ABSTRACT
Recently, industrial manufacturing has developed into additive manufacturing, benefiting from multi-item small-sized production and effective manufacturing. Importantly, Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing, which uses metal wires, is attracting worldwide attention for its high-quality metal product technology. Technological innovation that combines virtual physics with reality through big data communication, such as process variables along with Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing, is an essential task for implementing smart manufacturing technology. Due to the characteristic of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing, numerous variable conditions exist, making it difficult to standardize robot's process path data generation algorithms and data application methods, and this data generation method is being studied as a core element technology. The present study generated foundation process implementation, simulation, and generated path data for robots in virtual space using RoboDK, which provides robot libraries from multiple manufacturers, and Python, which is a universal programming language. To implement the experimental data in practice, ABB's industrial six-axis robots IRB-6700 and Fronius TPS500i were used to control the arcing plasma heat source, and the process path worked the same as simulation. Based on the underlying experimental results, this process can be applied to generation of additive manufacturing in the Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing process for 3D models.
-
KEYWORDS: Robot simulator, WAAM, Motion control, Digital twin, Off-line programming, Virtual process
-
KEYWORDS: 로봇 시뮬레이터, 와이어 아크 적층 제조, 모션 제어, 디지털 트윈, 오프라인 프로그래밍, 가상 공정
1. 서론
로봇과 인공지능을 통해 가상과 현실이 연결되는 가상 물리 시스템은 4차 산업에서 큰 관심을 받고 있다.
1,2 제품 수명 주기 및 다품종 소량 생산과 로봇의 작용이 비중 있게 되면서 새로운 제조패러다임이 등장하고 있기 때문이며,
3,4 디지털 트윈이라 표현되는 가상 공간의 개념을 활용하여 제조를 수행하기 앞서 테스트하여 검증할 수 있기 때문이다.
5,6 한편 전통적인 용접 기술을 활용하여 금속 제품을 적층 제조하는 Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) 기술은 앞서 기술한 이슈에 대해 큰 잠재력을 가지고 있기 때문에 이에 대한 관심과 기대가 매우 높다.
7-10 산업에서 제품을 적층 제조하는 것에 대한 관심이 증가하는 이유는 주로 경제적이고 효율적인 생산 및 제조 기술 개발에 지속적인 목표가 있기 때문이고, 이에 따라 비교적 경제적으로 시스템을 구축할 수 있는 WAAM 공정에 대한 요소 기술 확보에 이목이 집중되고 있다.
11,12
기본적으로 용접 장비와 산업용 로봇을 사용하는 WAAM 공정에서 다관절 로봇의 공정 경로에 대한 모션 제어 및 알고리즘 개발은 핵심 요소이다.
13,14 이러한 요소 기술을 확보하기 위해 연구자들은 서보 드라이버를 연결한 3축 장비에 Computer Numerical Control (CNC) 가공 소프트웨어를 적용하거나 G-언어(Graphic Programming Language)를 사용하여 3축 Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) 소프트웨어에 적용하는 등 여러 방향의 연구를 진행하고 있다.
15,16
최근에는 산업용 6축 로봇의 모션 제어 및 가상 공정 시뮬레이션에 RobotStudio, Rhinoceros, Grasshopper, Roboguide, Catia V5 등 여러 가지의 소프트웨어가 사용되고 있고, 이를 이용해 다양한 분야에서 활발하게 연구가 진행 중이다.
17,18 그러나 로봇 소프트웨어 및 프로그램 언어에 대해 국가별 표준 규격이 제정되지 않아 제조사마다 각각의 고유 언어와 문법으로 프로그램을 제작해야 하고, 이러한 이유로 로봇 구성이 변경되면 새로운 방식의 프로그램 방법 및 개발 언어를 습득해야 한다.
19,20
본 연구에서는 다수 제조사의 산업용 로봇을 제어할 수 있는 범용 소프트웨어를 이용하여 ABB 6축 로봇의 매개 변수와 Tool Center Point (TCP) 초기 설정 및 Off-Line Programming (OLP)을 진행하였고, 이를 통해 로봇의 공구 경로 제어 및 공정에 대한 가상 공간에서의 시뮬레이션과 로봇 데이터를 생성하고, 실제 로봇에 입력하여 공정의 적층 모션을 구현하였다.
논문에서 제시한 새로운 접근 방식의 WAAM 가상 모션 제어 구현 방법은 로봇 시뮬레이터와 범용 프로그래밍 언어를 적용함으로써 제조사 및 기종에 대해 제한적이었던 기존의 로봇 프로그래밍 방식과 다르게 다양한 제조사의 로봇을 하나의 통일된 언어로 프로그래밍할 수 있고, 이를 응용하여 아크 플라즈마 열원의 제어 신호와 공정 변수에 따른 알고리즘을 포함한 데이터를 통해 최종적으로 3D 형상에 대한 아크 플라즈마 열원 기반의 금속 적층 제조 공정을 가상 공간에 구축하고 제어할 수 있다.
2. 하드웨어 및 소프트웨어 구성
WAAM 공정에서 공구 경로에 대한 동작을 수행하기 위한 장비로 ABB의 산업용 6축 로봇 IRB-6700 200/2.60을 사용하였다. 이 로봇은 2.6 m의 가동 범위와 200 kg의 가반 하중을 가지고 있으며 생성한 데이터에 대한 실제 공정을 구현하기 위해 아크플라즈마 열원 발생 장치인 Fronius-TPS500i 용접 토치를 로봇의 공구로 장착하였다.
실험에 사용된 로봇 제조사 ABB의 전용 프로그램 Robot Studio가 아닌 범용 로봇 시뮬레이터에서 가상 공간을 만들고 아크플라즈마 열원의 생성에 대한 제어 코드 및 프로세스가 적용된 로봇 데이터가 가상 공간 속 모션과 같이 실제 로봇에 적용되는지 확인하고, 이를 적층 제조 시스템에 적용하는 방법을 제시할 수 있도록 구성하였다.
구동하고자 하는 로봇 공정을 프로그래밍하는 방법은 로봇 제어기에 함께 설치되는 Teach Pendant를 이용하여 원하는 포인트에 직접 수동적으로 입력하는 방법과 시뮬레이터 및 프로그래밍 소프트웨어를 통해 로봇 데이터를 생성하는 방법이 있다.
21
전자는 사람이 직접 Teach Pendant를 조작하면서 로봇을 이동시켜 직관적인 좌표를 설정하기 때문에 현장에서 즉시 프로그래밍이 가능하지만, 단순한 동작 외 3D 형상을 적층하거나 정밀한 좌표를 입력하기에 적합하지 않다. 공구의 기준 좌표가 소수점 이하로 정밀해야 하거나 정교하게 반복된 작업 수행 또는 3D 형상에 대한 공정 알고리즘을 코딩하기 위해서는 소프트웨어를 이용하여 프로그래밍해야 한다.
21
RoboDK 소프트웨어는 OLP를 수행하기에 접근성이 좋고, 다수 로봇 제조사의 거의 모든 산업용 로봇 라이브러리를 제공하는 강력한 로봇 시뮬레이터이다. 이를 통해 가상의 3D 공간에서 산업용 로봇에 대한 제어 및 시뮬레이션을 쉽게 구현할 수 있고, 개발된 알고리즘을 적용시켜 다양한 로봇 데이터를 생성할 수 있다. 이러한 부분을 활용하여 실제 사용한 ABB 로봇을 시뮬레이터의 가상 공간에 생성한 것을
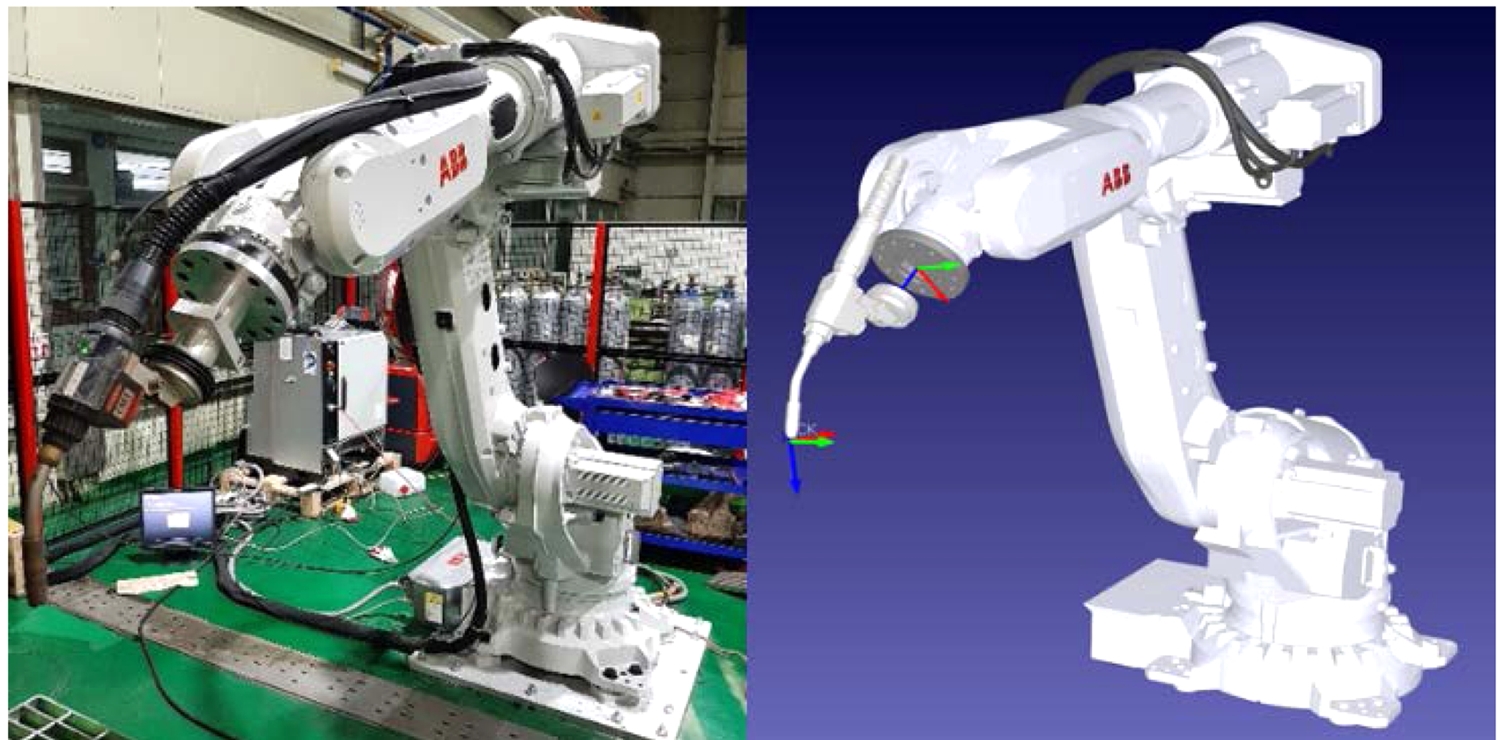
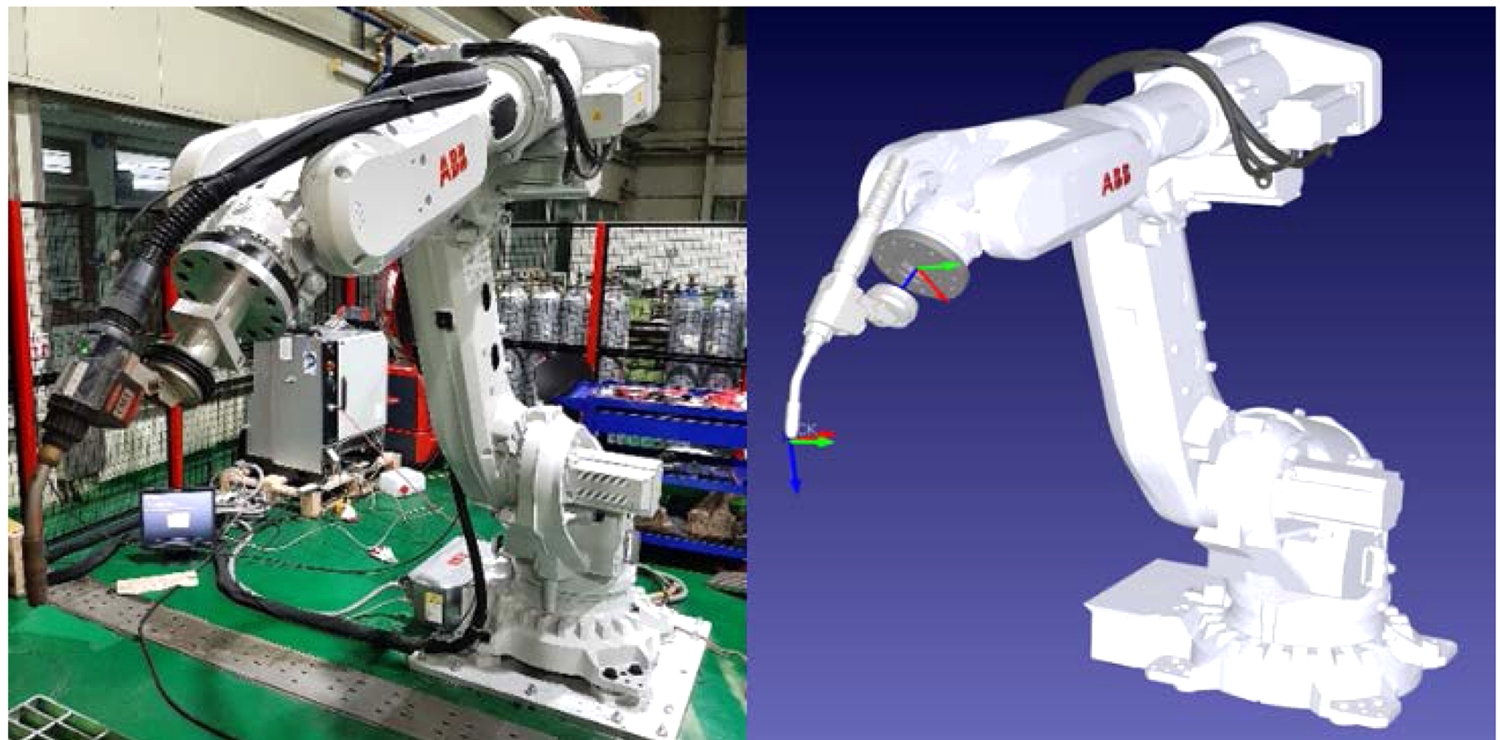
Fig. 1에 나타내었다.
Fig. 1 The six-axis robot of ABB (Left) and the six-axis robot of virtual ABB generated in the robot simulator (Right) were used in the experiment

RoboDK의 경우 많은 개발자들이 사용하고 있는 Python이나 MATLAB, C#과 같은 범용 프로그래밍 소프트웨어를 이용할 수 있기 때문에 거의 모든 로봇을 동일한 문법으로 제어할 수 있는 장점이 있고, 프로그래밍한 코드를 이용해 산업용 로봇에 대한 모션 데이터를 생성할 수 있다.
21
RoboDK에서 지원하는 Python Application Interface (API)는 시뮬레이터의 가상 공간에서 프로그램 코드의 작성, 검토, 수정을 진행하고, 핵심 공정 변수에 대한 알고리즘에 대해 독자적, 범용적으로 접근하여 산업용 로봇을 제어할 수 있다. 기본적으로 Python IDLE을 설정하여 사용하도록 하지만 Notepad++ 또는 Pycham과 같은 편집기를 적용하여 원하는 개발 환경을 구축할 수 있다.
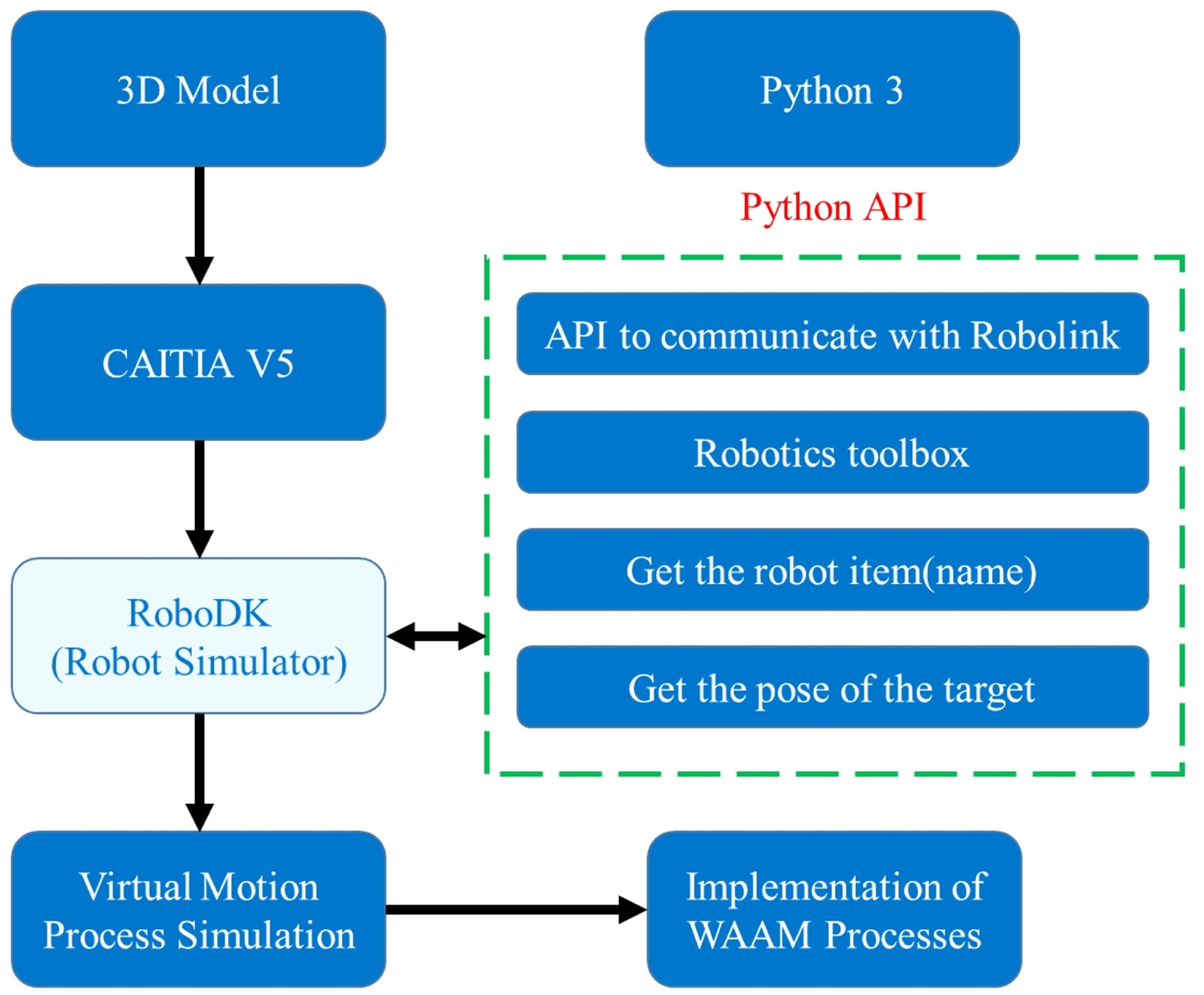
Fig. 2는 본 연구에서 제시한 방법론의 구조를 나타내고 있다. 적층 제조 공정을 구현하고자 하는 3D 형상 모델을 CATIA V5에서 생성하고, 로봇 시뮬레이터에서 객체에 대한 곡선 및 좌표를 생성하였다. 이때 목적하는 좌표에서 아크 플라즈마 열원 제어 명령을 추가로 수행하여 금속 와이어를 용융시키게 된다.
Fig. 2 Architecture of proposed methodology

경로 모션은 시뮬레이터에 구축한 가상 공간에서 시뮬레이션하고, 독자적인 로봇 모션은 Python API를 통해 Python 3에서 명령어를 입력하여 동작하였다. 가상 공간의 로봇 모션 시뮬레이션을 확인하고, 실제 ABB 로봇 데이터를 생성하여 WAAM 공정을 구현하였다.
3. 실험 방법
3.1 로봇 매개 변수 입력
초기 설정을 위해 ABB 6축 로봇 IRB-6700 200/2.60 모델의 매개 변수를 RoboDK에 생성한 가상 로봇 정보에 입력하였다. 이 변수는 사용하는 로봇의 작업 위치나 축의 방향, 속도 등을 고려하여 기본 단계에서 입력해 주어야 한다.
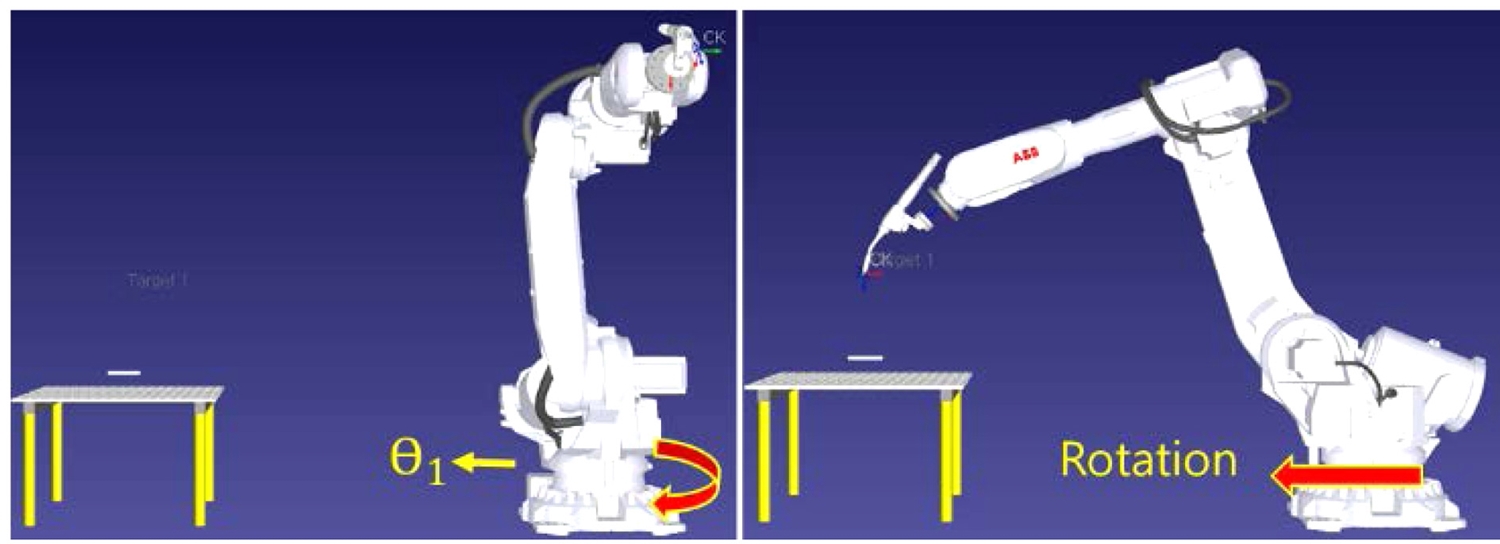
Fig. 3은 실제 실험 위치와 방향을 시뮬레이터의 가상 로봇에 입력한 것이다. 로봇의 홈 포지션에 대한 설정 단계이며, 6개의 관절 데이터 중 θ
1 이 -90.000 (deg)의 값을 갖는 위치에서 공정을 진행할 수 있도록 설정하였고, 가상의 로봇이 설정된 홈 포지션으로 이동한 것을 볼 수 있다.
Fig. 3The location and direction of the actual experiment are entered into the virtual robot of the robot simulator. Of the 6 joint data, θ1 indicates that the virtual robot has moved from a position with a value of -90.000 (deg) to the set home position
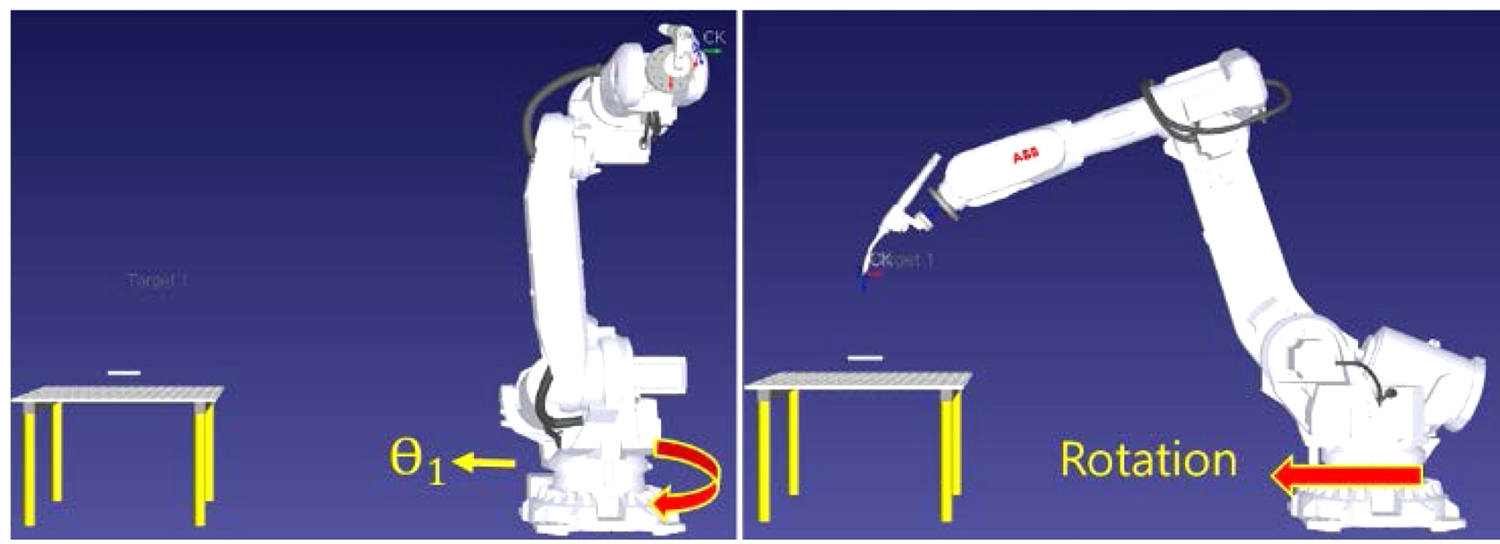
홈 포지션 설정과 함께 이 단계에서는
Table 1과 같이 로봇의 기본 이동 속도와 가속도, 조인트 속도 및 조인트 가속도 그리고 라운딩값을 설정할 수 있다. 또한 로봇의 현재 포지션과 각 축의 운동학 정보를 확인 및 입력할 수 있으며, 로봇 각 축의 한계를 설정할 수 있고, 이 설정으로 로봇 주위 장애물이나 시설 등 금지구역에 대한 제한이 가능하다. 여기서 기본 이동 속도는 임의의 속도 50 mm/s로 설정하였고, 그 외 매개 변수는 기본값으로 설정하였다.
Table 1Robot parameters
Table 1
|
Speed [mm/s] |
Joint speed [deg/s] |
Acceleration [mm/s2] |
Joint acceleration [deg/s2] |
|
50.0 |
200.0 |
1,500.0 |
150.0 |
3.2 TCP (Tool Center Point) 설정
산업용 로봇을 이용한 가상시스템을 구축할 때 TCP (Tool Center Point) 설정은 매우 중요한 단계이다. TCP는 로봇이 동작하는 공간 내 정의되는 모든 좌표의 기준이 된다. 즉, 해당 좌표를 기준으로 로봇축의 동작이 변화하며 프로그램 데이터에도 적용된다.
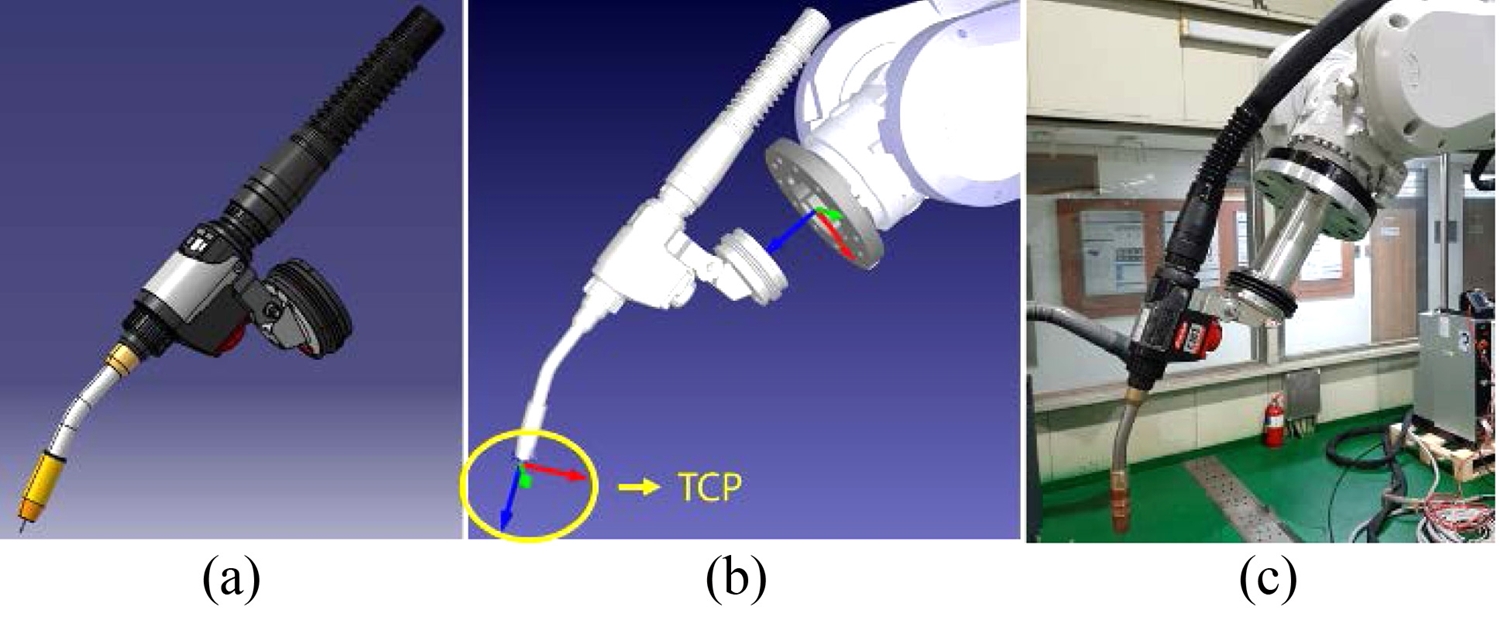
Fig. 4와 같이 WAAM 공정에 대한 적층 시뮬레이션 및 모션 제어를 위해 사용할 공구인 용접 토치의 3D 모델링 데이터를 가상 로봇에 장착하고, 공구 중심 좌표 설정을 진행하였다. 공구의 TCP 설정을 진행할 때 주의해야할 점은 실제 사용하는 공구와 모델링 데이터 그리고 축의 좌표 및 방향이 일치해야 이후 단계에서 정상적인 포지션으로 공정이 진행된다. 만약 TCP 설정을 진행하지 않으면 로봇은 공구 대신 손목의 좌표를 기준으로 움직이게 된다.
Fig. 4TCP configuration of IRB-6700 with welding torch (a) Robacta welding torch CATIA modeling, (b) Welding torch with TCP setup in Robodk, and (c) Actual setting of welding torch
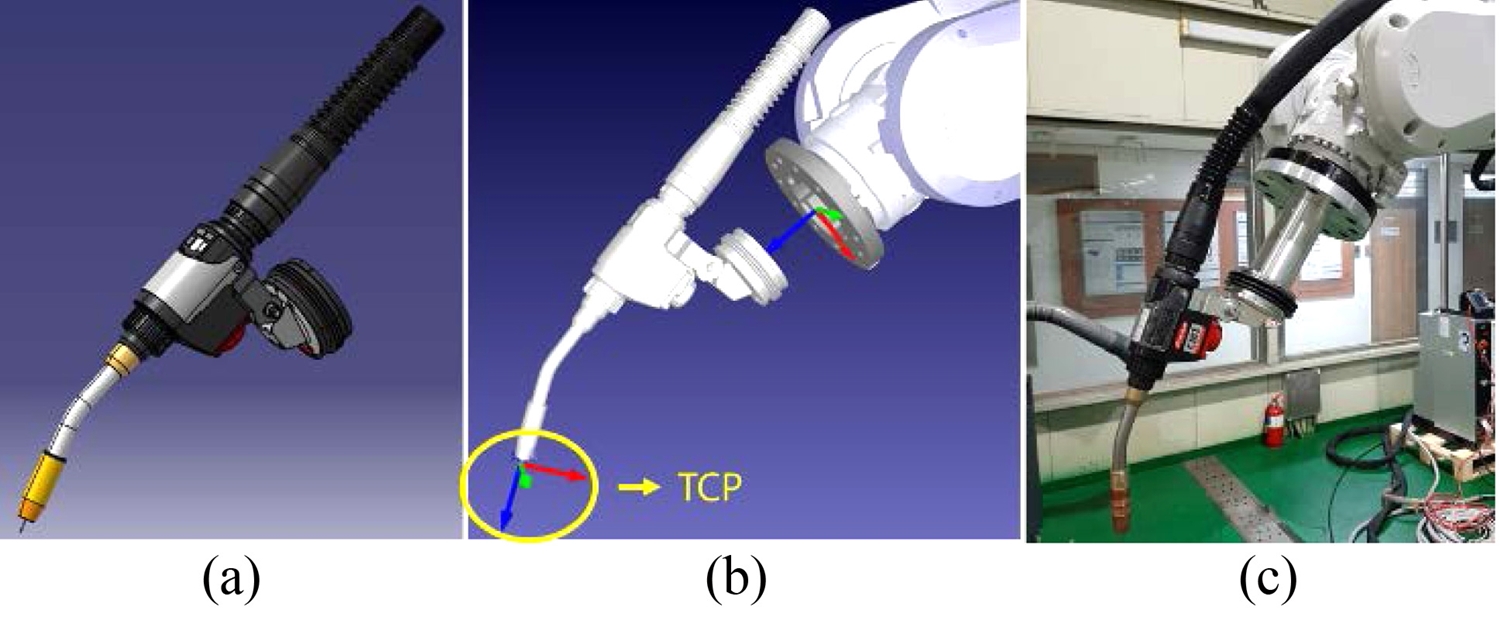
RoboDK에서 가상 스테이션에 위치한 공구 좌표계의 위치 및 방향을 지정하고, 용접 토치 노즐 아래 작업 위치에 배치한 후 설정 창에서 교정을 하면 TCP 설정은 완료된다. 이 과정에서 실제 작업 위치와 대조를 통해 오차를 최소화하는 것이 필요하다. 실험에 사용한 ABB 로봇은 산업용 로봇 성능 평가 국제표준규격(ISO 9283)에 따라 포즈에서 0.05, 경로에서 0.1 mm의 반복오차 정밀도를 가지고 있다. 이것은 같은 방향으로 동일한 명령 포즈에 N번 반복하여 도달된 포즈 및 경로의 근접성을 나타낸 것이며 30번 연속 반복하여 측정한 규격 성능이다.
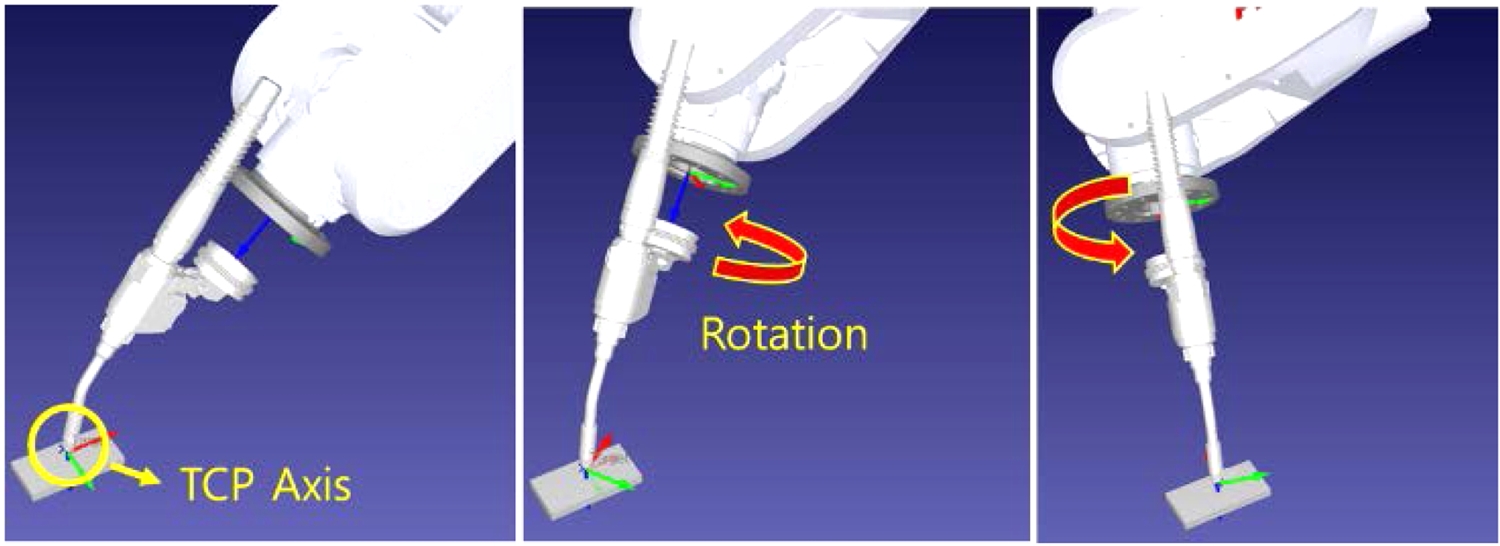
WAAM 공정의 가상 적층 모션에 대한 TCP 설정은 용접 토치의 가장 끝 위치에 설정해야 하고, 설정이 정상적으로 완료되면
Fig. 5처럼 툴 좌표를 기준점으로 로봇축을 이동 또는 회전할 수 있다.
Fig. 5The robot arm rotates around the working position by setting TCP at the torch destination
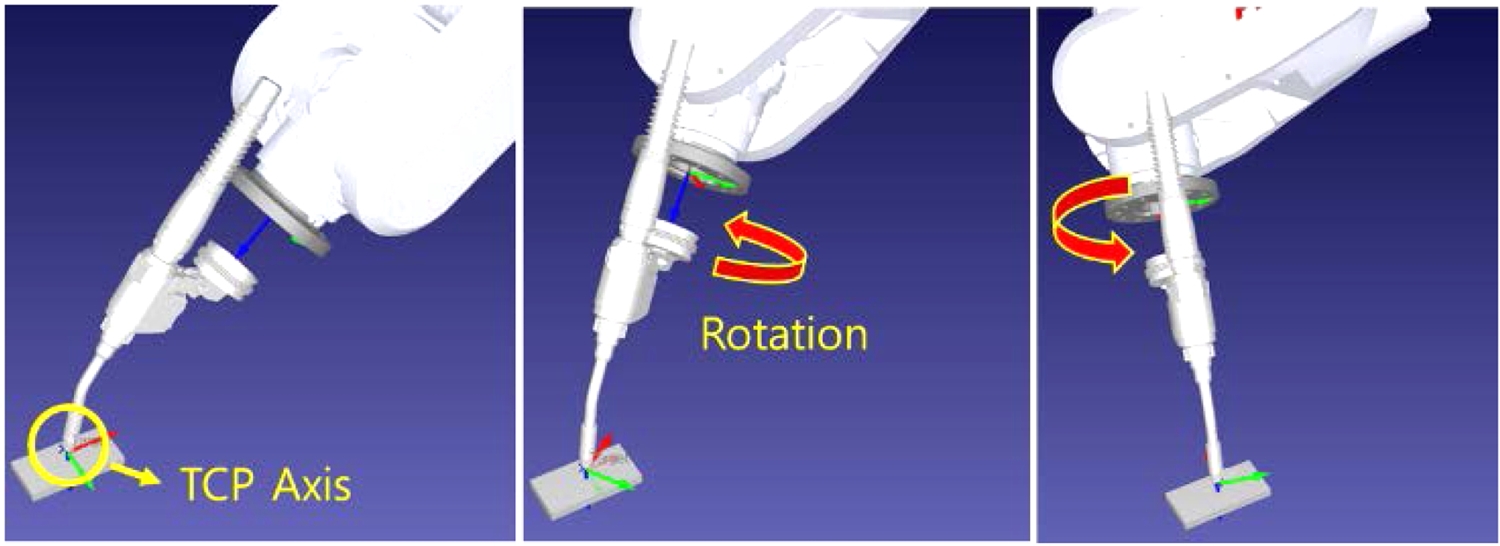
이것은 재료 와이어와 아크 플라즈마 길이를 합한 모재와의 거리 변수 CTWD (Contact Tip-to-Work Distance) 설정 시 영향을 줄 수 있으며, 이 변수는 아크 플라즈마를 열원으로 하는 금속 적층 공정에서 생성된 비드(Bead) 형상에 대해 영향을 줄 수 있는 변수 중 하나이기 때문에 실험하고자 하는 위치와 가상의 모델이 최대한 일치하게 설정 또는 교정해야 한다. 본 실험에서는 이 변수를 20 mm로 설정하여 실험하였다.
3.3 OLP (Off-Line Programming)
TCP가 정의된 RoboDK 가상 공간에서 실제 작업 좌표 데이터를 입력 및 교정한 후에 WAAM 공정 적용의 기본 단계인 용접 공정에 대한 OLP를 진행하였다. 이것은 용접 공정 알고리즘 및 아크 플라즈마 열원의 생성과 제어 프로그램 코드를 통해 공정에 대한 가상 시뮬레이션 및 로봇 모션을 구현할 수 있는 핵심적인 단계이다.
Python API (Application Program Interface)를 이용하여 실제 공정을 구현하기 위한 로봇 팔의 동작 알고리즘 및 직선 용접 모션을 이행하는 코드를 입력하고 Python 기본 IDLE을 개발환경으로 하여 RoboDK와 연동하기 위한 Robolink 및 RoboDK 모듈을 삽입 후 로봇과 좌표에 해당하는 아이템 변수를 선언 및 지정하였다. 아이템 동작 코드를 통해 TCP가 직선으로 동작하도록 프로그래밍하였고, 입력한 코드는 RoboDK의 메인 프로그램에서 실행하였다. 이것은 Python 프로그램의 기본 IDLE에서 개별적으로도 실행 가능하다.
이후 단계에서 아크 플라즈마를 열원으로 사용하여 로봇 용접 및 적층하기 위해서는 로봇의 모션 경로를 제어하는 것과 함께 통신으로 연결된 용접기에서 열원을 발생시켜야 한다. 이것은 RoboDK에서 API를 통해 포스트 프로세서로 생성한 데이터를 직접 편집하는 방법 또는 프로그램 이벤트 기능을 이용해 제어 코드를 입력하는 방법으로 제어할 수 있다.
Table 2에 나타낸 명령어를 프로그램 이벤트 기능을 사용하여 ABB 로봇의 아크플라즈마 열원 제어 신호로 입력하여 최종적으로 생성되는 로봇 데이터에 추가되도록 하였다.
Table 2Program events
Table 2
|
Function |
Arc plasma signal code |
|
Path start |
ArcLStart |
|
Path finish |
ArcLEnd |
3.4 가상 공정 시뮬레이션 및 구현
선행 과정에서 금속 와이어를 용융 시킬 공구 경로의 시작 및 종료 지점에 아크 열원 제어 신호를 추가하여 생성한 최종 데이터를 이용해
Fig. 6과 같이 공정의 가상 시뮬레이션과 실제 ABB 로봇에 적용하는 실험을 진행하였다.
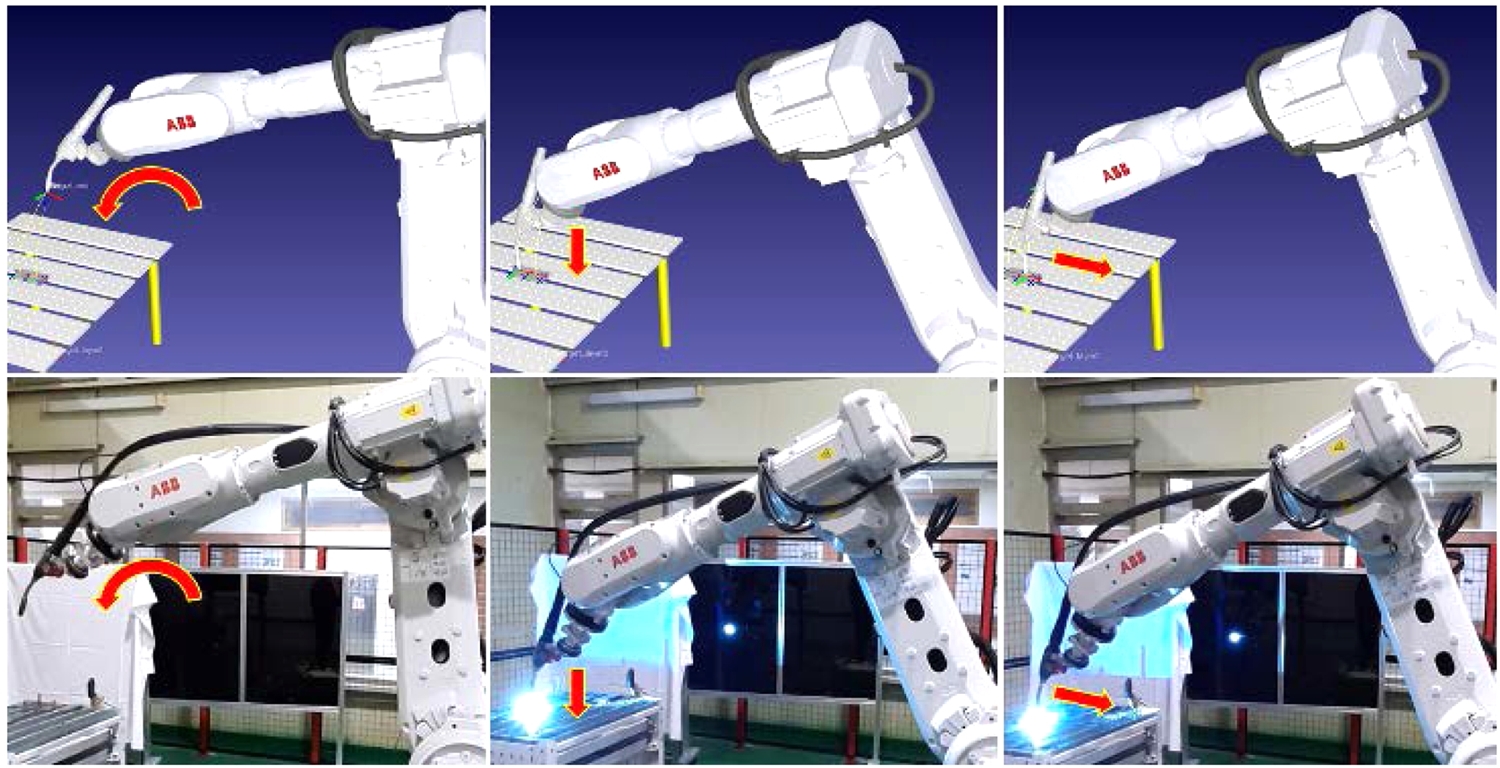
Fig. 6의 상단은 시뮬레이터에 구축된 가상 공간에서 공정 알고리즘과 매개 변수 및 TCP, 작업 좌표 교정을 완료한 ABB 로봇으로 용접 공정의 가상 시뮬레이션을 구현한 것이다. 시뮬레이터에서 공정 좌표와 제어 명령, Python Code가 포함된 메인프로그램을 생성, 실행하여 통합된 가상 시뮬레이션을 진행하였다. 그리고 포스트 프로세싱으로 생성한 로봇 데이터를 실제 ABB 로봇에 입력하여
Fig. 6의 하단과 같이 시뮬레이션과 동일한 공정을 수행할 수 있음을 확인하였다.
Fig. 6Simulation of virtual linear welding operations in the direction of the robot's main body (Top), ABB robot performing the same process as simulation (Bottom)

실험에 적용한 금속 와이어 재료와 전류, 전압 및 용접 속도 변수 조건은
Table 3과 같이 설정하였으며, 이는 용접 공정을 통해 비드의 형상 확보가 가능한 임의의 값으로 설정하였다. 실험은 공정 변수나 용적 이행 모드, 금속 비드의 품질보다는 산업용 로봇의 금속 적층 모션에 대해 시뮬레이터를 적용한 가상 공정 시뮬레이션 및 아크 플라즈마 신호 제어 그리고 실제 로봇의 모션 구현에 중점을 두고 진행하였다.
Table 3Welding condition
Table 3
|
Wire |
Current [A] |
Voltage [V] |
Welding speed [mm/s] |
|
Steel |
252 |
25.9 |
10 |
3.5 WAAM 공정 적용 및 결과
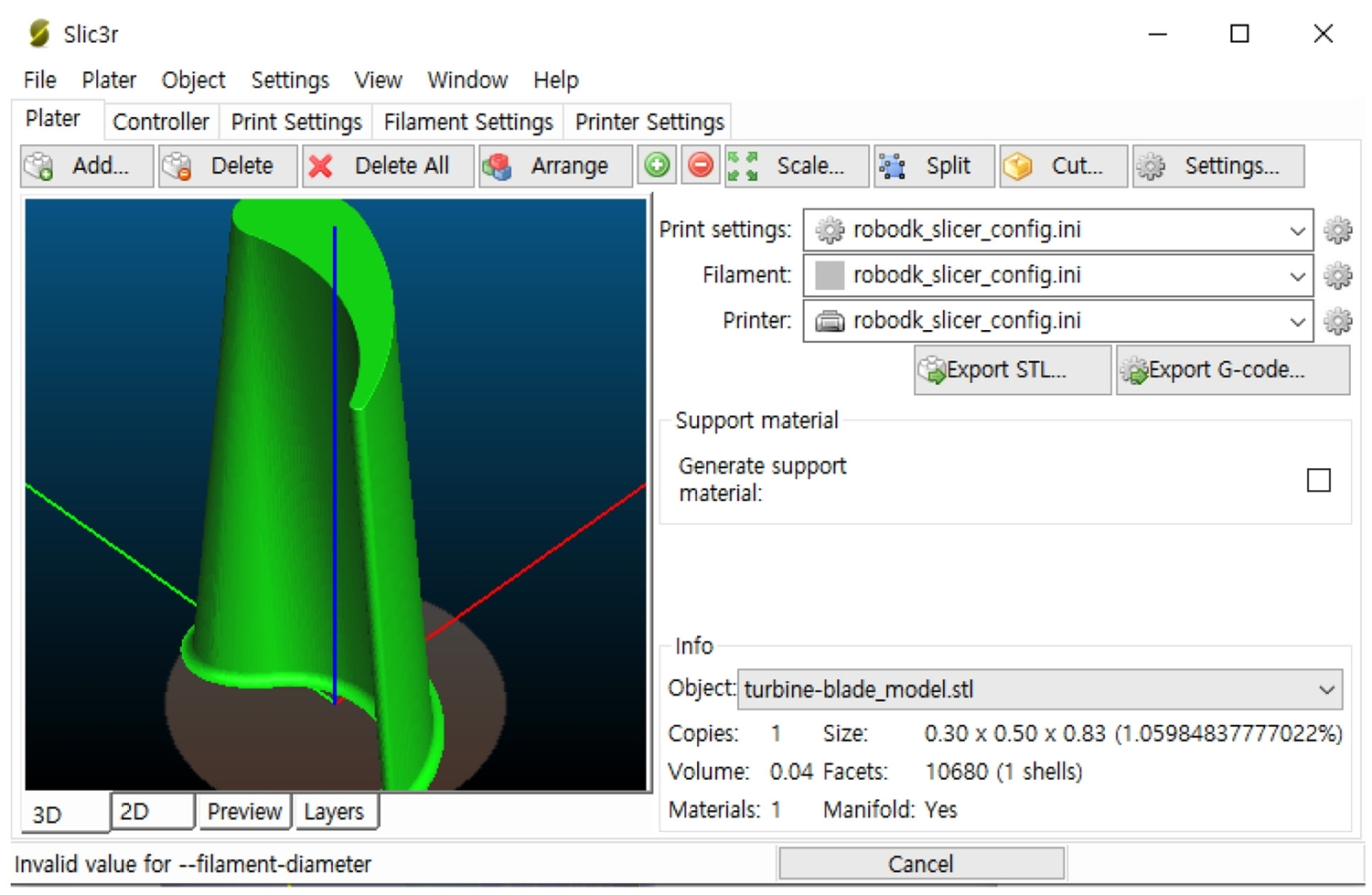
선행 실험 결과를 바탕으로 터빈 블레이드 모양의 3D 형상에 대한 WAAM 공정 기반의 적층 모션을 구현하는 실험을 진행하였다. 슬라이싱을 진행하고자 하는 3D 데이터는 .STL 형식을 사용하여
Fig. 7과 같이 오픈소스 기반 소프트웨어 Slic3r에 입력하였다.
22-24
Fig. 7Import turbine blade type 3D model into open source process experiments software Slic3r

이것은 기본적으로 폴리머 기반의 재료를 적층하는 FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) 방식의 내부 알고리즘 기준으로 슬라이싱되며, 사용자가 개발한 알고리즘을 적용하여 G-Code 데이터를 출력할 수 있다. 이것을 응용하면 WAAM 공정을 기반으로 한 3D 형상 슬라이싱 및 자동 모션 데이터 생성이 가능한데, 이 방법에서는 서포트 구조를 사용할 수 없는 금속 적층 특성의 반영, 아크 열원 제어 신호 연동 등에 관한 추가적인 연구가 적용되어야 한다.
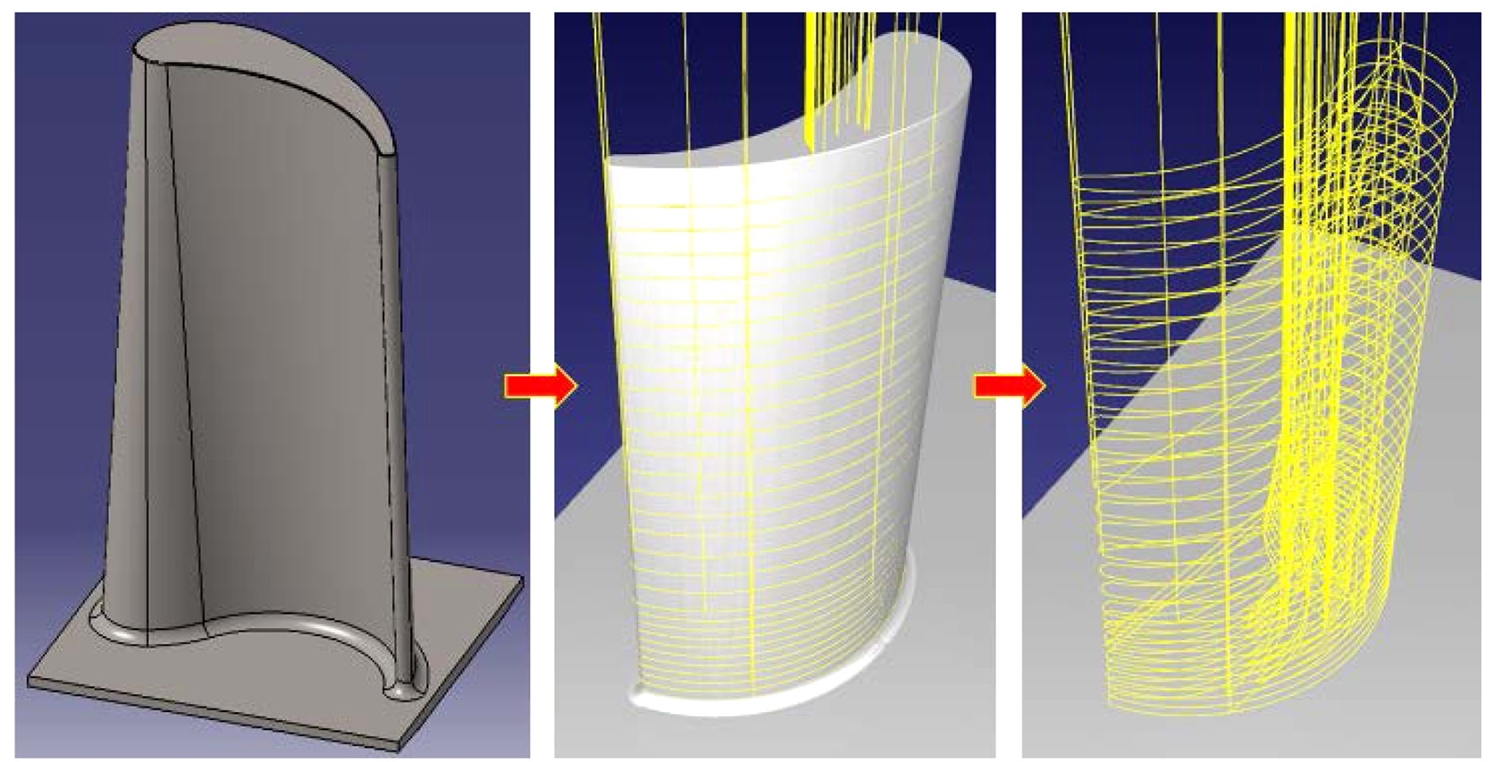
두 번째 방법으로 3D 설계 프로그램 CATIA V5를 이용하여 3D 형상에 대해 슬라이싱한 것을
Fig. 8에 나타내었다. 경로간 채우기 간격과 슬라이싱 높이는 금속 플레이트 시편에서 초층 공정 실험을 통해 열원 조건별 비드 형상을 관찰하여 비교적 적층이 진행되는 형상이 관찰된 임의의 조건으로 설정하였다. 이러한 공정은 반복 실험을 통해 최적 조건을 도출할 수 있다.
실험한 비드 형상 수치를 적용하여 CATIA V5에서 3D 형상을 슬라이싱하고, 그 데이터를 로봇 시뮬레이터에 구축된 가상 공정에 적용하였다. 여기에 공정 속도 및 열원 제어 지점, 이동 정밀도, 진행 방향 및 순서 등을 입력하여 통합적인 적층 모션 계획에 적용하였고, 로봇 시뮬레이터의 가상 스테이션에서 최종적으로 3D 모델 형상에 대한 적층 모션을 제어하였으며 모션에 대한 로봇 데이터를 생성하였다.
Fig. 8After slicing the 3D model with CATIA, planning the robot's Additive Manufacturing motion with RoboDK

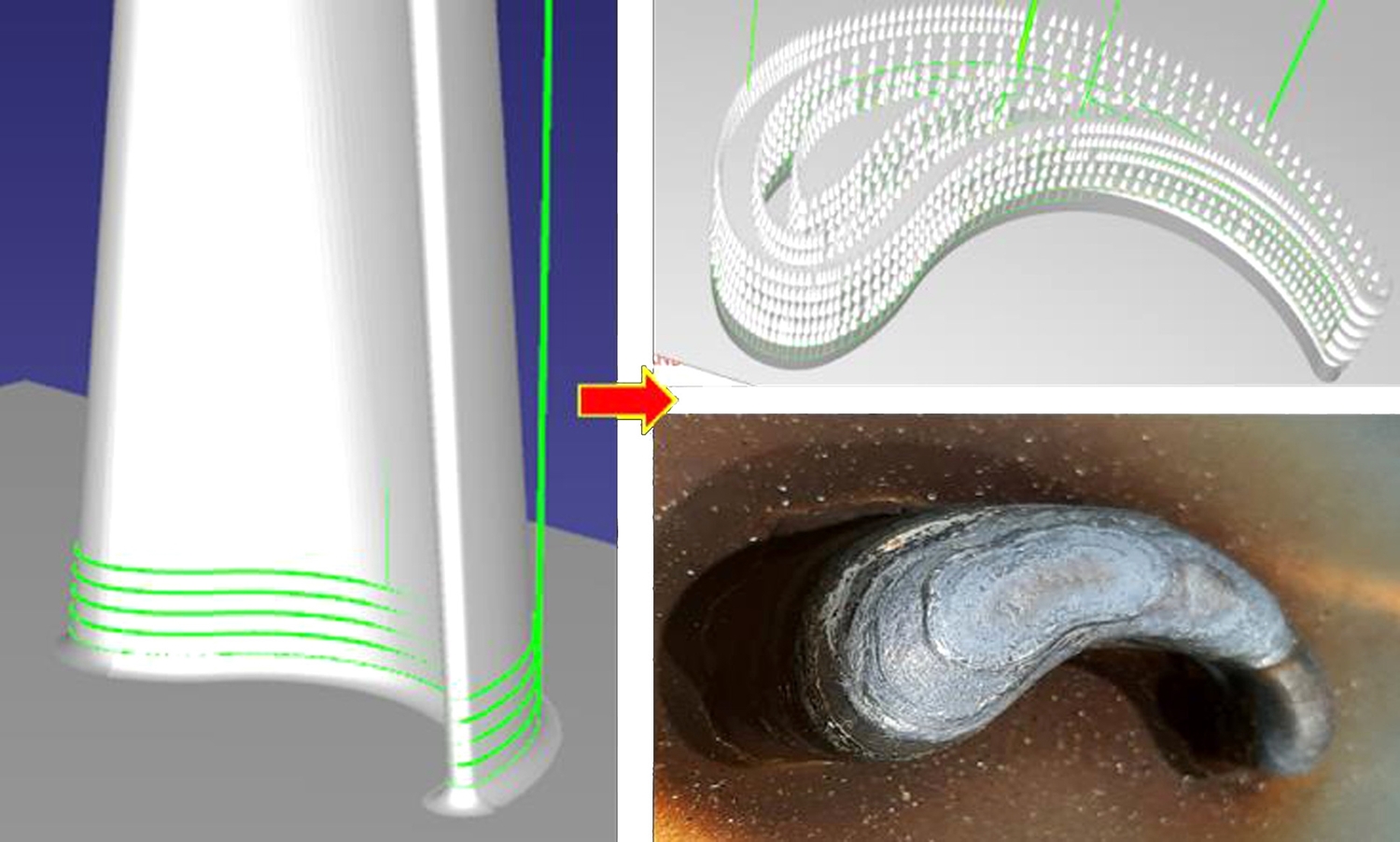
슬라이싱 실험을 바탕으로
Fig. 9와 같이 3D 형상의 하단을 형성하는 5 Layers에 대한 적층 모션을 계획하여 실제 적층 실험을 진행하였다. 적층 조건은 3.4절의
Table 3과 동일하게 진행하였고, 보호 가스는 Ar 15 l/min, 토치는 기본적으로 아래 보기 자세로 진행하였으며 계획된 적층 모션에 따라 ABB 로봇의 TCP가 동작하며 WAAM 공정이 구현되는 것을 확인하였다.
Fig. 9Plan the WAAM motion of part of the 3D model and conduct process experiments

제시한 방법을 WAAM에 적용하는 실험에서 임의의 변수로 생성한 비드의 폭은 약 7.5, 높이는 2 mm로 가상 공간에 적용되었고, 각 Layer의 CTWD는 1.5 mm 높이를 유지하며 약 10 mm 높이의 블레이드 형상을 적층 제조하는 공정이 시뮬레이션 되었다. 이를 통해 생성된 데이터를 입력한 실제 로봇 동작은 원하는 지점에서의 아크 열원 점화 및 유지, 소거 등 지정한 높이 및 방향으로 토치를 이동시키는 모션이 진행되었고, 용융된 금속은 가상의 형상과 매우 흡사하였다.
향후 온도 및 토치의 각도, 다양한 비드의 형상, 용락, 균열 등 WAAM 공정에 대해 영향이 큰 변수에 대한 연구 결과를 추가 적용한다면 3D 모델에 대한 최종 형태를 적층 제조하는 것까지 구현할 수 있을 것으로 예상된다.
4. 결론
산업용 6축 로봇과 금속 와이어를 사용하는 적층 공정에 대한 가상 공간에서의 공정 시뮬레이션 및 모션 제어 구현을 위해 다양한 제조사의 로봇 라이브러리를 지원하는 로봇 시뮬레이터를 적용하였다.
ABB IRB-6700 로봇에 대한 용접 공정 모션을 제어하고 아크플라즈마 열원을 발생시키는 명령 코드 입력을 통해 직선 용접 공정에 대한 가상 공간에서의 시뮬레이션을 진행하였다.
실험 과정을 통해 얻어진 로봇 데이터를 동일한 실제 ABB 6축 로봇에 입력하여 모션 제어 및 구현 실험을 진행하였고, 실험 결과는 로봇 시뮬레이터 가상 스테이션 내에서 진행된 공정 시뮬레이션과 일치하였다.
실험한 용접 공정의 구현 결과를 WAAM 공정에 적용하기 위해 3D 모델링 데이터와 설정한 비드 형상 수치를 Slic3r 또는 CATIA V5에 적용하여 슬라이싱하고, RoboDK 가상 공간에서 적층 공정에 대한 모션을 계획하여 실제 ABB 산업용 6축 로봇의 적층 모션을 구현하였다.
연구의 결과는 공정 알고리즘에 대한 다수의 산업용 다축 로봇의 가상 모션 제어 및 구현 방법으로 WAAM 공정에 적용함으로써 금속 적층 제조 방법 중 보다 경제적이고 효율적인 적층 제조 시스템 구축 및 스마트 제조기술 개발에 기여할 수 있으며, 아크 플라즈마 열원을 사용하는 금속 적층 시스템의 범용 소프트웨어 개발에 응용할 수 있다.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
본 연구는 2021년도 교육부의 재원으로 한국연구재단의 지원을 받아 수행된 지자체-대학 협력 기반 지역혁신 사업(No. 2021RIS-003) 및 과학기술정보통신부 및 정보통신기획평가원의 지역지능화혁신인재양성(Grand ICT 연구센터) 사업(No. IITP-2021-2016-0-00318)과 한국연구재단의 지원을 받아 수행되었음(No. NRF-2019R1A5A8083201).
REFERENCES
- 1.
Zhou, K., Liu, T., and Zhou, L., “Industry 4.0: Towards Future Industrial Opportunities and Challenges,” Proc. of the 12th International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (FSKD), pp. 2147-2152, 2015.
10.1109/FSKD.2015.7382284
- 2.
Qi, Q. and Tao, F., “Digital Twin and Big Data towards Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0: 360 Degree Comparison,” IEEE Access, Vol. 6, pp. 3585-3593, 2018.
10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2793265
- 3.
Rauschnabel, P. A., Brem, A., and Ro, Y., “Augmented Reality Smart Glasses: Definition, Conceptual Insights, and Managerial Importance,” Unpublished Working Paper, The University of Michigan-Dearborn, 2015.
- 4.
Mourtzis, D., “Simulation in the Design and Operation of Manufacturing Systems: State of the Art and New Trends,” International Journal of Production Research, Vol. 58, No. 7, pp. 1927-1949, 2020.
10.1080/00207543.2019.1636321
- 5.
Cheng, J., Zhang, H., Tao, F., and Juang, C.-F., “Dt-II: Digital Twin Enhanced Industrial Internet Reference Framework towards Smart Manufacturing,” Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, Vol. 62, Paper No. 101881, 2020.
10.1016/j.rcim.2019.101881
- 6.
Bilberg, A. and Malik, A. A., “Digital Twin Driven Human-Robot Collaborative Assembly,” CIRP Annals, Vol. 68, No. 1, pp. 499-502, 2019.
10.1016/j.cirp.2019.04.011
- 7.
Rodrigues, T. A., Duarte, V., Miranda, R., Santos, T. G., and Oliveira, J., “Current Status and Perspectives on Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM),” Materials, Vol. 12, No. 7, Paper No. 1121, 2019.
10.3390/ma12071121
- 8.
Müller, J., Grabowski, M., Müller, C., Hensel, J., Unglaub, J., et al., “Design and Parameter Identification of Wire and Arc Additively Manufactured (Waam) Steel Bars for Use in Construction,” Metals, Vol. 9, No. 7, Paper No. 725, 2019.
10.3390/met9070725
- 9.
Azarian, M., Yu, H., and Solvang, W. D., “Integrating Additive Manufacturing into a Virtual Industry 4.0 Factory,” Proc. of the International Workshop of Advanced Manufacturing and Automation, pp. 587-594, 2020.
10.1007/978-981-33-6318-2_73
- 10.
Knezović, N. and Topić, A., “Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM)-A New Advance in Manufacturing,” Proc. of the International Conference-New Technologies, Development and Applications, pp. 65-71, 2018.
10.1007/978-3-319-90893-9_7
- 11.
Feucht, T., Lange, J., Erven, M., Costanzi, C. B., Knaack, U., et al., “Additive Manufacturing by Means of Parametric Robot Programming,” Construction Robotics, Vol. 4, No. 1, pp. 31-48, 2020.
10.1007/s41693-020-00033-w
- 12.
Frazier, W. E., “Metal Additive Manufacturing: A Review,” Journal of Materials Engineering and performance, Vol. 23, No. 6, pp. 1917-1928, 2014.
10.1007/s11665-014-0958-z
- 13.
Ahn, C. W., Kim, D. H., Kim, C. K., and Cho, Y. T., “Development of a Software for Path Planning in Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing,” Journal of the Korean Society for Precision Engineering, Vol. 37, No. 2, pp. 149-155, 2020.
10.7736/JKSPE.019.088
- 14.
Ding, D., Pan, Z., Cuiuri, D., and Li, H., “A Practical Path Planning Methodology for Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing of Thin-Walled Structures,” Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, Vol. 34, pp. 8-19, 2015.
10.1016/j.rcim.2015.01.003
- 15.
Li, F., Chen, S., Wu, Z., and Yan, Z., “Adaptive Process Control of Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing for Fabricating Complex-Shaped Components,” International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 96, No. 1, pp. 871-879, 2018.
10.1007/s00170-018-1590-0
- 16.
Venturini, G., Montevecchi, F., Bandini, F., Scippa, A., and Campatelli, G., “Feature Based Three Axes Computer Aided Manufacturing Software for Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing Dedicated to Thin Walled Components,” Additive Manufacturing, Vol. 22, pp. 643-657, 2018.
10.1016/j.addma.2018.06.013
- 17.
Nguyen, L., Buhl, J., and Bambach, M., “Continuous Eulerian Tool Path Strategies for Wire-Arc Additive Manufacturing of Rib-Web Structures with Machine-Learning-Based Adaptive Void Filling,” Additive Manufacturing, Vol. 35, Paper No. 101265, 2020.
10.1016/j.addma.2020.101265
- 18.
Jonsson Vannucci, T., “Investigating the Part Programming Process for Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing,” M.Sc. Thesis, Luleå University of Technology, 2019.
- 19.
Lyu, H., Li, M., Li, Z., Guo, J., Liu, Y., et al., “The Implementation of Tool Path Generation for the Robot Application,” Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, pp. 1145-1150, 2018.
10.1109/ROBIO.2018.8664802
- 20.
Bedaka, A. K., Vidal, J., and Lin, C.-Y., “Automatic Robot Path Integration Using Three-Dimensional Vision and Offline Programming,” The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 102, No. 5, pp. 1935-1950, 2019.
10.1007/s00170-018-03282-w
- 21.
- 22.
Ranellucci, A., “Reprap, Slic3r and the Future of 3D Printing,” Low-cost 3D Printing for Science, Education, and Sustainable Development, pp. 75-82, 2013.
- 23.
Ravi, P. and Shiakolas, P. S., “Effects of Slicing Parameters on Measured Fill Density for 3D Printing of Precision Cylindrical Constructs Using Slic3r,” SN Applied Sciences, Vol. 3, No. 3, pp. 1-10, 2021.
10.1007/s42452-021-04398-7
- 24.
Pires, J. N. and Azar, A. S., “Advances in Robotics for Additive/Hybrid Manufacturing: Robot Control, Speech Interface and Path Planning,” Industrial Robot: An International Journal, Vol. 45, No. 3, pp. 311-327, 2018.
10.1108/IR-01-2018-0017
Biography
- Chang Jong Kim
Integrated Ph.D. candidate in the Department of Smart Manufacturing Engineering, Changwon National University. His research interest is wire arc additive manufacturing and software.
- Seok Kim
Professor in the Department of Smart Manufacturing Engineering, Changwon National University. His research interest is digital lithography system and additive manufacturing with functional materials.
- Young Tae Cho
Professor in the Department of Smart Manufacturing Engineering, Changwon National University. His research interest is additive manufacturing, welding and precision manufacturing system.