ABSTRACT
This paper reports the effectiveness of the introduction of NGDG-SOFC (Natural Gas-Fueled Distributed Generation Solid Oxide Fuel Cell) as a solution to social problems that could arise in the unification era due to the power shortage in North Korea. Under the actual operating conditions of the plant, a stack that operates at a voltage of 33.87 V and current of 31.24 A was modeled with a gross output of 1.06 kW and a net output of 1.00 kW considering the balance of plant (BOP) consumption power. Considering the average primary energy consumption in the ASEAN countries in 2020, 2,870 MW was estimated as the amount of power generation required in North Korea. Also, the gross area of the plant and the annual fuel cost were estimated. Consequently, it is concluded that the area of 861 km2 which corresponds to 0.71 percent of the gross area of North Korea, and fuel cost of about 1,474 million $/year are required. The introduction of NGDG-SOFC plants is believed to follow the global trend of renewable energy and resolving the power shortage in North Korea in an eco-friendly manner.
-
KEYWORDS: Solid oxide fuel cell, Fuel cell modeling, North Korea, Power shortage, Pipeline nature gas
-
KEYWORDS: 고체산화물형 연료전지, 연료전지 모델링, 북한, 전력난, 배관천연가스
NOMENCLATURE
SOFC Balance of Plant Equivalent Voltage
SOFC Balance of Plant Power Consumption
SOFC Single-Cell Reversible Voltage
Gibbs Free Energy Difference of Products and Reactants
Enthalpy Difference of Products and Reactants
Lower Heating Value of Hydrogen
Higher Heating Value of Methane
Enthalpy Difference of Stream Reforming Reaction
Enthalpy Difference of Water-Gas Shift Reaction
Actual Surface of the Electrode Concentration of Reactant
Reference Reactant Conctration
Actual Surface of the Electrode Concentration of Product
Reference Product Concentration
Charge Transfer Coefficient
SOFC Electrical Efficiency
SOFC Fuel Utilization Efficiency
Operating Time of SOFC-Plant
Supply Molar Flow Rate of Hydrogen
Supply Molar Flow Rate of Methane
Supply Heating Value of Methane
1. 서론
1970년대 이후로 남한의 발전량이 북한의 발전량을 추월하기 시작했다.
1 남한은 경제 성장 및 기술 발전에 힘입어 원자력, 신재생에너지와 같은 발전설비들을 다변화하면서 발전량을 크게 늘려왔다.
1 반면 북한의 발전량은 2018년 기준 남한 발전량의 6.2% 수준에 머무르고 있다.
1 북한의 저조한 발전량은 전력난으로 이어졌고, 이는 후진국형 산업구조와 맞물려 북한경제의 악순환을 야기했다.
2 이에 북한은 2013년 ‘재생 에네르기법’을 제정해 발전설비를 다변화하고 규모를 확대하려는 노력을 해왔지만 북한의 독자적인 기술로는 한계라는 분석이 지배적이다.
3 결국 통일시대에 발전량과 이로 야기된 자본력의 차이가 발생할 것이고, 구 동, 서독의 통일 과정에서 발생한 여러 사회 문제들이 반복해 야기될 수 있다. 이를 극복하기 위해선 근본적인 문제해결방안이 촉구되어야 한다.
구 동, 서독의 사례에서 문제해결방안의 열쇠를 찾을 수 있다. 과거 동독은 현재의 북한과 유사한 갈탄연소 기반의 화력발전 중심의 발전 형태를 가지고 있었다.
4 반면 서독은 원자력, 수력, 화력발전 등의 발전원을 다변화했다.
4 동, 서독의 발전 형태는 통일 이후에 서독 정부 주도 4단계 과정(자유화 단계, 향후 에너지 정책 모색 단계, 갈등 해소 및 정착 단계)을 거쳐 현재 상태로 정착하게 되었다.
4 하지만 그 과정에서 갈탄발전 폐지에 따른 석탄 경제의 붕괴, 동독 기업의 구조조정에 따른 동독 시민들의 반발, 기업 헐값 매각 등의 사회적 문제가 야기됐다.
4 남북 통일 이후의 발전 정책에서도 앞선 서독 정부 주도 4단계 과정의 선례를 바탕으로 근래에 강조되고 있는 기후 문제에 적극적으로 대응할 수 있는 적절한 해결책을 강구해야 한다.
북한과 같은 개발도상국에선 중앙 집중형 발전소와 같은 대규모 발전소를 건립하는 것에 대해 부담감을 가지고 있다. 중앙 집중형 발전소는 높은 송배전 인프라 구축 비용뿐만 아니라 송배전 시 발생하는 손실 또한 매우 높기 때문이다.
5 하지만 분산 발전은 건설 비용을 아끼고 송배전 시 발생하는 추가 전력 손실 또한 막을 수 있다. 더욱이 연료전지를 분산발전으로 활용할 경우 기존 중앙집중형 발전소와 달리 친환경적이기에 발전량 대비 배출가스를 크게 줄일 수 있다.
6 또한 스택으로 쌓아 올리는 연료전지의 특성 때문에 타 재생에너지 발전시스템에 비해 요구되는 부지의 면적이 작고, 가동률의 기복이 현저히 적어 북한의 분산발전시스템에 적합하다고 판단된다.
7
대한민국 현 정부는 7월 14일, 제7차 비상경제회의에서 ‘한국판 뉴딜’에 대한 추진 계획을 발표했다. 그리고 그린뉴딜 정책을 통해 수소를 주 에너지원으로 사용하는 수소경제를 추진할 것이라고 발표했다. 정부의 방침에 따라 2040년까지 차량, 선박, 발전, 가정용, 수소 생산 및 저장 전 분야를 아우르는 수소경제를 구축하게 될 것이다. 수소경제에너지의 연료로 사용되는 수소는 연료전지를 통해 발전된다. 연료전지는 에너지를 충전해 사용하는 2차 전지와는 달리 전지 스택으로 직접 연료를 공급받아 발전한다. 연료전지는 전해질 종류와 사용 목적에 따라 분류된다. SOFC (Solid Oxide Fuel Cell), PAFC (Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell), MCFC (Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell), PEMFC(Proton-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell)는 발전용으로 사용되고, 그 중 부하 변동에 상대적으로 유연한 PEMFC는 수송용으로도 이용된다. 연료전지는 분리판(Bipolar Plate), 가스확산층(Gas Diffusion Layer), 촉매층(Catalyst Layer), 전해질(Electrolyte)과 기타 누설 방지용 부재 등으로 구성되어 있다. 대표적인 발전용 연료전지인 SOFC의 연료극(Anode)에는 천연가스, 수소 등의 연료가 주입되고 공기극(Cathode)에는 공기가 주입된다. 연료극과 공기극에서 각각 수소, 산소의 산화, 환원 반응이 발생한다. 환원 반응으로 생긴 산소이온은 전해질을 통해 연료극으로 이동해 수소이온과 반응하여 물을 생성한다. 또한 산화반응으로 생긴 전자는 집전체(Current Collector)로 이동해 전류가 흐르게 된다. 이러한 단위셀들이 스택을 구성하고, 이 스택들로 SOFC 발전 시스템을 이룬다. 특히 천연가스를 연료로 사용하는 분산 발전 SOFC 시스템을 NGDG (Natural Gas-fueled DistributedGeneration)-SOFC라고 한다.
연료전지 상용화의 큰 걸림돌은 높은 가격의 백금 촉매와 수소이다.
8 특히 수소는 전 세계적으로 인프라가 부족하기에 아직 한계점으로 남아있다.
9 하지만 전해질로 세라믹을 사용하는 연료전지인 SOFC는 600-1,000
oC의 고온으로 작동되기에 비용이 많이 드는 백금 촉매를 사용하지 않고, 상대적으로 저렴한 촉매를 사용해도 연료와 공기를 충분히 산화, 환원시킬 수 있다.
10,11 또한 순수 수소와 더불어 천연가스, 메탄올, 나프타 등을 사용할 수 있는 연료 유연성을 가지고 있다. 여러 장점을 가지고 있는 SOFC는 연료 단가와 유지보수 측면에서 북한의 분산발전에 적합하다고 판단된다.
10,11 전 세계적으로 연료전지를 이용한 발전 플랜트 규모가 증가하고 있는 추세이다.
12 국내의 사례를 비추어보면 분당 8.35MW, 화성 19.80MW 그리고 파주에 8.10MW급의 SOFC가 가동 중이며 점차 그 규모를 확대할 계획에 있다.
13,14
본 연구의 목표는 북한 전력난 해소를 위한 SOFC 분산발전 도입의 실효성을 검증하는 것이며, 이는 세 가지 방향으로 수행된다. 첫 번째로 실제 운전 조건을 고려한 연료전지 모델링으로 현실적인 스택 총 출력과 전기 효율을 계산해 북한 SOFC 발전 플랜트 도입의 실효성에 대해 검증하였다. 두 번째로 아세안(Association of Southeast Asian Nations, ASEAN) 국가들의 2020년 에너지 소비량 평균값을 목표 발전설비용량으로 설정해 북한 행정구역별 인구밀도에 따른 SOFC 발전 플랜트 기대 발전량 및 단지 면적을 정량적으로 추산하였다. 세 번째로 목표 발전량을 달성하기 위해 발생하는 연간 연료비용을 추산하였다.
2. 문제 정의 및 모델링
2.1 북한의 발전설비 현황과 문제 정의
북한은 2018년 기준 8,150 MW의 발전설비 용량을 보유하고 있고, 이 중 수력발전설비는 58.8%이며, 화력발전설비는 41.2%이다.
15 같은 해 한국이 보유하고 있는 119,092 MW에 비해 현저히 낮은 설비용량이다.
15 북한이 이러한 격차를 줄이기 위해 막대한 비용을 투자하여 발전설비를 확충하는 것은 매우 어렵기 때문에 장기적인 계획이 필요하다고 판단된다. 북한의 2018년 설비용량을 1990년대와 비교하면, 수력발전설비는 498MW, 화력발전설비는 510MW가 증설되어 각각 약 11, 17% 증가하였다.
15 같은 기간 동안 남한의 수력 및 화력발전설비가 약 265, 715% 증가한 것과 비교하면 상당히 낮은 수치이다.
15 이렇게 낮은 발전설비의 증가율은 그만큼 노후된 설비가 심각하다고 판단된다.
북한의 발전설비 이용률은 2018년 기준 34.8%이고, 같은 해남한의 발전설비 이용률은 54.7%이다.
15,16 낮은 설비 이용률은 발전설비의 노후화와 부품 공급 부족에 의한 유지보수 문제의 이유가 가장 크다. 발전설비의 대부분은 30년을 초과했고, 20년 미만의 설비들도 잦은 고장과 기술적인 문제, 부품 부족, 원료 부족 등 유지보수의 어려움을 겪고 있다.
17
2018년 기준 북한의 발전 전력량은 24,900 GWh로 1990년의 27,700GWh보다 낮았으며, 2018년 남한의 발전 전력량인 570,600 GWh의 23분의 1 수준에 그쳤다.
16 2017년 기준으로는 북한 인구의 44%가 전기를 제대로 공급받지 못하고 있고,
18 북한보다 전력난이 심한 나라는 세계 최빈곤 지역을 포함해 15개국에 불과하다.
19
2017년 남한의 1인당 1차 에너지 소비량은 5.88 TOE (Ton of Oil Equivalent)로,
20 같은 해 OECD 평균인 1.86 TOE와 세계 평균인 4.10 TOE보다 높은 수준이다.
21 특히, 급속한 경제 성장과 인구 증가, 산업화 및 도시화 등을 겪고 있는 아세안의 경우 1인당 에너지 소비량 평균값은 1990년에서 2.5배 수준으로 증가했고,
22,23 2020년 1.1 TOE에서 2040년까지 1.4 TOE로 에너지 수요가 크게 증가할 전망이다.
24,25 2040년까지 에너지 효율화로 인한 선진국의 1인당 에너지 소비량은 감소하지만, 세계 인구의 다수를 차지하는 중국, 인도, 아세안 등은 에너지 소비 수준이 개선됨에 따라 에너지 수요도 증가하게 되어 세계 에너지 소비 수준의 격차는 점차적으로 좁혀질 것이다.
24
이에 반해 북한의 1인당 1차 에너지 소비량은 2017년 0.45 TOE에서 2018년 0.57 TOE로 26.7%가 증가했지만 세계적인 기준에 비해 현저히 낮은 수준이다.
20,21 북한은 이러한 이유로 만성적으로 극심한 전력난을 겪고 있지만 북한 당국은 오히려 전기 절약을 강조하고 있다. 이를 해결하기 위해 급속한 경제 성장과 산업화를 겪고 있는 아세안 국가들을 기준으로 추가 발전설비를 단계적으로 확충할 필요성이 있다.
23
본 연구에서는 북한의 행정구역별 인구에 따른 1차 에너지 소비량을 아세안의 기준으로 하여 북한에 필요한 발전설비를 추산한다. 북한의 1인당 1차 에너지 소비량이 아세안의 기준을 거쳐 OECD 평균, 세계 평균, 남한과 같아지기 위한 발전설비는 장기적으로 증설되어야 한다. 발전설비는 NGDG-SOFC 플랜트로 확충하고, 단일 셀과 스택 모델링을 수행함으로써 예상 설비 용량을 계산한다. 예상 설비용량 계산을 위해 NGDG-SOFC 플랜트의 가동률은 연간 100% 조건으로 가정한다.
2.2 SOFC 1-D모델링
2.2.1 단일 셀(Single-Cell) 모델링
NGDG-SOFC 모델링을 수행하기위해, 먼저 단일 셀의 1-D 모델링을 수행한다.
식(1)의 단일 셀의 작동전압(Operating Voltage,
Vcell)은 열역학적 가역 전압(Reversible Voltage,
Ethermo)에서 활성화 손실(Activation Loss,
ηact), 저항 손실(Ohmic Loss,
ηohmic)과 농도 손실(Concentration Loss,
ηconc)을 뺀 값이다.
10
열역학적 가역 전압은 H
2-O
2 연료전지의 온도, 반응물과 생성물의 농도 및 분압에 따라 결정되는 가역 전압이며,
식(2)를 통해 나타냈다.
11
∆G^는 총괄반응의 깁스 자유에너지(Gibbs Free Energy) 변화량을 나타낸다. 깁스 자유에너지는 화학종과 온도에 따라 변화하며, 전기화학 반응의 자발성과 비자발성을 예측할 수 있는 열역학적 변수이다. 본 연구에서는 셀 온도 873 K, 절대압력 2.04 bar 조건
10,26에서 열역학적 가역 전압을 계산한다.
활성화 손실은 전기화학 반응이 진행되기 위해 발생하는 에너지 손실로, 전극에서의 반응 속도와 밀접한 관계가 있다. 활성화 손실을 계산하기 위해
식(3)과 같은 Butler-Volmer식을 사용한다.
그러나 계산의 복잡성 때문에 Butler-Volmer식은 일반적인 가정을 통해 Tafel식으로 나타낼 수 있다. 반응 속도는 반응온도에 비례하며 SOFC의 경우 PEMFC보다 높은 운전온도로 활성화 손실이 상대적으로 적은 특징이 있다. 활성화 손실이 적은 경우 전류밀도(Current Density,
j)와 활성화 손실은 선형적인 관계로 가정할 수 있다.
10,27 따라서 본 연구에서의 전류밀도와 활성화 손실의 관계는 선형적으로 가정한다.
SOFC의 MEA (Membrane Electrode Assembly) 제조 방식, 연료극과 공기극의 구성 물질에 따라 교환전류밀도(Exchange Current Density,
j0)가 결정되며 이는 활성화 손실에 가장 큰 영향을 끼치는 변수이다. 발전용 SOFC는 연료극 기반 MEA (Anode-Supported MEA) 방식으로 제조했을 때 뛰어난 성능을 보이며 일반적으로 연료극으로는 Ni-YSZ Cermet, 공기극으로 LSM과 전해질로 YSZ를 사용하는 것으로 알려져 있다.
10,11,28-30 따라서 본 연구는 MEA의 제조 방법과 구성 물질에 대한 타당한 교환전류밀도값을 가정하기 위해 실험 및 해석적 연구로 모델링을 수행한 Ni
31와 Kenjo et al.
32의 값을 사용한다.
저항 손실은 전해질과 전극에서의 이온 전도와 전자 전도로 발생하는 전기적 저항에서 비롯된 손실을 의미한다. 전자와 이온의 질량 차이가 크기 때문에 전자 전도로 발생한 저항은 무시할 수 있으며, 본 연구에서는 이온 전도로 발생하는 손실만 고려한다. 저항 손실은 전류밀도와 비면적 저항(Area Specific Resistance, ASRohmic)의 곱으로 계산한다.
농도 손실은 촉매층에서의 반응물의 고갈로 발생하는 손실이다. 촉매층에 도달한 반응물의 농도 감소로 발생하는 Nernst 손실과 반응 속도 저하로 발생하는 손실의 영향을 합친 결과이다. 전류밀도가 증가할수록 농도 손실의 영향이 커지며, 농도 손실은 한계 전류밀도(Limiting Current Density, jL)와 전하 전달계수(Charge Transfer Coefficient, α)값에 따라 결정된다.
실제 연료전지 시스템의 운전에선 누설전류, 연료의 크로스오버 그리고 비정상적 반응으로 인한 기생 손실(Parasitic Loss)이 발생한다.
10 따라서 본 연구는 실제 운전 조건 모사를 위해 누설 전류밀도(Leakage Current Density,
jleak)의 영향을 고려한다. 누설전류는 활성화 손실과 농도 손실에 영향을 끼치며, 저항 손실은 실제 작동 전류값에 의해 결정되므로 영향에서 제외한다. 따라서 언급한 모든 손실들과 누설 전류의 영향을 고려한 단일 셀의 작동전압을
식(4)를 통해 나타냈다.
작동전압을 토대로 SOFC 시스템의 전기 효율(Electrical Efficiency,
εelec)을 계산한다. 전기 효율을 나타낸
식(5)는 수소의 저위 발열량(Lower Heating Value,
ΔH^LHV,H2)에 대한 깁스 자유에너지의 비를 나타내는 이상적인 열역학적 효율(Ideal Efficiency,
εideal), 열역학적 전압에 대한 실제 작동전압의 비인전압 효율(Voltage Efficiency,
εvoltage) 그리고 수소의 과급률(Stoichiometric Factor,
λ)로 결정되는 연료 이용 효율(Fuel Utilization Efficiency,
εfuel)의 곱으로 계산한다.
SOFC의 높은 운전온도로 생성물은 수증기이며, 이는 액상으로 존재하는 PEMFC와 다른 특징이다. 따라서 SOFC 전기 효율은 증발 잠열을 제외한 저위 발열량을 기준으로 계산한다. 실제 SOFC 효율은 50%를 상회하는 수준이며, 35-45%인 PEMFC보다 높은 편으로 알려져 있다.
33,34
자체 생산전력으로 연료전지 시스템을 운전하기 위해선 블로어(Blower)를 포함한 기계·전기적 보조 장치가 필요하며, 이를 BOP (Balance of Plant)라고 한다. 따라서 전압 효율을 계산하기위해
식(5),
식(6)에 나타난 BOP 등가전압(
VBOP)의 영향을 고려한다. NGDG-SOFC의 BOP 소비전력(
PBOP)은 총 생산전력의 약 5% 수준으로 알려져 있다.
35 식(6)의 BOP 소비전력에서 운전 전류(
Ioper)를 나눈 값을 나타내는 BOP 등가전압을
식(5)에 대입하여 전압 효율을 계산한다.
10
2.2.2 스택(Stack) 모델링
스택 모델링을 수행하기 위해 먼저 단일 셀의 작동전압과 효율을 계산했다. 스택 모델링을 진행하기 위해선 스택의 순출력(Net Stack Power) 목표치가 필요했고, 추가적으로 셀의 활성화 면적, 스택을 구성하는 단일 셀의 개수 그리고 단일 셀의 운전 전압 선정이 필요하다.
발전용 SOFC의 단일 셀 운전 범위는 전압 0.7-0.9 V, 전류 0.3-0.5 A/cm
2이며, 스택 출력은 0.5-3.0 kW 수준으로 알려져 있다.
35,36 본 연구에서는 스택당 순출력 1.0 kW, 단일 셀 운전 전압 약 0.8 V, 스택을 구성하는 단일 셀의 활성화 면적은 100 cm
2 그리고 스택당 단일 셀 40개가 직렬로 적층되는 조건에서 모델링을 수행한다.
37,38
북한의 필요 발전설비에 따른 SOFC 플랜트의 설치 면적을 고려한다. SOFC 플랜트는 스택들과 BOP로 구성된 여러 개의 모듈이 배치되어 있으며, 부대시설을 포함한 면적으로 추산한다. 따라서 현재 운영중인 SOFC 플랜트들의 발전 용량과 면적을
Table 1에 나타냈으며, 발전설비 1MW당 약 300 m
2의 면적이 요구된다.
39,40
Table 1The current state of commercialized SOFC plants39,40 (Adapted from Refs. 39 and 40 on the basis of OA)
Table 1
Administrative
district |
Power generation
[MW] |
Gross area
[m2] |
|
Hwaseong |
19.80 |
7,017 |
|
Paju |
8.10 |
2,000 |
|
Bundang |
8.35 |
1,880 |
2.3 필요 연료량 모델링과 인프라
2.3.1 필요 연료량 모델링
수소의 과급률은
식(7)과 같이 연료전지에서 발생하는 총 전류(Total Current,
Itotal)로 결정되는 소비 유량에 대한 공급 유량의 비로 정의되며, 이를 통해 공급 수소의 몰 유량(Molar Flow Rate,
υH2,supply)을 계산한다. 본 연구에서 수소의 과급률은 일정 조건으로 가정한다.
10
천연가스의 주성분은 메탄(CH4)이며 소량의 다른 탄화수소 성분들로 구성된다. 본 연구에서는 계산의 단순화를 위해 천연가스가 순수 메탄으로 이루어졌다고 가정한다.
천연가스의 개질 과정은 증기 개질(Stream Reforming, SR)과 수성가스 전환(Water-Gas Shift, WGS) 과정으로 이루어진다. 먼저 SR 과정은 고온의 천연가스와 수증기가 혼합되어
식(8)과 같이 일산화탄소와 수소가 발생하는 흡열 반응이다. 이때 발생한 일산화탄소는 수증기와 반응하여
식(9)와 같이 추가적인 수소가 발생하게 되는데 이것이 WGS 과정이다.
10
식(8)과
식(9)의 반응을 결합하면, 이론적으로 메탄 1 mol당 수소 4 mol이 발생한다. 개질 과정을 통해 메탄 대비 발생하는 수소의 몰분율을 수소 수득률(Hydrogen Yield)이라고 한다. 따라서
식(8),
식(9)의 이상적인 수소 수득률은 4이다. 그러나 실제 개질 과정에선 열 손실, 불완전한 화학 반응과 탄소 침적 현상 등으로 인해 발생 수소의 양은 감소한다. 본 연구는 개질 과정의 수소 수득률에 대한 해석 및 실험 결과의 검증을 수행한 Khzouz et al.
41의 결과값을 사용한다.
발전에 필요한 메탄의 공급 열량(
FCH4, supply)은 메탄의 고위 발열량(Higher Heating Value,
∆H^HHV,CH4), 메탄의 공급 몰 유량(
υCH4,supply)과 운전 시간(
toper)의 곱으로 계산되며
식(10)을 통해 나타냈다.
2.3.2 천연가스 인프라
NGDG-SOFC 기반 발전설비를 확충하면서 연료로 쓰이는 천연가스의 인프라도 고려해야할 사항이다. 카타르, 캐나다, 이란, 미국과 러시아는 2018년 기준 세계 가스 생산의 절반 이상을 차지하는 세계 5대 가스 생산국으로 알려져 있다. 이 중 러시아는 2017년 기준 세계 1위의 천연가스 매장량 보유국이면서 2018년 기준 세계 2위의 천연가스 생산국이다.
46
일반적으로 LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas)는 복잡한 액화-재기화(Liquefaction-Regasification) 설비를 필요로 하며 수송비용이 추가적으로 들기 때문에 지리적, 경제적 요인을 고려해서 선택한다.
47 남한은 지리적으로 반도에 속하지만, 분단 국가라는 특수한 상황 때문에 일본과 같은 섬나라의 특성을 가진다. 이러한 이유로 남한은 2018년 기준 일본 중국에 이어 세계 3위의 LNG 수입국으로 천연가스의 전량을 LNG로 수입하고 있기 때문에
48 천연가스 산업 변화에 따라 경제적으로 많은 영향을 받게 된다.
한편 PNG (Pipeline Natural Gas)는 LNG에 비해 사업 준비 기간이 길지만 액화 및 재기화설비와 대규모의 저장소가 필요없으며 운영비는 상대적으로 낮은 특징이 있다.
49 남한의 지리적 상황과 PNG의 장점으로 남한은 1990년대 초반부터 러시아에서 PNG를 도입하기 위한 가스관 연결을 시도한 바가 있다. 2008년 한·러 정상회담을 통해 남·북·러 가스관 건설 공사에 대한 합의를 체결했지만, 남·북의 정치적, 군사적 문제로 최근까지도 실현되지 못하는 실정이다.
50
남·북·러 PNG 사업은 러시아 사할린 지역에서 생산한 천연가스를 블라디보스토크와 북한을 경유해 한국으로 도입하는 대규모 사업이다. PNG 구축 시 러시아에서 남한까지 총 1,122 km의 파이프 라인 건설이 요구된다.
51 일반적으로 약 3,500 km 이하에서 PNG가 LNG보다 경제성이 있다고 알려져 있기 때문에 러시아를 통한 PNG 도입은 LNG보다 합리적이다.
52 한편 2017년 기준 남한의 도시가스 보급률은 평균 83%로 높은 수준의 인프라를 갖추고 있다.
53 따라서 남·북·러 PNG 사업을 통해 안정적인 가스 공급망을 확보한다면 남·북 모두 가스 관련 사업의 발전과 가스 도입단가를 낮출 수 있을 것이라 기대된다.
일반적인 PNG의 수송원가는 약 294 $/TJ수준으로 LNG 대비 3분의 1 수준이다.
54 2019년 러시아 Gazprom사의 천연가스 평균 판매가격은 약 5,592 $/TJ이다.
55 수송 원가를 고려하였을 때, 러시아의 천연가스를 PNG로 북한에 공급하기 위해서는 약 5,886 $/TJ의 비용이 요구된다. 거리에 따라 증가하는 LNG 선박 수송비와 유지보수 및 건설비를 고려할 때 PNG가 LNG에 비해 경제적이다.
50 따라서 본 연구는 NGDG-SOFC 플랜트를 운영하는데 필요한 연료를 공급하기 위해 러시아에서 천연가스를 도입하는 PNG 방식을 고려하여 북한의 행정구역별 필요 연료량과 비용을 추산한다.
3.1 SOFC 스택 성능
스택의 성능 모델링을 위해 열역학적 전압, 활성화 손실, 저항 손실, 농도 손실을 계산했다. 계산에 사용한 물성치값은
Table 2를 통해 나타냈다.
Table 2
Table 2
|
Parameter |
Value |
Reference |
|
Temperature [K] |
873 |
[10] |
|
Pressure [bar] |
2.04 |
[26] |
Anode exchange current density, j0,an
[A/cm2] |
0.53 |
[27,31] |
Cathode exchange current density, j0,ca
[A/cm2] |
0.04 |
[32,42,43] |
|
Charge transfer coefficient, α
|
0.50 |
[44,45] |
|
Area specific resistance, ASRohmic [Ω·cm2] |
0.04 |
[10] |
|
Limiting current density, jL [A/cm2] |
2.00 |
[10] |
|
Leakage current density, jleak [A/cm2] |
0.01 |
[10] |
|
Stoichiometric factor, λ
|
1.2 |
[10] |
|
Hydrogen yield [molH2/molCH4] |
2.5 |
[41] |
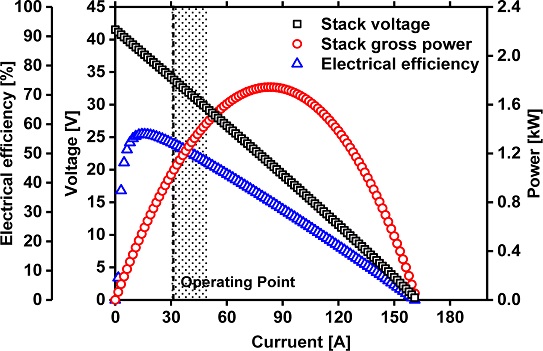
Fig. 1은 모델링한 SOFC 스택의 분극 곡선(PolarizationCurve)을 나타낸 그림이며 운전점(Operating Point)을 함께 나타냈다.
Table 2와
식(4)를 통해 단일 셀의 작동전압을 계산했다. 스택의 출력전압은 40개의 단일 셀이 직렬로 적층되었기 때문에 단일 셀 전압과 적층된 단일 셀의 개수의 곱으로 스택의 출력전압을 계산한다.
Fig. 1Polarization curve of a SOFC stack (40 unit cells are stacked)
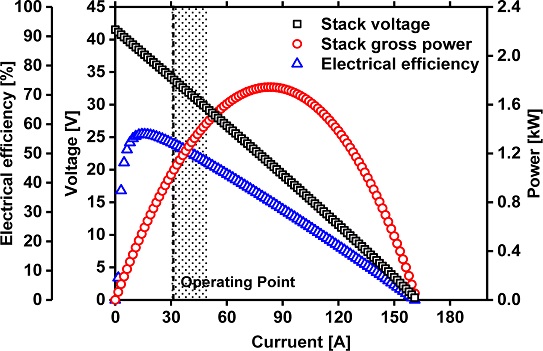
스택의 운전점 설정은 앞서 언급한 발전용 SOFC의 단일 셀 운전 범위
35-38를 참고했으며, 운전 범위를 충족하면서 스택의 BOP 소비전력을 고려한 순출력이 1.00 kW가 되는 지점을 운전점으로 설정한다. 계산 결과 스택의 운전점은 전압 33.87 V, 전류 31.24 A로 나타났다. 스택의 총 출력(Gross Stack Power)은 1.06 kW, 순출력은 1.00 kW이며 전기 효율은 53.3% 수준으로 나타났다. 운전점에서 단일 셀은 전압 0.847 V, 전류 0.312 A/cm
2로 나타났다. 이는 앞서 가정한 목표 값과 일반적인 SOFC 전기 효율에 부합하는 결과로 판단된다.
3.2 필요 설비용량 및 면적
북한의 인구는 2018년 북한의 행정구역과 인구 비중을 적용하여 재구성하였다.
56-58 Table 3은 북한에 필요 설비용량과 면적을 나타낸다.
Table 3Additional power generation capacity by administrative district of North Korea
Table 3
Administrative
district |
Population |
Gross area
[km2] |
Power generation
[MW] |
|
Pyongyang |
3,228,395 |
111 |
370 |
|
Rason |
211,986 |
9 |
30 |
|
Nampho |
1,058,736 |
36 |
120 |
|
North Pyongan |
2,936,923 |
99 |
330 |
|
South Pyongan |
3,302,199 |
114 |
380 |
|
North Hamgyeong |
2,293,008 |
78 |
260 |
|
South Hamgyeong |
3,300,022 |
114 |
380 |
|
North Hwanghae |
2,550,342 |
87 |
290 |
|
South Hwanghae |
2,486,829 |
84 |
280 |
|
Gangwon |
1,590,356 |
54 |
180 |
|
Chagang |
1,399,037 |
48 |
160 |
|
Ryanggang |
774,166 |
27 |
90 |
|
Total |
25,132,000 |
861 |
2,870 |
2018년 북한의 1인당 에너지 소비량인 0.57 TOE에서 2020년 아세안 국가의 평균 에너지 소비량인 1.1 TOE로 증설을 위해 북한 인구에 따른 전력량을 계산한다.
20,24,25 1 TOE는 4,695 kWh로 환산하고,
59 에너지 전환 효율은 약 40%로 하여 설비용량을 추산한 결과 북한 전체에 약 2,870MW의 추가 설비가 필요하다.
60
앞서 모델링한 SOFC 스택당 순출력 값을 기준으로 BOP와 부대시설을 고려할 때, 북한 전체에 약 861 km2의 면적이 요구된다고 판단된다. 이는 북한 전체 면적의 0.71%에 해당하는 수치이다.
2018년 북한 발전설비 8,150MW에서 2,870MW를 추가로 신설하는 것은 북한의 자본과 기술의 부족으로 인해 외부의 협력이 불가피하다. 본 연구에서 산정한 발전설비를 NGDG-SOFC 플랜트로 북한에 추가 신설한다면 2018년의 설비용량 대비 35.2%를 재생에너지로 보급하는 효과가 있다. 물론 북한의 경제 성장에 따른 발전설비를 전부 재생에너지로 확충하는 데는 한계가 있지만, 전 세계적인 신재생에너지 전환 정책에 따른 방향성을 맞추는데 의의가 있다.
3.3 필요 연료량
북한의 연간 추가 발전량 값을 바탕으로
Table 2에 나타낸 수소 수득률과
식(10)을 이용하여 메탄의 연간 필요 열량을 계산한다. 발전에 필요한 스택의 연간 필요 열량은 87,242 MJ/year로 계산된다. 이는 실제 NGDG-SOFC 플랜트의 1 kW 발전을 위한 연간 필요 열량인 65,870 MJ/year와 크게 다르지 않은 수준이다.
26
북한의 행정구역별 필요 발전량 값을 바탕으로 연간 필요 열량을 계산한다.
Table 4는 북한의 행정구역별 메탄 필요 열량을 나타낸다. 계산 결과 북한의 필요 열량은 250,386 TJ/year 수준이 필요하며, 인구 수가 가장 많은 평안남도와 함경남도에 각 33,153 TJ/year로 가장 큰 열량이 필요할 것으로 예상된다.
Table 4Annual heating value requirements of methane by the administrative district of North Korea
Table 4
|
Administrative district |
Heating value [TJ/year] |
|
Pyongyang |
32,280 |
|
Rason |
2,618 |
|
Nampho |
10,470 |
|
North Pyongan |
28,790 |
|
South Pyongan |
33,153 |
|
North Hamgyeong |
22,684 |
|
South Hamgyeong |
33,153 |
|
North Hwanghae |
25,301 |
|
South Hwanghae |
24,428 |
|
Gangwon |
15,704 |
|
Chagang |
13,959 |
|
Ryanggang |
7,852 |
|
Total |
250,386 |
NGDG-SOFC 플랜트에 메탄을 공급하기 위해 러시아에서 생산된 가스를 PNG 방식으로 도입하는 비용을 앞서 산출한 단가를 바탕으로 계산한다. 가동률 100% 조건에서 250,386 TJ/year의 메탄을 북한으로 공급할 때 필요한 비용은 약 1,474 million $/year 수준으로 예상된다.
2019년 12월 기준 spot-LNG의 평균 가격은 약 6,066 $/TJ으로,
61 이를 통해 계산한 LNG의 가격은 약 1,519 million $/year 수준이다. spot-LNG는 계약 기간을 포함하지 않는 화물을 기준으로 거래되는 LNG 가격을 뜻하는데, Henry Hub나 JKM (Japan Korea Marker)의 물가지수와 연동되는 가격은 제외된다.
61 LNG 방식으로 메탄을 공급하기 위해서는 LNG 선박의 수송비용이 추가적으로 발생하기 때문에 PNG 방식으로 러시아에서 가스를 도입하는 방안이 더 경제적으로 판단된다.
남·북·러 PNG 사업이 현실화되어 북한 및 남한에 러시아산 천연가스를 수송한다면 북한은 안정적 공급망 확보 및 수송비 절감을 통한 경제 효과와 SOFC 플랜트를 통한 전력난 해소에 기여할 수 있다. 남한도 경제 효과와 더불어 천연가스 수입선의 다변화와 남북관계 개선을 통해 한반도 통일에 대한 정치적인 문제에도 긍정적인 영향을 끼칠 것으로 기대된다.
4. 결론
본 연구는 북한의 전력난으로 인해 통일시대에 발생할 여러 사회적 문제를 해결하기 위한 대안으로써 NGDG-SOFC 모델링과 목표 발전설비용량 선정 및 행정구역별 플랜트 기대 발전량, 단지 면적 그리고 연간 연료비용을 정량적으로 추산하였다. 먼저 운전점 전압 33.87V, 전류 31.24 A에서 총 출력 1.06 kW, BOP 소비전력을 고려한 순출력 1.00 kW인 스택 모델링을 수행했다. 그리고 일반적인 SOFC 전기 효율에 부합하는 정도인 53.28%로 효율이 계산되어 북한 SOFC 발전 플랜트 도입의 실효성에 대해 검증하였다.
북한에 필요한 발전설비용량은 아세안 국가들의 2020년 에너지 소비량 평균값에 도달하기 위한 값인 2,870MW로 계산되었다. 또한 현재 운영중인 SOFC 플랜트들을 기준으로 발전량 1 MW당 약 300 m2의 면적이 요구됨을 추산하였다. 이를 기준으로 인구밀도에 비례해 행정구역별 SOFC 발전 플랜트 기대 발전량 및 단지 면적을 정량적으로 추산하였다. 따라서 목표 발전설비용량인 2,870MW를 달성하기 위해선 861 km2 면적이 요구되며 이는 북한 전체 면적의 약 0.71%에 해당하는 면적임을 확인했다.
마지막으로 목표 발전량을 달성하기 위해 발생하는 연간 연료비용을 추산했다. 먼저 북한의 연간 추가 발전량 값을 바탕으로 메탄의 필요 열량은 250,386 TJ/year 수준으로 계산되었다. 연료 조달 방법은 통일 시 가시화될 남·북·러 PNG 사업의 가스 공급망을 LNG 대비 경제적인 이유로 선택했다. 따라서 PNG 방식 메탄의 연료비용은 1,474 million $/year 수준으로 추산된다.
NGDG-SOFC 플랜트를 건설하는 것은 북한의 전력난을 친환경적으로 해소하며 구 동·서독의 사례와 같은 석탄 경제의 붕괴, 동독 기업의 구조조정과 기업 헐값 매각과 같은 사회적 문제에 대응할 수 있다. 더욱이 전 세계적인 신재생에너지 전환 트랜드에 따르는데 그 의의가 있다. 따라서 NGDG-SOFC 플랜트 구축이행을 위해선 정부의 종합적인 검토와 정책적 지원이 필수적일 것으로 판단된다.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
권오빈, 차현진, 최희수 저자의 본 연구에 대한 기여도는 동일합니다. 본 연구는 과학기술정보통신부 기초연구사업(No. NRF-2020R1C1C1009191) 지원에 의한 연구입니다.
REFERENCES
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
Yoon, J. Y., “State of North Korea’s Power Industry and Germany’s Integration Cases,” Korea Development Institute Review of the North Korean Economy, Vol. 5, pp. 17-31, 2016.
- 5.
- 6.
Shin, S. B., Jun, S. Y., Song, H. J., Park, J. J., Maken, S., et al., “Study of Fuel Cell CHP-Technology on Electricity Generation Sector Using Leap-Model,” Journal of Energy Engineering, Vol. 18, No. 4, pp. 230-238, 2009.
- 7.
- 8.
Appleby, A., “Issues in Fuel Cell Commercialization,” Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 58, No. 2, pp. 153-176, 1996.
10.1016/S0378-7753(96)02384-1
- 9.
Eberle, U., Müller, B., and Von Helmolt, R., “Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles and Hydrogen Infrastructure: Status 2012,” Energy & Environmental Science, Vol. 5, No. 10, pp. 8780-8798, 2012.
10.1039/c2ee22596d
- 10.
O'hayre, R., Cha, S. W., Colella, W., and Prinz, F. B., “Fuel Cell Fundamentals”, John Wiley & Sons, 3rd Ed., 2016.
10.1002/9781119191766
- 11.
Larminie, J., Dicks, A., and McDonald, M. S., “Fuel Cell Systems Explained,” John Wiley & Sons, 2nd Ed., 2003.
10.1002/9781118878330
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
Kim, K. S., “North Korea Energy Statistics,” Korean Energy Economics Institute, 2015.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
Korean Energy Economics Institute, “International Comparison of Energy Statistics,” 5th Ed., 2019.
- 22.
- 23.
Shin, Y. S., Kim, S. H., Yoon, J. H., and Jeong, H. L., “How to Expand Korea-ASEAN Industrial Cooperation,” Korea Institute for Industrial Economics & Trade, Vol. 899, 2018.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
Park, J. G., Kim, S. Y., and Bae, J. M., “Numerical Modeling of Physical Property and Electrochemical Reaction for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells,” Transactions of the Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers B, Vol. 34, No. 2, pp. 157-163, 2010.
10.3795/KSME-B.2010.34.2.157
- 28.
Neofytidis, C., Dracopoulos, V., Neophytides, S., and Niakolas, D., “Electrocatalytic Performance and Carbon Tolerance of Ternary Au-Mo-Ni/GDC SOFC Anodes under CH4-Rich Internal Steam Reforming Conditions,” Catalysis Today, Vol. 310, pp. 157-165, 2018.
10.1016/j.cattod.2017.06.028
- 29.
Wu, J. and Liu, X., “Recent Development of SOFC Metallic Interconnect,” Journal of Materials Science & Technology, Vol. 26, No. 4, pp. 293-305, 2010.
10.1016/S1005-0302(10)60049-7
- 30.
Singhal, S. C., “Solid Oxide Fuel Cells for Power Generation,” Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Energy and Environment, Vol. 3, No. 2, pp. 179-194, 2014.
10.1002/wene.96
- 31.
Ni, M., “The Effect of Electrolyte Type on Performance of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Running on Hydrocarbon Fuels,” International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Vol. 38, No. 6, pp. 2846-2858, 2013.
10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.12.055
- 32.
Kenjo, T. and Nishiya, M., “LaMnO3 Air Cathodes Containing ZrO2 Electrolyte for High Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells,” Solid State Ionics, Vol. 57, Nos. 3-4, pp. 295-302, 1992.
10.1016/0167-2738(92)90161-H
- 33.
Huang, X., Zhang, Z., and Jiang, J., “Fuel Cell Technology for Distributed Generation: An Overview,” Proc. of the IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, pp. 1613-1618, 2006.
10.1109/ISIE.2006.295713
- 34.
Mohiuddin, A., Rahman, A., Chemani, M. F., and Zakaria, M. B., “Investigation of PEM Fuel Cell for Automotive Use,” IIUM Engineering Journal, Vol. 16, No. 2, pp. 69-78, 2015.
10.31436/iiumej.v16i2.605
- 35.
- 36.
Halinen, M., “Improving the Performance of Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Systems,” Ph.D. Thesis, Aalto University, 2015.
- 37.
Mohammed Ajmal, A., Nisanth, N., and Yogeshwari, R., “Bloom Box,” International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology, Vol. 69, pp. 85-89, 2019.
10.14445/22315381/IJETT-V67I3P216
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
Khzouz, M. and Gkanas, E. I., “Experimental and Numerical Study of Low Temperature Methane Steam Reforming for Hydrogen Production,” Catalysts, Vol. 8, No. 1, p. 5, 2018.
10.3390/catal8010005
- 42.
Hussain, M., Li, X., and Dincer, I., “Mathematical Modeling of Planar Solid Oxide Fuel Cells,” Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 161, No. 2, pp. 1012-1022, 2006.
10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.05.055
- 43.
Costamagna, P., Costa, P., and Antonucci, V., “Micro-Modelling of Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Electrodes,” Electrochimica Acta, Vol. 43, Nos. 3-4, pp. 375-394, 1998.
10.1016/S0013-4686(97)00063-7
- 44.
DiGiuseppe, G. and Licon, G. M., “A Modeling Study of the Effect of Cathode Delamination on SOFC Performance,” Proc. of the International Conference on Fuel Cell Science, Engineering and Technology, pp. 133-142, 2008.
10.1115/FuelCell2008-65030
- 45.
Chan, S., Khor, K., and Xia, Z., “A Complete Polarization Model of a Solid Oxide Fuel Cell and Its Sensitivity to the Change of Cell Component Thickness,” Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 93, Nos. 1-2, pp. 130-140, 2001.
10.1016/S0378-7753(00)00556-5
- 46.
- 47.
Kim, Y. T., “Strategic Review of US LNG Import: Economic and Political Implications for South Korea,” National Strategy, Vol. 23, No. 4, pp. 61-90, 2017.
10.35390/sejong.23.4.201711.003
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
Korea Institute for National Unification, “Effectiveness, Issues and Challenges of South Korea, North Korea and Russian Gas Pipeline Projects (2011),”
http://repo.kinu.or.kr/handle/2015.oak/1800 (Accessed 16 MARCH 2021)
- 51.
Yoon, S. H., “Study of Economic Impact of the SK-NK-Russia Gas Line: Case of South Korea,” Russian Studies, Vol. 22, No. 2, pp. 259-280, 2012.
10.22414/rusins.2012.22.2.259
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
Kim, J. M., Lee, W. H., Kim, J. K., and Kim, B. S., “Russian Natural Gas and Gangwon-do,” Research Institute for Gangwon, Vol. 90, 2011.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
Kim, S. C., “Recent Trends in North Korea’s Socio-Economic Foundation,” The Korea Transport Institute, 16th Ed, 2017.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
Yoo, J. G., “Trends and Implications of Energy Supply and Demand through Energy Balance Analysis,” National Assembly Research Service, Vol.71, 2019.
- 61.
Biography
- Obeen Kwon
M.S student in the School of Mechanical Engineering, Soongsil University in Seoul, Republic of Korea. His research interest is PEMFC and SOFC.
- Hyeonjin Cha
M.S. student in the School of Mechanical Engineering, Soongsil University in Seoul, Republic of Korea. His research interest is PEMFC, SOFC and Glucose Fuel Cell.
- Heesoo Choi
M.S. student in the School of Mechanical Engineering, Soongsil University in Seoul, Republic of Korea. His research interest is PEMFCs for transportation.
- Hongnyoung Yoo
M.S. student in the School of Mechanical Engineering, Soongsil University in Seoul, Republic of Korea. His research interest is enhancing performance of flexible fuel cells, especially flexible PEMFCs.
- Jaeyeon Kim
M.S. student in the School of Mechanical Engineering, Soongsil University in Seoul, Republic of Korea. His research interest includes micro porous layer modification, fuel cell degraded catalyst layer recovery and water management through micro porous layer treatment.
- Hyeok Kim
M.S student in the School of Mechanical Engineering, Soongsil University in Seoul, Republic of Korea. Her current research interest includes flow channel of bipolar plates, operating conditions and analysis of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy in PEMFCs.
- Taehyun Park
Assistant Professor in the School of Mechanical Engineering, Soongsil University in Seoul, Republic of Korea. He received his Ph.D. in Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering from Seoul National University. His research interest is fuel cells (PEMFCs and SOFCs) and their systems for FCEVs, power plants and portable power sources.