ABSTRACT
This paper presents an improved input shaping method to eliminate vibration during circular interpolation of a flexible 2-axis positioning system. Due to the time delay introduced by input shaping, simultaneous 2-axis positioning with circular interpolation results in a certain amount of errors from the intended track or trajectory. This study investigated the track errors associated with circular interpolation caused by input shaping for a flexible 2-axis positioning system. The following three strategies for reducing such errors were proposed: velocity reduction in circular interpolation, adjustment of the time delay between 2 axes commands, and employment of a velocity profile compensation function. Simulations were performed to discuss the pros and cons of the three proposed strategies. Experiments were also performed to validate the results. Simulation and experiments showed that the track errors due to input shaping can be sufficiently reduced by combined use of the proposed strategies.
-
KEYWORDS: Circular interpolation, Input shaping, Residual vibration, 2-Axis positioning system
-
KEYWORDS: 원호보간, 입력성형, 잔류진동, 2축 이송계
1. 서론
다양한 산업에 널리 활용되는 이송계는 생산성 향상을 위해 고속화가 진행되어 왔다. 고속화에 따른 빠른 이송과 방향 전환 추세에 대응하기 위해서는 이송계 및 관련 장치에서 발생하는 진동의 억제가 매우 중요하다. 이송계로 인해 발생하는 진동은 전체 시스템의 성능과 수명에 악영향을 미치기 때문이다. 이 같은 이송계와 관련된 진동을 억제하는 방법으로 입력성형기법(Input Shaping Method)이 많이 활용되고 있다
[1-
3].
입력성형기법은 탄성을 갖는 이송계나 주변장치의 잔류진동을 효과적으로 제거하는 개루프제어(Open-Loop Control)기법이다. 추가적인 하드웨어 없이 쉽게 구현이 가능하여 다양한 방면에서 사용되고 있다
[1,
2]. 입력성형기법은 편의성과 유용성이 부각되면서 적용 대상이 확대되어 왔다
[3]. 근래에는 그 적용분야가 초기 조건에 의한 진동이나 강제진동에 대해서도 확대되어 왔다
[4,
5]. 또한 입력성형기법에 대한 유용성을 기반으로 공학용 시뮬레이터로 널리 활용되는 Simulink에도 그 모델링 및 해석 모듈이 탑재된 바 있다
[6].
이송계를 원활하게 활용하기 위해 보간기(Interpolator)가 널리 사용되고 있으며 보간에 따른 오차를 최소화하기 위한 다양한 방법이 연구되고 있다
[7]. 특히, 다축 이송을 하는 과정에서 불가피하게 적용되는 코너링(Cornering) 운동은 급격한 가속도 변화와 진동발생 등의 문제점을 야기하며 이를 개선하기 위한 보간 방법이 많이 연구되어 왔다
[8,
9]. 앞서 설명한 바와 같이 입력 성형기법은 이송계의 자체 발생 진동을 효과적으로 억제할 수 있는 수단이지만 보간법과 같이 활용되는 경우는 많지 않았다.
본 논문에서는 코너링을 포함하여 다양한 목적에서 널리 활용되는 원호보간에 입력성형기법을 적용하는 방법에 대해 연구하였다. 동시 작동되는 2개의 축을 가진 이송계에서 2축을 동시 이송하면서 개별 축에 입력성형을 적용할 경우 동기화에 문제가 발생할 수 있다
[10,
11]. 원호보간 시에 입력성형기법을 적용하면 입력성형이 유발한 시간 지연에 의해 사용자가 요구하는 기준명령 궤도로부터 이탈할 수 있다. 특히 원호보간 이송속도가 높은 경우에는 이러한 문제점이 두드러지게 나타나게 된다. 본 연구에서는 이와 같이 탄성을 가진 2축 이송계에서 원호보간과 입력성형을 할 경우 나타나는 궤도 오차 문제를 분석하고 이를 개선하기 위한 방안을 제시하였다.
먼저 탄성을 갖는 2축 이송계의 동적 모델을 이용하여 원호보간 시의 진동발생과 입력성형기법 적용 시의 문제점을 검토하였다. 특히, 원호보간에서 입력성형기법을 적용한 경우 발생되는 궤도 오차의 특성을 집중적으로 검토하였다.
다음으로 입력성형기법 적용과정에서 발생하는 이 같은 궤도 오차를 보상할 수 있는 3가지 방안을 검토하였다. 궤도 오차를 최소화하기 위해 이송계 속도 프로파일을 조정한 후 입력성형을 적용하는 방식으로서 원호보간 구간에서 속도를 조절하는 방식, 이송축 간의 시간 지연을 조절하는 방식 그리고 궤도 오차 양상을 고려한 속도 프로파일 보상함수 도입 방식 등이다. 시뮬레이션을 통해 각 방법의 장점과 한계점에 대해 토의하였다. 그리고 개발된 방법을 실제 2축 이송계를 포함한 반도체 장비에 적용하여 그 타당성에 대해 검증하였다.
본 논문은 다음과 같이 구성된다. 2장에서 탄성이 있는 2축 이송계에 대한 원호보간 이송 시 진동 및 입력성형 적용 시의 문제점에 대해 살펴보았고, 3장에서는 원호보간에서 입력성형기법 적용 시의 문제점을 개선하기 위한 방안들을 제시하고, 시뮬레이션을 통해 검토한 내용을 기술하였다. 4장에서는 이 개선 방안들을 실험을 통해 검증한 내용을 담고 있으며, 마지막 5장에서는 결론을 기술하였다.
2. 원호보간에서의 입력성형기법
2.1 2축 이송계 진동 특성 모델링
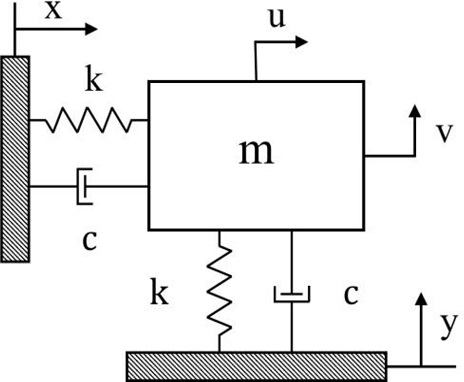
Fig. 1은 본 연구에서 고려한 직교 2축 이송계의 진동 모델 개념도를 보여주고 있다. 강체인 이송체의 질량이 m이고 두 방향의 강성 k 및 감쇠계수 c가 동일하다고 가정한다. 이러한 2축 이송계에 대해 다음
식(1)과
식(2)와 같은 운동방정식을 얻을 수 있다.
Fig. 1Conceptual model of a flexible 2-axis positioning system
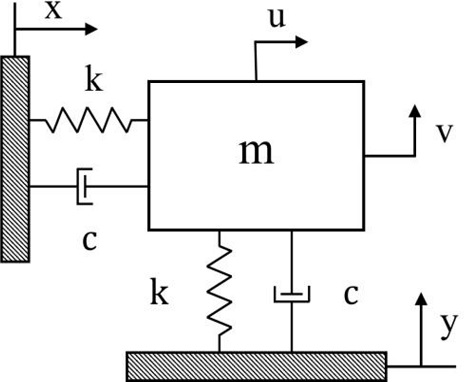
여기서, x, y는 두 방향의 이송변위명령, 그리고 u, v는 각방향에 대응되는 이송변위를 나타내며 ξ, ωn은 각각 감쇠비와 고유진동수로서 ξ=c2mk', ωn=km 이다.
2.2 원호보간 이송에서의 입력성형기법 적용
본 연구에서 고려한 궤도(Track) 및 속도 프로파일을
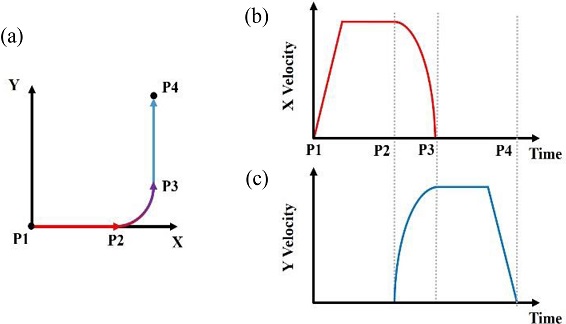
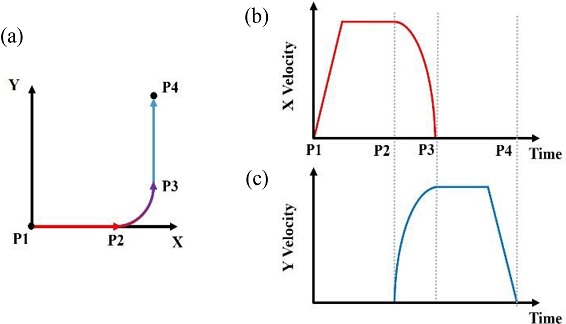
Fig. 2에서 보여주고 있다. 본 궤도는 2축 이송계를 사용할 때 코너링을 위한 전형적인 원호보간 과정이다.
Fig. 2(a)에 보여주는 바와 같이 직선이송과 원호보간 이송이 조합된 궤도로서 X축부터 가속하여 일정속도에 도달한 상태에서 Y축과 동시 원호보간이 이루어지는 형태이다. 이 같은 이송궤도를 만들기 위한 XY 속도 프로파일을
Figs. 2(b)와
2(c)에 나타내었다. P1이 X축 이송이 시작되는 지점이고, P2는 원호보간이 시작되어 X, Y축이 동시 이송이 시작되며, P3점에서 원호보간이 완료되면서 X축 이송은 멈추고 Y축 직선이송이 시작되어 최종적으로 P4점에서 정지한다. 따라서 X축 속도 프로파일은 직선이송을 위한 가속, 등속 구간과 원호보간을 통해 감속하는 구간으로 구성되며, Y축 속도 프로파일은 원호보간을 통해 증속하고 원호보간 완료 후 등속 및 감속 구간으로 이루어진 직선운동 구간으로 구성된다. 그림에서 볼 수 있는 바와 같이 X, Y축이 원호보간이 진행되는 과정이 동시에 진행되도록 속도 프로파일 진행 시점을 설정하였다. 각 구간별 이동거리는 속도 프로파일을 적분하여 결정할 수 있다.
Fig. 2Track and velocity profiles used in simulation (a) Track, (b) X-axis profile, and (c) Y-axis profile
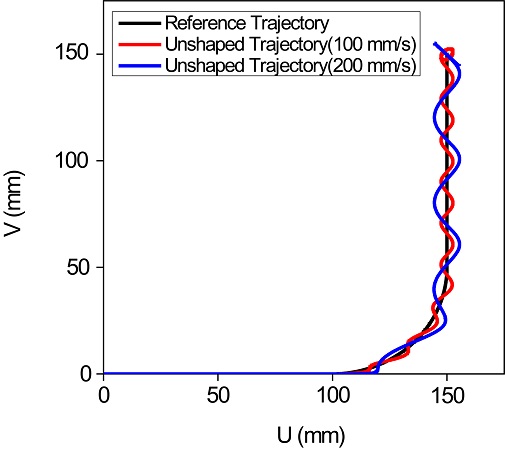
Figs. 3은
2에 보인 속도 프로파일로 2축 이송계를 이송한 경우 진동체의 궤적(Trajectory)을 보여주고 있다. 계산에 사용된 고유진동수와 세부적인 이송 조건은
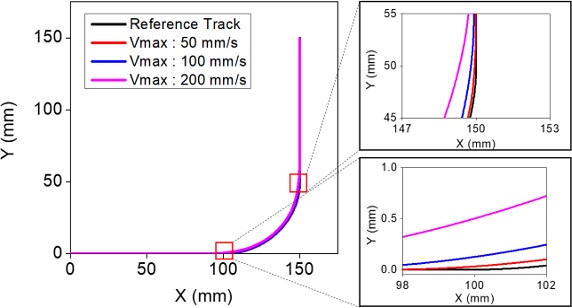
Table 1과 같다. 최대 이송 속도를 100, 200 mm/s로 하여 이송시킨 경우 잔류진동으로 인해 검은 실선으로 표시된 기준 궤도로부터 크게 벗어나는 것을 볼 수 있다. 또한 속도를 높이면 이 같은 진동체의 궤적 오차는 더욱 커짐을 알 수 있다.
Fig. 3Comparison of the reference trajectory and the actual trajectory subject to vibration
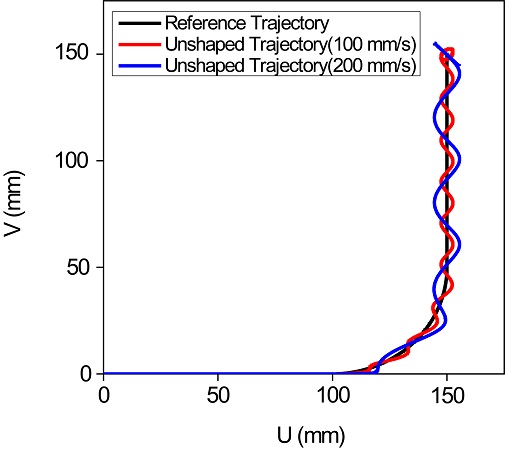
Table 1Parameters for simulation
Table 1
|
Parameter |
Unit |
Value |
|
Natural frequency |
Hz |
5 |
|
Damping ratio |
- |
0 |
|
Linear distance |
mm |
200 |
|
Circle radius |
mm |
50 |
|
Maximum velocity |
mm/s |
50/100/200 |
|
Acceleration time |
sec |
0.05 |
|
Deceleration time |
sec |
0.05 |
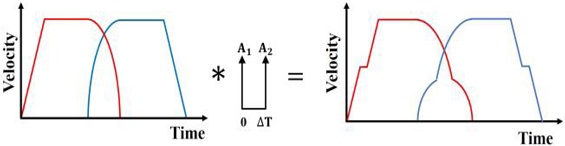
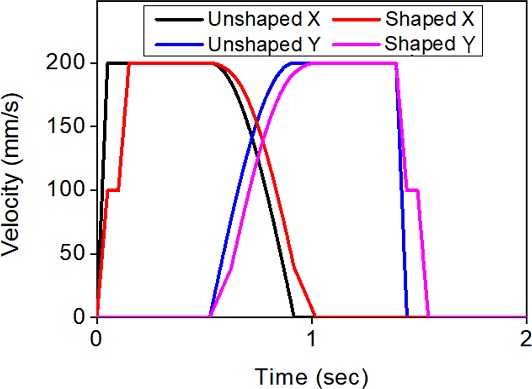
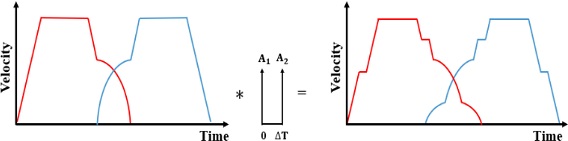
Figs. 4는 이 같은 진동을 없애기 위해 각 축별 속도 프로파일에 ZV 입력성형을 실행하는 과정을 예시하였으며, 5는 기준 속도 프로파일과 입력성형된 속도 프로파일을 비교해서 보여주고 있다. 이같이 성형된 입력에 의해 얻어지는 궤도를
Fig. 6에서 보여주고 있다. 이같이 수정된 궤도를 사용하면
Fig. 3에서 보였던 잔류진동을 완벽히 제거할 수 있지만 원호 구간에서 기준 궤도를 이탈하게 된다.
Table 2는 오차율(기준 원호와 입력성형된 원호궤도 간의 면적 오차를 원호면적으로 나눈 비)를 보여주고 있다.
Fig. 4ZV input shaping process for the simulated velocity profiles
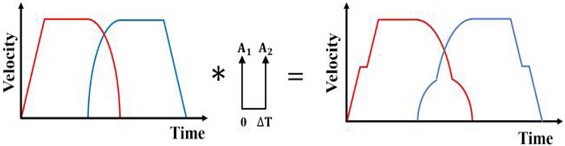
Fig. 5Comparison of unshaped and shaped velocity profiles
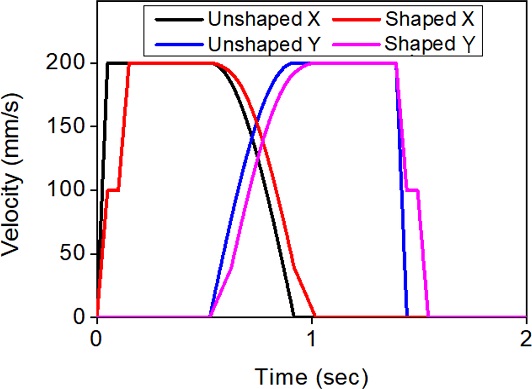
Fig. 6Comparison of desired and command shaped tracks
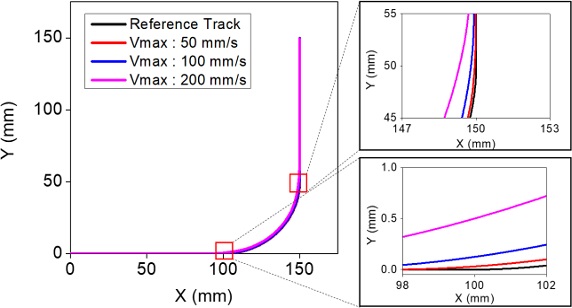
Table 2Percentile error of the shaped track from the reference track during circular interpolation
Table 2
Max. Velocity
[mm/s] |
Percentile error of track
[%] |
|
50 |
0.25 |
|
100 |
1.00 |
|
200 |
3.95 |
Table 2에서 속도를 높이면 오차율이 급격히 증가하는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 원호궤도의 시점과 종점을 주목해보면 입력성형을 적용한 경우 원호의 시점과 종점에서 기준 원호와 차이가 나는 것을 볼 수 있다. 이 차이는 입력성형 시 유발된 시간 지연이 X축 원호보간 시점과 종점을 변화시켜 Y축과의 동기화에 오차를 발생시킨 것이다. 다음 장에는 이 같은 오차를 억제하기 위한 방법을 제시하였다.
3. 원호보간 이송을 위한 입력성형기법의 개선
3.1 속도 프로파일 개선: 원호보간 구간 진입속도 감속
원호보간 속도가 높으면 오차가 커지므로 원호보간에서의 구간속도를 감속하는 것은 비교적 쉽게 적용할 수 있는 개선책이 될 수 있다.
Fig. 7은 기존의 시뮬레이션 조건에서 원호보간 진입속도를 40% 감소시킨 경우의 기준 속도 프로파일과 입력성형기법을 적용한 속도 프로파일을 예시한 것이다.
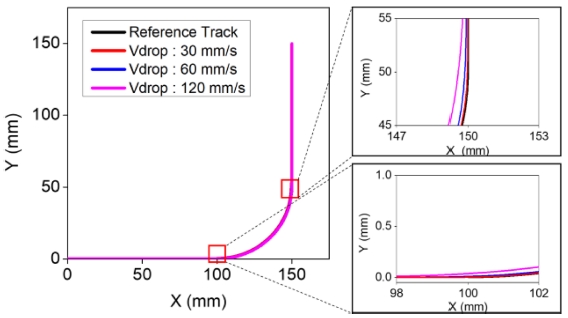
Fig. 8은 이 경우에 대한 원호구간 궤도를 나타낸 것이다. 감속을 통해 입력성형에 의한 궤도 오차가 크게 감소하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
Tables 3은
2에서와 마찬가지로 조건에 따른 오차율을 나타내고 있다. 감속에 의한 개선효과를 확인할 수 있지만 기준속도가 높아지면 개선에 한계가 있음을 확인할 수 있다.
Fig. 7Comparison of unshaped and shaped commands for X and Y velocity profiles modified with reduced circular interpolation velocity
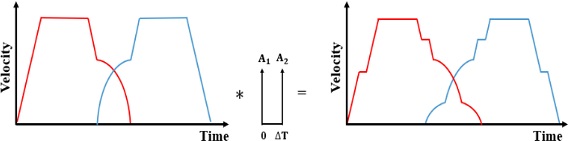
Fig. 8Comparison of desired and input shaped tracks with reduced circular interpolation velocity
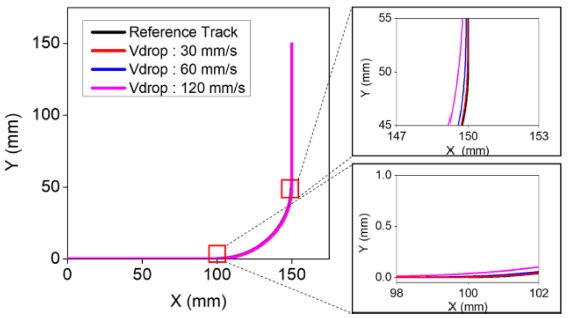
Table 3Percentile error of the shaped track from the reference track subject to 40% velocity reduction
Table 3
Max. Velocity
[mm/s] |
Reduced velocity
[mm/s] |
Percentile error of
track [%] |
|
50 |
30 |
0.06 |
|
100 |
60 |
0.25 |
|
200 |
120 |
0.99 |
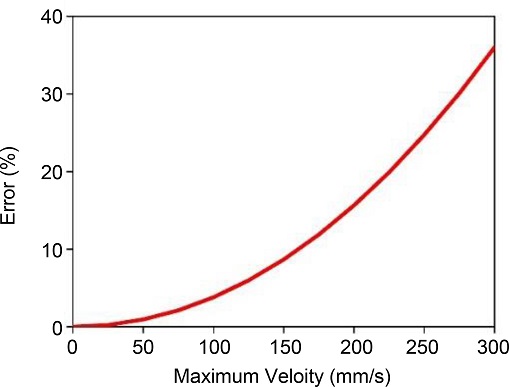
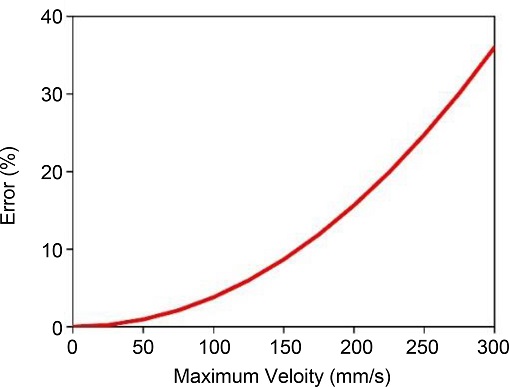
Fig. 9는 원호보간 진입속도와 오차율의 관계를 보여주고 있다. 진입속도를 낮추고 입력성형을 적용하게 되면 잔류진동 제거와 궤도 오차 저감효과를 동시에 얻을 수 있지만 원호보간 구간에서의 속도가 낮아짐으로 인해 작업시간 손실이 발생할 수 있으므로 사용이 제한될 수 있다.
Fig. 9Percentile error of track with changing the circulating velocity
3.2 속도 프로파일 개선: 시간 지연 조정
입력성형에 의한 시간 지연으로 인해 X, Y축 원호보간 시점과 종점이 일치하지 않는 문제점이 발생한다. 이 같은 문제점을 개선하기 위해 ZV 입력성형 시 발생되는 다음의 시간 지연 Δ를 보상하였다.
여기서 Δ는 입력성형 시 적용되는 시간 지연에서 기존 직선 이송 구간과 입력성형을 적용하여 늘어난 직선이송 구간에 대한 시간 차이(Δτ)를 뺀 값이다. 이를 Y축의 원호보간 시작점에 반영하여 변화된 X축 원호보간 시작점과 맞춤으로써 X, Y축 동시 원호보간을 시작할 수 있도록 Y축 속도 프로파일에 적용하였다.
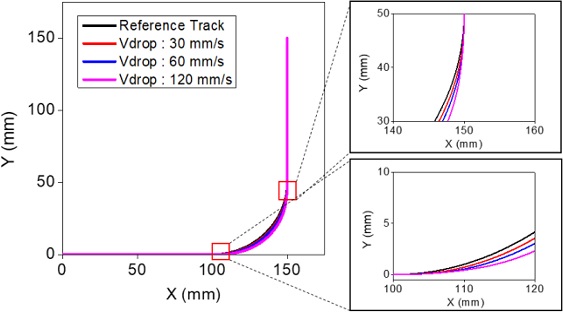
Fig. 10은
식(3)으로 주어진 시간 지연을 Y축 이송에 적용한 경우의 궤도를 보여주고 있다. 속도 변화에 따른 궤도 변화를 비교할 수 있도록 3가지 속도를 비교해서 보여주고 있다. 원호의 시점과 종점이 잘 일치하고 있으나 궤도 오차가 커지는 것을 볼 수 있다. 특히 궤도가 기준 원호의 바깥측으로 커지는 것을 확인할 수 있으며 매우 큰 오차가 나타나고 있다.
Table 4는 이 경우에 대한 오차율을 보여주고 있다. 원호보간 시점/종점이 일치되었으나 오차율이 크게 증가하여 그대로 적용하는 것은 부적절할 것으로 판단된다.
Fig. 10Comparison of desired and shaped tracks that compensate the mismatch in the XY commands due to the input shaping induced delay
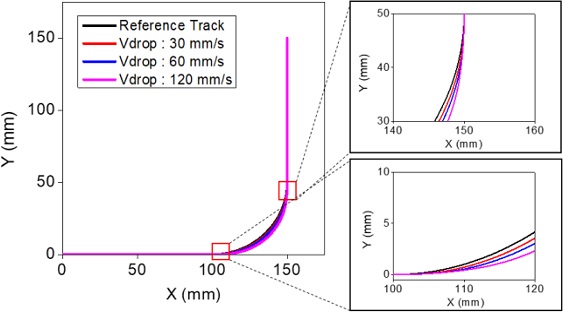
Table 4Percentile error of the shaped track from the reference track with 40% velocity reduction and delay compensation
Table 4
Max. Velocity
[mm/s] |
Reduced velocity
[mm/s] |
Percentile error of
track [%] |
|
50 |
30 |
1.81 |
|
100 |
60 |
3.41 |
|
200 |
120 |
6.05 |
3.3 보상함수 도입
앞서 설명한 개선방법을 사용할 경우 발생되는 궤도 오차의 양상을 고려하여, 원호보간 시 속도를 조절할 수 있도록 속도 프로파일을 개선하는 방안을 고려하였다.
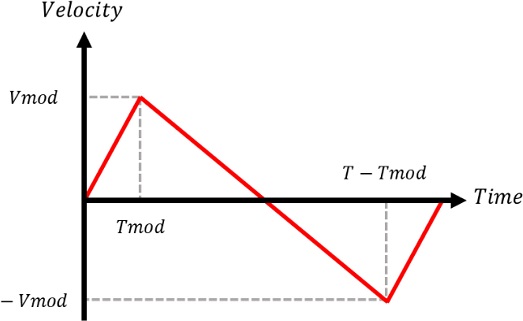
Fig. 11은 사용된 속도 프로파일 보상함수를 보여주고 있다. 이 보상함수는 오차의 패턴을 참조하여 정의하였으며, Y축 원호보간 구간 속도 프로파일에 합산하여 적용하였다. 이 보상함수를 기준 속도 프로파일에 합산하여 적용해도 최종위치는 변화되지 않도록 중심점 대칭 형태로 구성하였다. 이 함수를 활용하기 위해 완전탐색법(Exhaustive Method)을 사용하여 오차율을 최소화할 수 있는 Vmod와 Tmod를 결정하였다.
Fig. 11Compensation function for the reference velocity profile to improve the accuracy in circular interpolation
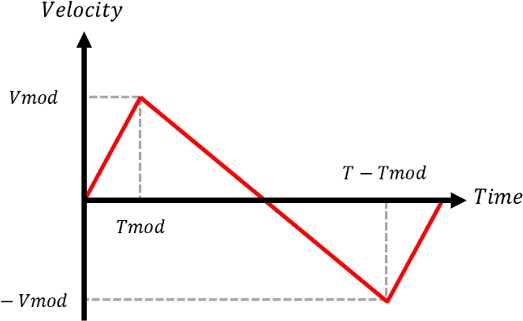
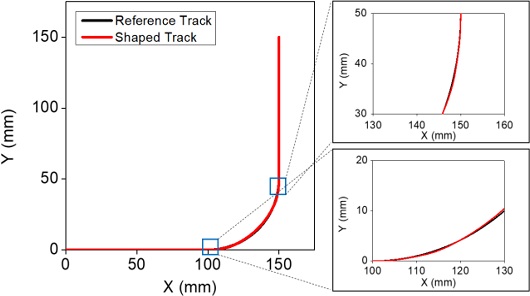
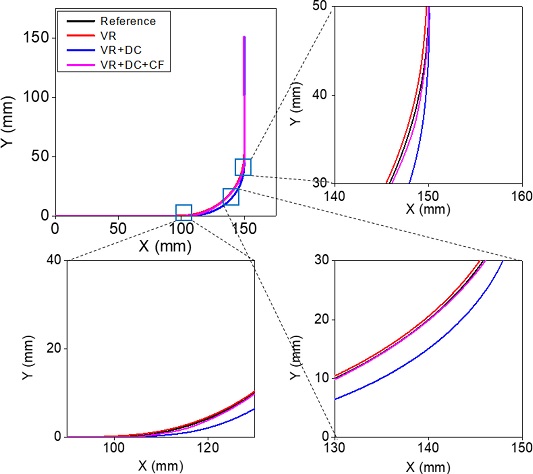
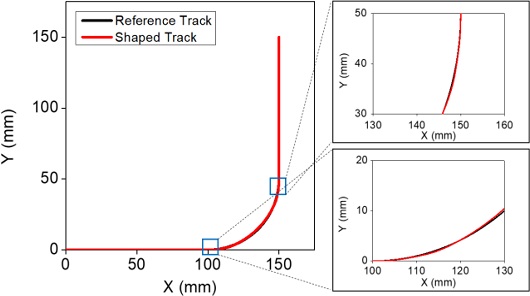
Fig. 12는 진입속도 200 mm/s에서 40% 감속과 보상함수를 적용했을 때의 입력성형된 명령에 의한 원호보간 궤도를 보여주고 있다. 여기서는 Vmod를 28 mm/s, Tmod를 0.0492 s를 적용하였다. 결과에서 볼 수 있는 바와 같이 원호보간 시점과 종점을 정확히 일치시키고 궤도 오차를 획기적으로 줄일 수 있음을 볼 수 있는데 이때 오차율은 0.74%이다.
Fig. 12Comparison of desired and command shaped tracks with and without compensation function employed
4. 실험 및 토의
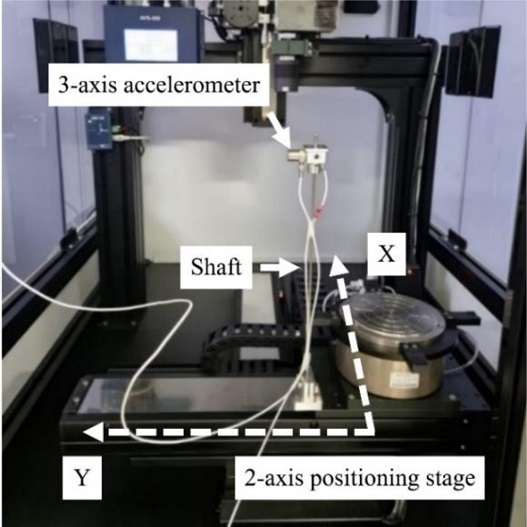
제안된 입력성형기법의 성능을 실험적으로 검증하기 위해
Fig. 13과 같은 반도체 장비의 XY 스테이지를 사용하였다. 사용된 XY 스테이지는 최대속도 700 mm/s, 최소가속시간 0.03 sec, 각 축의 최대이동거리는 300 mm의 사양이다.
Fig. 13 Experimental system
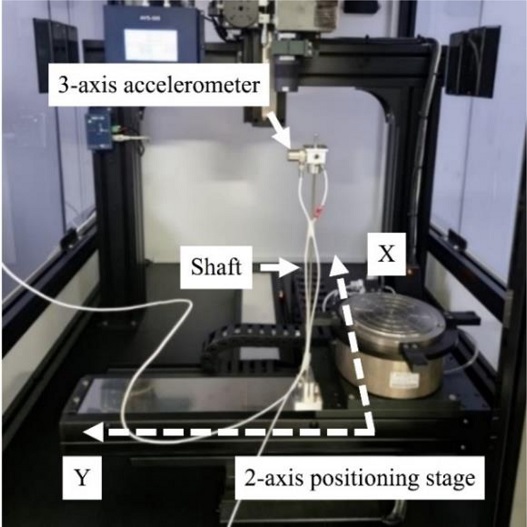
2축 이송이 가능한 XY 스테이지에 X, Y축의 고유진동수가 같은 등방성인 탄성축을 배치하였다. 축 끝단에서 진동 응답을 측정하기 위해 설치한 3축 가속도계가 진동계의 질량으로도 작용하게 된다. 모션컨트롤러는 델타타우사의 PMAC을 사용하였으며 위치, 속도, 시간을 설정할 수 있는 소프트웨어를 통해 명령을 입력하였고 서보계는 토크제어 모드를 사용하였다. 설치된 상태의 고유진동수는 5.15 Hz이고, 직선운동 구간은 100 mm, 최대속도는 200 mm/s로 설정하였다. 시간 지연 보상값은 0.056 s로 결정하였고, Vmod, Tmod는 시뮬레이션을 통해 얻은 값을 기초로 실험을 통해 조정하였고, 각각 최대속도의 16%와 0.0436 s를 적용하였다.
시뮬레이션에서 다루었던 3가지 경우를 실험에 고려하였다. 즉 ① 진입속도감소만 고려한 경우, ② 진입속도감소에 시간 지연 보상을 추가로 고려한 경우 그리고 ②, ③에 추가로 보상함수까지 적용한 경우이다.
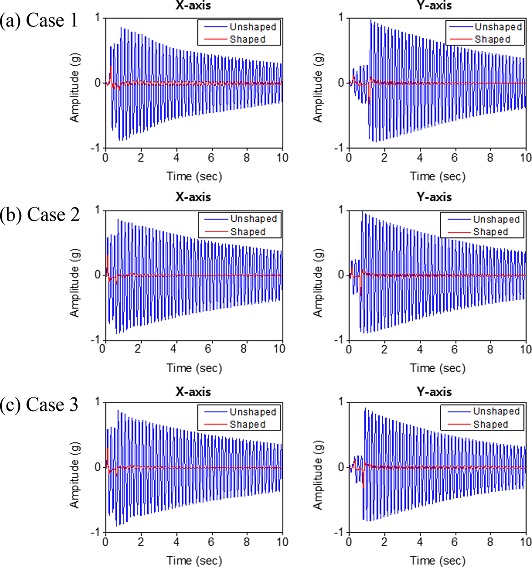
Fig. 14는 입력성형 적용 전후의 두 방향진동(가속도)을 보여주고 있다.
Fig. 14에서 볼 수 있는 바와 같이 모든 경우의 진동이 완벽하게 억제된 것을 볼 수 있다. 한편
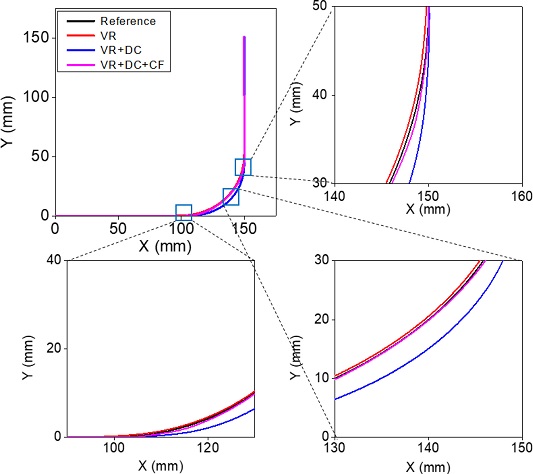
Fig. 15는 이 경우에 대한 궤도를 예시하고 있다. 시뮬레이션을 통해 확인한 바와 같이 단순히 속도를 저감하거나 시간 지연 보상만으로는 다소의 오차가 발생함을 확인할 수 있다. 결과를 통해 볼 수 있는 바와 같이 보상함수까지 포함시킨 경우 가장 양호한 결과를 보이고 있으며 오차율이 1% 미만으로 발생함을 확인하였다.
Fig. 14 Measured accelerations before and after applying the proposed input shaping for circular interpolation with max speed of 200 mm/s. (a) Case 1: 40% velocity reduction (VR) (0.6 Vmax), (b) Case 2: 40% velocity reduction (VR) + delay compensation (DC), and (c) Case 3: 40% velocity reduction (VR) + delay compensation (DC) + employing compensation function (CF)
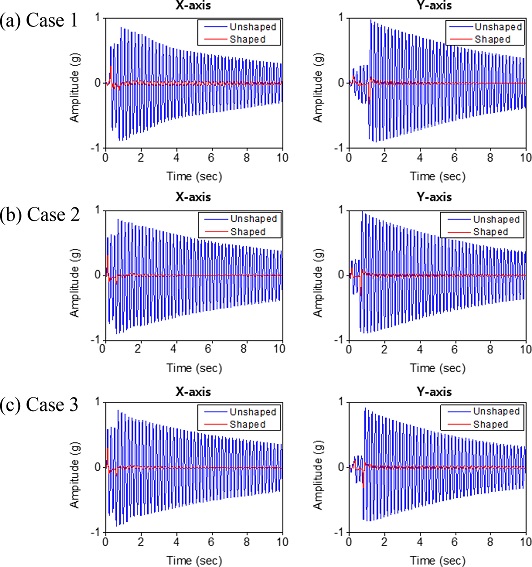
Fig. 15 Measured tracks for three different methods applied: VR, VR + DC, VR + DC + CF (Refer to Fig. 14 for abbreviations)
5. 결론
본 논문에서는 진동체 특성을 갖는 2축 이송계의 원호보간에 입력성형기법을 적용했을 때의 문제점을 분석하고 이를 개선하는 방안을 제시하였다. 입력성형을 적용하면 과도진동이나 잔류진동은 억제되지만 개별 축에 적용되는 시간 지연으로 인해 속도 프로파일이 변경되면서 원호구간 궤도가 의도된 궤도에서 이탈하게 되며, 원호보간 구간의 진입속도가 높아지면 이 오차는 더욱 증가함을 확인하였다. 이 같은 궤도 오차를 개선하기 위해 원호보간 구간 진입속도를 감속하는 방법과 2축 간의 시간 지연 차이를 보상하는 방법 그리고 속도보상함수를 도입하는 방법 등 3가지 방안을 제시하였다. 제시된 방법을 시뮬레이션과 실험을 통해 비교 평가하였다. 제안된 3가지를 조합하는 방식을 통해 진동을 억제하고 원호보간 시점/종점오차를 제거할 수 있으며, 원호궤도 오차도 1% 미만의 수준으로 억제할 수 있음을 확인하였다.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
본 논문은 중소벤처기업부의 창업성장기술개발사업의 지원을 받아 연구되었으며 관계자 여러분에게 감사드립니다.
REFERENCES
- 1.
William, S., Seering, W., (2007), Command generation for dynamic system, woodruff school of mechanical engineering, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- 2.
Hong, S. W., (2014), Input shaping method for mechanical vibration control, Choas Book.
- 3.
Singhose, W., (2009), Command shaping for flexible systems: A review of the first 50 years, International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 10(4), 153-168.
10.1007/s12541-009-0084-2
- 4.
Newman, D., Hong, S.-W., Vaughan, J. E., (2018), The design of input shapers which eliminate nonzero initial conditions, Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 140(10), 101005.
10.1115/1.4039668
- 5.
Kobilov, A., Hong, S. W., (2020), Delay-time adjustable input shaping method for positioning systems subject to repetitive motion, Journal of the Korean Society for Precision Engineering, 37(1), 25-34.
10.7736/JKSPE.019.104
- 6.
Piedrafita, R., Comin, D., Beltrán, J. R., (2018), Simulink® implementation and industrial test of input shaping techniques, Control Engineering Practice, 79, 1-21.
10.1016/j.conengprac.2018.06.021
- 7.
Lee, C.-Y., Kim, S. H., Ha, T. I., Min, J., Hwang S.-H., Min, B.-K., (2018), CNC algorithms for precision machining: State of the art review, Journal of the Korean Society for Precision Engineering, 35(3), 279-291.
10.7736/KSPE.2018.35.3.279
- 8.
Sencer, B., Ishizaki, K., Shamoto, E., (2015), High speed cornering strategy with confined contour error and vibration suppression for CNC machine tools, CIRP Annals, 64(1), 369-372.
10.1016/j.cirp.2015.04.102
- 9.
Lee, C.-Y., Min, J., Min, B.-K., (2017), Limiting tool path error generated by corner blending of CNC interpolator, Journal of the Korean Society for Precision Engineering, 34(10), 695-700.
10.7736/KSPE.2017.34.10.695
- 10.
Zhao, P., Zhou, Y., Zhou, R., (2018), A new trajectory optimizing method using input shaping principles, Shock and Vibration, 2018, 4173253.
10.1155/2018/4173253
- 11.
Gu, M.-M., Sim, J.-U., Oh, H.-I., Kwon, S-W., Hong, S.-W., (2020), Linear interpolation input shaping method for anisotropic 2-Axis positioning system. Proceeding of the Conference on the Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1667.
Biography
- Jin Uk Sim
He received his B.E. degree in Mechanical Engineering from Andong National University in 2018. He is currently pursuing his M.E. degree course in the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Kumoh National Institute of Technology, Korea. His research interest includes vibration control and command shaping.
- Pil Kyu Choi
He received his B.E and M.E. degrees in Mechanical Engineering of Kumoh National Institute of Technology, Korea in 2016 and 2022, respectively. He is currently working for Korea Dow Chemical Co. Ltd.. His research interest includes vibration monitoring and control.
- Sun-Woong Kwon
He received his M.E. and Ph.D degrees in Mechatronics Engineering from Kumoh National Institute of Technology, Korea in 2014 and 2019, respectively. He is currently a principal researcher in Photomechanic, Co., Ltd.. His research interest includes vibration control and bearing modeling and analysis.
- Seong-Wook Hong
He received his M.S. and Ph.D degrees in Mechanical Engineering from KAIST, Korea in 1985 and 1989, respectively. He is a professor in the Department of Mechanical System Engineering of Kumoh National Institute of Technology, Korea. His research interest includes command shaping, bearing modeling and analysis, structural dynamics analysis.