. 5와 같은 착용형 로봇을 구성하였다. 착용형 로봇의 각 팔은 3자유도 구성되었으며 약 7.5 kg의 자중을 갖는다. 또한 사용자의 동작 의도를 반영하기 위한 ATI의 Mini45 F/T 센서와 부하물의 무게를 측정하기 위한 봉신의 CDFSC 로드셀이 포함되어 있다. 제어 주기는 1 ms로 설정되었다.
Fig. 5 Power assist robot for the verification
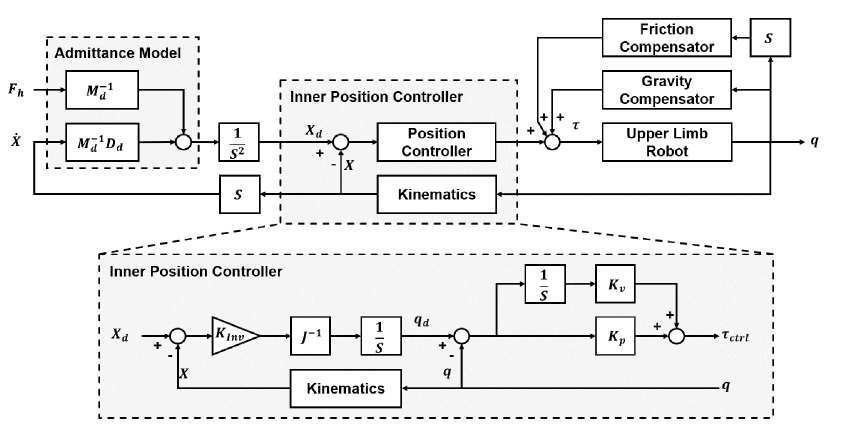
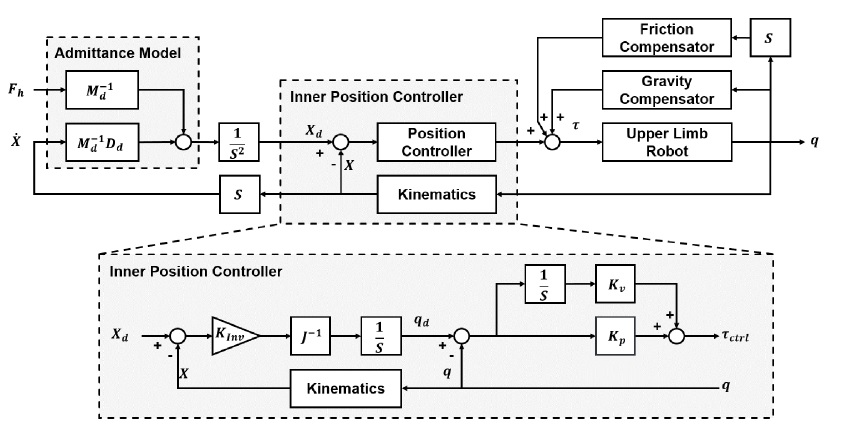
3자유도를 갖는 착용형 로봇의 각 팔을 제어하기 위한 제어기의 블록선도는
Fig. 6과 같다. 제안된 제어기는 어드미턴스 모델, 내부 위치 제어기, 중력 보상기 그리고 마찰 보상기로 구성된다. 3자유도 로봇 팔의 어드미턴스 모델은
식(3)을 기반으로
식(12) 그리고
식(13)과 같이 구성된다.
X와
Xd는 각각 착용형 로봇 팔의 말단 위치와 사용자 동작 의도로부터 생성된 목표 위치로 3 × 1 행렬이다.
Md와
Dd는 각각 목표 무게와 댐퍼로 3 × 3 대각 행렬이다. 그리고 상호 작용 힘
Fh는 3 × 1 행렬로 구성된다.
내부 위치 제어기는 어드미턴스 모델을 통해 구해진 목표 위치
Xd를 추종하기 위한 직교 좌표 공간에서의 위치 제어기와 낮은 역구동성을 갖는 착용형 로봇의 마찰을 극복하고 목표 위치를 추종하기 위한 관절 공간에서의 위치 제어기로 구성된다. 직교 좌표 공간에서의 위치 제어기는
식(14)와 같이 로봇 관절의 선속도와 말단 장치의 선속도 사이의 상관관계인 자코비안 행렬
J를 기반으로
식(15)와 같이 추종 오차에 비례하는 피드백 제어기로 구성된다. 그리고 로봇은
J -1(q)가 특이점에 도달하지 않는 범위 내에서만 구동한다.
Kinv는 역기구학의 비례 게인으로 수렴 속도를 결정한다.
그리고 qd를 추종하기 위한 관절 공간에서의 위치 제어기는 비례-미분 제어기로 구성되어 토크를 출력한다. Kp와 Kv는 각각 비례, 미분 게인이다.
중력 보상기는 로봇 팔의 자중뿐만 아니라 로드셀을 통해 측정된 부하 무게 역시 보상한다. 그리고 마찰 보상기는 높은 기어비를 갖는 각 관절의 마찰을 보상한다.
4. 시뮬레이션 검증
4.1 시뮬레이션 환경 구성
본 장에서는 부하 무게 증가에 따른 가변 어드미턴스 제어기의 성능을 시뮬레이션을 통해 먼저 검증한다. MATLAB Simulink를 기반으로 구성된 시뮬레이터에서는 로봇 모델을 1 ms의 제어 주기로 시뮬레이션하게 된다. 제안된 제어기의 순수한 성능을 검증하기 위해 중력 보상기는 물성 오차 없이 로봇 및 부하 무게를 보상한다.
Fig. 6Block diagram of the proposed admittance controller for the power assist robot
제어 파라미터들은 30 kg의 고중량 물체를 이송하기 위해 높은 기어비와 낮은 역구동성을 갖는 시스템 환경을 고려하여 관절 마찰을 극복하도록 설정되어야 한다. 이에 관절 공간에서의 위치 제어 게인 kp와 kv는 각각 10,000 N/m와 200 Ns/m로 강인하면서도 임계 감쇠하도록 설정되었다. 또한 역기구학의 비례게인 kinv 역시 20,000 N/m로 충분히 강인하게 설정되었다. 어드미턴스 파라미터의 초기값은 단계적으로 구성된 위치 제어기들로 인해 둔감해진 시스템의 응답성을 높이기 위하여 Md,0는 0.0001 kg으로 민감하게 설정되었으며 Dd,0는 안정성 확보를 위하여 상대적으로 높은 0.5 Ns/m로 설정되었다.
시뮬레이션 환경에서 가상의 사용자 힘을 생성하기 위한 사람의 임피던스 모델은
식(16)과 같다.
Xh는 3 × 1 행렬로 가상의 사람 손 위치를 의미한다.
Mh,
Dh 그리고
Kh는 사람 상지의 무게, 댐퍼 그리고 강성을 의미하는 3 × 3 대각 행렬이다.
Mh,
Dh 그리고
Kh의 각 요소들은 실험적으로 측정된 사람 임피던스를 기반으로 각각 1.27 kg, 12.02 Ns/m 그리고 176.39 N/m로 설정되었다.
14
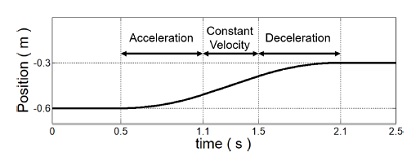
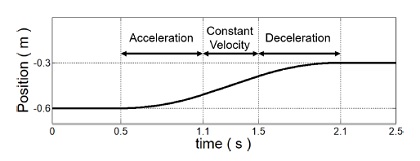
시뮬레이션에서 가상의 사람 손 위치는 사용자가 부하물을 들어올림을 모사하여
Fig. 7과 같이 Z축으로 0.3m 이동한다. 목표 이동 속도는 실험적으로 측정된 사람 상지의 포인트 투 포인트 이동에 대한 최대 속도를 참고하여 0.3 m/s로 설정되었다.
17 목표 이동 속도를 도달하기 위한 가감 속도는 0.5 m/s
2으로 설정하였다.
Fig. 7Virtual human trajectory along the z-axis for simulation verification
4.2 시뮬레이션 결과
Fig. 7과 같은 사용자 궤적이 주어졌을 때
Md,0와
Dd,0로 고정된 어드미턴스 파라미터를 갖는 제어기의 시뮬레이션 결과는
Fig. 8과 같다.
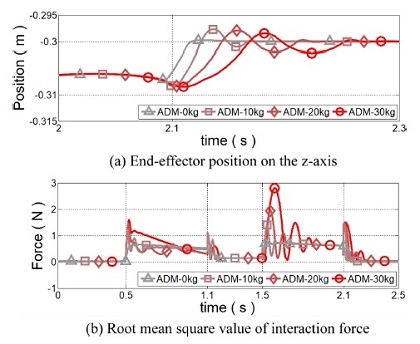
Fig. 8의 회색에서부터 빨간색 선은 무부하부터 30 kg까지의 부하 무게에 따른 제어 성능을 나타낸다.
Fig. 8(a)는 사용자가 물건을 이송하고 정지할 때의 로봇 거동을 나타낸다.
Fig. 8(b)는 부하 무게를 들어올리기 위해 사용자에게 요구되는 상호 작용 힘을 나타낸다. 고정된 어드미턴스 파라미터를 갖는 제어기는 부하 무게가 증가하더라도 등속 운동 시에 사용자에게 0.1 N의 동일한 상호 작용 힘을 요구하였다. 하지만 가속 혹은 감속 시에는 부하 무게에 의한 관성의 증가로 인해 요구되는 상호 작용 힘이 증가하게 됨을 알 수 있다. 특히 감속을 시작하는 1.5초에는 30 kg의 부하 무게를 이겨내고 감속하기 위해 무부하 대비 5배 증가한 상호 작용 힘이 발생하였고, 이로 인해 사용자가 의도하지 않은 진동을 유발하였다. 이와 같은 동작 의도를 벗어난 진동은 사용자에게 불안감을 야기시킬 수 있다.
5
Fig. 8Simulation results of the admittance controller with fixed parameters when the load mass increases
따라서 가변 어드미턴스의 가중치 파라미터
α는 힘 증강 로봇 착용 시 사용자가 느낄 불안감을 제거하기 위하여 진동이 적게 발생하도록 설정되어야 한다. 이에 본 논문에서는 정지 시 발생하는 오버슈트(Overshoot)와 링백(Ringback) 사이의 양진폭(Peak-to-Peak)이 가장 적은
Md,0 대비
α의 비율을 시뮬레이션을 통해 구하였다.
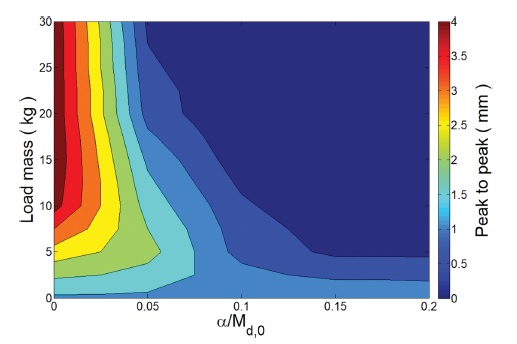
Fig. 9는
Fig. 7과 같은 사용자 모션에 대하여
Md,0 대비
α의 비율이 0에서 0.2 사이의 값을 가질 때 부하 무게에 따른 양진폭의 크기를 표현한 등고선 그래프이다.
Fig. 9The contour plot for peak-to-peak between overshoot and ringback in simulation which preformed using various α to Md,0 ratios and load masses
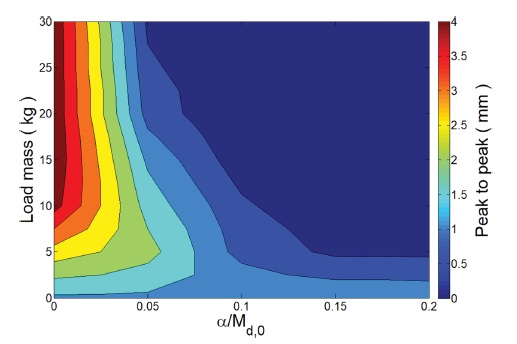
Fig. 9에서 부하 무게가 0 kg인 무부하 상태에서의 양진폭의 크기는 모두 동일하다. 이는 부하 무게가 0 kg이므로
Md,0 대비
α의 비율이 증가하더라도 어드미턴스 파라미터가 변하지 않고 동일하기 때문이다. 이와 같은 무부하 상태에서는 민감하게 설정된
Md,0 그리고
Dd,0로 인해 약 1.4 mm의 양진폭이 발생하였다.
Md,0 대비 α의 비율이 0인 경우는 고정된 어드미턴스 파라미터를 갖는 제어기의 결과를 의미하며 부하 무게가 증가할수록 양진폭이 증가하고 최대 부하 무게 30 kg에서는 약 4.0 mm 크기의 진동이 발생하였다.
반면 Md,0 대비 α의 비율이 증가한 가변 어드미턴스 제어기들의 결과는 고중량 물체 이송 시 양진폭이 감소하였다. 특히 0.15의 비율부터는 5 kg 이상의 부하 물체 이송에도 제어기가 과도 감쇠되어 진동이 발생하지 않았다. 따라서 Md,0 대비 α의 비율이 크게 설정되면 설정될수록 사용자에게 전달되는 양진폭의 크기가 감소하기 때문에 사용자가 느낄 불안감을 방지할 수 있다. 하지만 과도한 감쇠 효과는 사용자에게 높은 상호 작용 힘을 요구하게 된다. 이에 본 논문에서는 부하 물체 이송 시 사용자 안전을 최우선으로 하면서도 과도한 감쇠 효과로 인한 사용자 부담을 방지하기 위해 Md,0 대비 α의 비율을 0.15로 설정하였다.
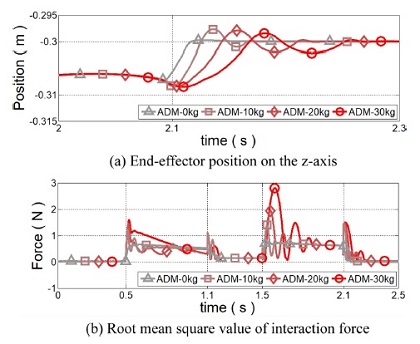
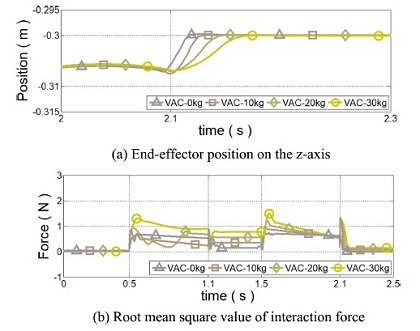
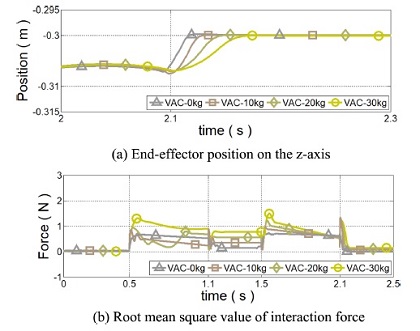
Fig. 10 회색에서 초록색 선은
Md,0 대비
α의 비율이 0.15일 때 무부하부터 30 kg까지 서로 다른 부하 무게에 대한 가변 어드미턴스 제어기의 성능을 보인다. 제안 제어기는 등속 운동 구간에서 부하 무게가 증가할수록 사용자에게 요구되는 상호 작용 힘이 증가하였다. 이는 부하 무게의 증가에 따라 어드미턴스 파라미터가 둔감하게 설정되기 때문이다. 반면 정지를 위해 감속을 시작할 때 제안된 가변 어드미턴스 제어기는 고정된 파라미터를 갖는 어드미턴스 제어기보다 진동이 억제되며 상호 작용 힘이 절반으로 감소되는 것이 확인되었다. 따라서 보다 안정적으로 착용형 로봇에서 사용될 수 있음을 알 수 있다.
Fig. 10Simulation results of the proposed variable admittance control when the load mass increases
5. 실험 검증
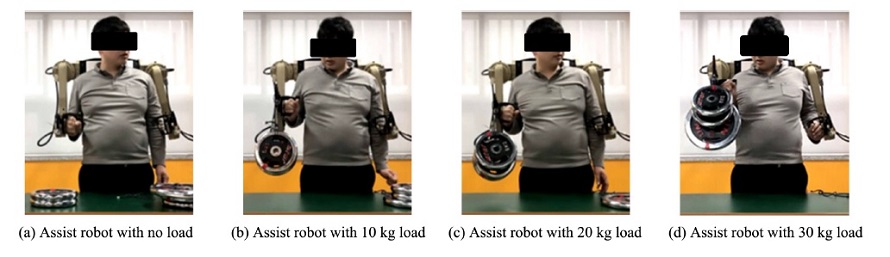
본 장에서는 제안된 제어기를
Fig. 5의 힘 증강 로봇에 적용하여 실험 검증한다. 이를 위해 사용자는
Fig. 11과 같이 무부하에서 30 kg까지 다양한 부하 무게에 대하여 실험을 수행하였다. 실험 환경에 적용된 가변 어드미턴스 제어기 및 내부 위치 제어기 게인들은 시뮬레이션과 동일하게 설정되었다. 그리고 어드미턴스 파라미터를 조절하는 부하 무게는 부하물을 들어올리는 적화 과정에서 실시간으로 측정되며, 이송 과정에서는 적화 과정에서 측정된 값을 유지하고 부하물을 내려놓는 적재 과정에 서 다시 0 kg으로 초기화된다.
Fig. 11 The experiment setup for performance verification of the proposed controller according to variable load masses
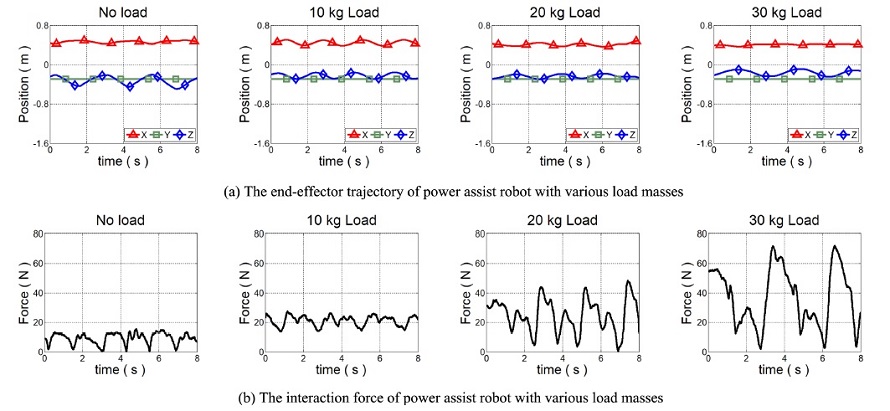
Fig. 12는 각 실험의 동작 궤적 및 상호 작용 힘을 나타낸다.
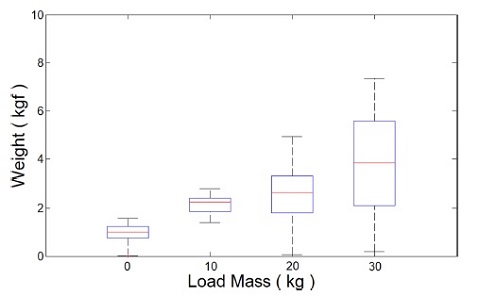
Fig. 13은
Fig. 12의 동작 과정에서 부하 무게에 따라 사용자가 느낀 중량감을 상자 수염 그림으로 표현한 것이다. 상자 수염 그림에서 상자의 크기는 제1사분위수에서 제3사분위수까지의 크기이다. 상자 안의 가로줄은 제2사분위수인 중앙값이다. 상자 위아래로 뻗어 있는 선분은 1, 3사분위수의 ±1.5배에 있는 경계선 이내에서 최대, 최솟값을 의미한다. 각 실험에서 사용자가 느끼는 중량의 중앙값 및 최댓값은
Table 1과 같다.
Fig. 12 The experiment results of the proposed variable admittance controller according to the variable load masses
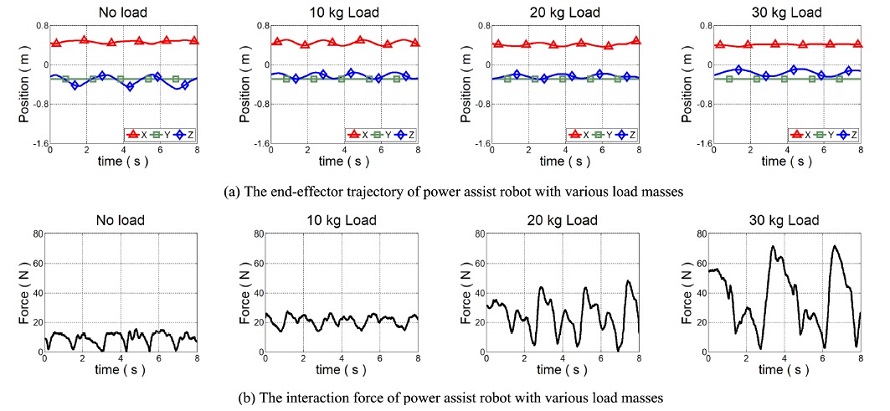
Fig. 13 Box whisker plot for the perceived load weight of the user in each experiment
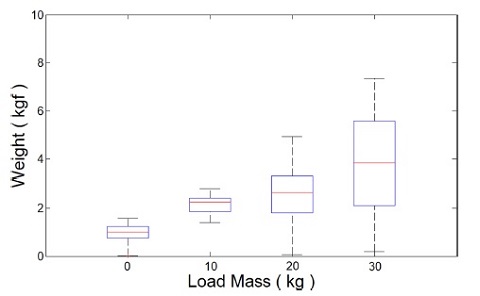
Table 1 Load weight perceived by the user in each experiment
Table 1
|
Task [kg] |
Median [kgf] |
Maximum [kgf] |
|
0 |
1.0 |
1.6 |
|
10 |
2.2 |
2.8 |
|
20 |
2.6 |
4.9 |
|
30 |
3.8 |
7.3 |
실험 결과 사용자는 무부하 상태에서 역구동성이 낮은 시스템 구성에도 불구하고 약 1 kgf의 무게감을 느끼며 민감하게 착용형 로봇을 제어할 수 있었다. 부하 물체 이송 과정에서는 힘 증강 로봇의 자중 대비 최대 5배에 달하는 부하 무게가 시스템 동역학에 큰 영향을 미치게 되었지만 제안한 부하 무게 증가에 따른 어드미턴스 파라미터 조절을 통해 제어기의 불안정을 방지하고 사용자와 안정적으로 협력 상태를 유지할 수 있었다. 또한 시뮬레이션에서의 결과와 같이 부하 무게에 비례하여 사용자 부담이 증가하였지만 힘 증강 로봇 미 착용 시 30 kg의 중량 물체를 이송하기 위해 사용자가 부담했어야할 중량감은 30 kgf인 것에 비해 힘 증강 로봇이 최소 75.7% 이상의 부담을 지원하면서 사용자가 느낄 최대 부하를 7.3 kgf 이하로 관리할 수 있었다.
6. 결론
사용자와 상시 접촉 상태에 있는 착용형 힘 증강 로봇의 제어기는 사용자의 동작 의도에 민감하게 반응하면서도 사용자의 안전을 보장하기 위해 항상 제어 안정성을 유지하여야 한다. 사용자의 동작 의도에 순응한 제어를 위하여 일반적으로 어드미턴스 제어기가 사용된다. 어드미턴스 제어기는
Fig. 2(a)의 안정성 분석 결과에서 확인된 바와 같이 사용자의 인체 강성과 부하 무게로 인한 시스템 동역학 변화로 인해 불안정해질 수 있다. 본 논문에서는 부하 무게로 인한 제어 불안정성에 주목하고, 부하 무게에 따라 어드미턴스 파라미터를 조절하는 가변 어드미턴스 제어기법을 제안하였다. 제안된 제어기는 시뮬레이션 및 실험을 통해 무부하 운동 시에는 어드미턴스 파라미터를 낮게 설정하여 약 1.0 kgf의 상호 작용 힘으로 민감하게 반응하고 무거운 물체를 이송 시에는 어드미턴스 파라미터를 높게 설정하여 제어 안정성을 확보면서도
Table 2와 같이 사용자 부담을 최소 72% 이상 저감하는 성능을 증명하였다.
Table 2 Reduction ratio of required force to load weight
Table 2
|
Task [kg] |
Median [%] |
Minimum [%] |
|
10 |
78.0 |
72.0 |
|
20 |
87.0 |
75.5 |
|
30 |
87.3 |
75.7 |
이와 같이 본 논문에서는 착용형 힘 증강 로봇에 적용되는 어드미턴스 제어기의 불안정 요소 중 하나인 부하 무게를 센서를 통해 측정하고 이를 기반으로 어드미턴스 파라미터를 조절하여 제어 불안정에 대응하였다. 추후 연구에서는 사람마다 서로 다른 인체 강성과 실시간으로 변하는 사용자의 동작 의도와 같이 센서 측정 혹은 예측하기 어려운 착용자로 인해 발생되는 불안정 요소에 대응하여 제어 안정성을 확보하는 가변 어드미턴스 제어기법에 대해 연구를 진행할 계획이다.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
이 논문은 방위사업청 핵심기술연구개발 사업의 지원을 받아 수행된 연구 결과입니다(과제명: 고하중 상하지 근력증강로봇의 통합운동 제어기술).
REFERENCES
- 1.
Kong, K. and Jeon, D., “Design and Control of an Exoskeleton for the Elderly and Patients,” IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, Vol. 11, No. 4, pp. 428-432, 2006.
10.1109/TMECH.2006.878550
- 2.
Perry, J. C., Rosen, J., and Burns, S., “Upper-Limb Powered Exoskeleton Design,” IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, Vol. 12, No. 4, pp. 408-417, 2007.
10.1109/TMECH.2007.901934
- 3.
Kiguchi, K., Imada, Y., and Liyanage, M., “Emg-Based Neuro-Fuzzy Control of a 4DOF Upper-Limb Power-Assist Exoskeleton,” Proc. of the 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 3040-3043, 2007.
10.1109/IEMBS.2007.4352969
- 4.
Kiguchi, K. and Hayashi, Y., “An EMG-Based Control for an Upper-Limb Power-Assist Exoskeleton Robot,” IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), Vol. 42, No. 4, pp. 1064-1071, 2012.
10.1109/TSMCB.2012.2185843
- 5.
Peer, A., “Design and Control of Admittance-Type Telemanipulation Systems,” Technische Universität München, p. 211, 2008.
- 6.
Parthiban, C. and Zinn, M. R., “A Simplified Approach to Admittance-Type Haptic Device Impedance Evaluation,” Proc. of the IEEE Haptics Symposium, pp. 587-590, 2014.
10.1109/HAPTICS.2014.6775521
- 7.
Kim, H., Kwon, J., Oh, Y., You, B. J., and Yang, W., “Weighted Hybrid Admittance-Impedance Control with Human Intention Based Stiffness Estimation for Human-Robot Interaction,” Proc. of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 1-6, 2018.
10.1109/IROS.2018.8594435
- 8.
Tsumugiwa, T., Fuchikami, Y., Kamiyoshi, A., Yokogawa, R., and Yoshida, K., “Stability Analysis for Impedance Control of Robot in Human-Robot Cooperative Task System,” Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systems, and Manufacturing, Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 113-121, 2007.
10.1299/jamdsm.1.113
- 9.
Duchaine, V. and Gosselin, C. M., “General Model of Human-Robot Cooperation Using a Novel Velocity Based Variable Impedance Control,” Proc. of the Second Joint EuroHaptics Conference and Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, pp. 446-451, 2007.
10.1109/WHC.2007.59
- 10.
Shahriari, E., Kramberger, A., Gams, A., Ude, A., and Haddadin, S., “Adapting to Contacts: Energy Tanks and Task Energy for Passivity-Based Dynamic Movement Primitives,” Proc. of the 17th International Conference on Humanoid Robotics, pp. 136-142, 2017.
10.1109/HUMANOIDS.2017.8239548
- 11.
Lecours, A., Mayer-St-Onge, B., and Gosselin, C., “Variable Admittance Control of a Four-Degree-of-Freedom Intelligent Assist Device,” Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 3903-3908, 2012.
10.1109/ICRA.2012.6224586
- 12.
Jung, S. and Hsia, T., “Force Tracking Impedance Control of Robot Manipulators for Environment with Damping,” Proc. of the 33rd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, pp. 2742-2747, 2007.
10.1109/IECON.2007.4460025
- 13.
Dimeas, F. and Aspragathos, N., “Online Stability in Human- Robot Cooperation with Admittance Control,” IEEE Transactions on Haptics, Vol. 9, No. 2, pp. 267-278, 2016.
10.1109/TOH.2016.2518670
- 14.
Tsuji, T., Morasso, P. G., Goto, K., and Ito, K., “Human Hand Impedance Characteristics during Maintained Posture,” Biological Cybernetics, Vol. 72, No. 6, pp. 475-485, 1995.
10.1007/s004220050150
- 15.
Duchaine, V. and Gosselin, C. M., “Investigation of Human- Robot Interaction Stability Using Lyapunov Theory,” Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 2189-2194, 2008.
10.1109/ROBOT.2008.4543531
- 16.
Gallagher, W., Gao, D., and Ueda, J., “Improved Stability of Haptic Human-Robot Interfaces Using Measurement of Human Arm Stiffness,” Advanced Robotics, Vol. 28, No. 13, pp. 869-882, 2014.
10.1080/01691864.2014.900162
- 17.
Nishikawa, K. C., Murray, S. T., and Flanders, M., “Do Arm Postures Vary with the Speed of Reaching” Journal of Neurophysiology, Vol. 81, No. 5, pp. 2582-2586, 1999.
10.1152/jn.1999.81.5.2582
Biography
- Hyomin Kim
Ph.D. candidate in the Division of Robotics at Kwangwoon University. His research interest is physical human-robot interaction.
- Hyunseok Park
Senior Research Engineer in the Robot Development Team, Hyundai Rotem. His research interests are wearable and rehabilitation robot.
- Woosung Yang
Professor in the Division of Robotics at Kwangwoon University. His research interests are wearable and industrial robot.